Astatine: Astatine is one of the least abundant elements on Earth. Furthermore, it is short-lived, undergoing quick radioactive decay by releasing positively charged alpha particles to achieve nuclear stability. Hence, astatine, particularly its isotope astatine-211, is an attractive candidate for a form of radiation therapy for cancer treatment, called targeted alpha-particle therapy.
Unlike other forms of radiation that can penetrate deeper into the body, damaging both healthy and cancerous tissue, alpha particles travel a short distance and lose their energy. Thus, when astatine-211 is positioned in or near cancerous tissue, its emitted alpha particles travel deep enough to destroy the cancer cells but leave healthy tissue minimally harmed. Also, the short half-life of astatine-211, or time taken for half of its atomic nuclei to decay, means that it loses its radioactivity quickly and is less toxic than other radiopharmaceuticals that are long-lived.

Burns
Burns noted, however, that the half-life of astatine is a double-edged sword. Since the element has a very low natural abundance, astatine-211 is artificially made by bombarding bismuth with high-speed alpha particles. Once created, astatine-211 begins to decay immediately, he said, starting the clock on how long it will last.
“Every 7.2 hours, half of the produced astatine-211 decays away and is no longer usable for treatment,” said Burns. “So, the time taken from when it's produced to when it can go into the patient becomes very critical. If a purification process takes 4 hours, for example, that means it’s around half of astatine’s half-life; you've lost a third of the material you've made.”
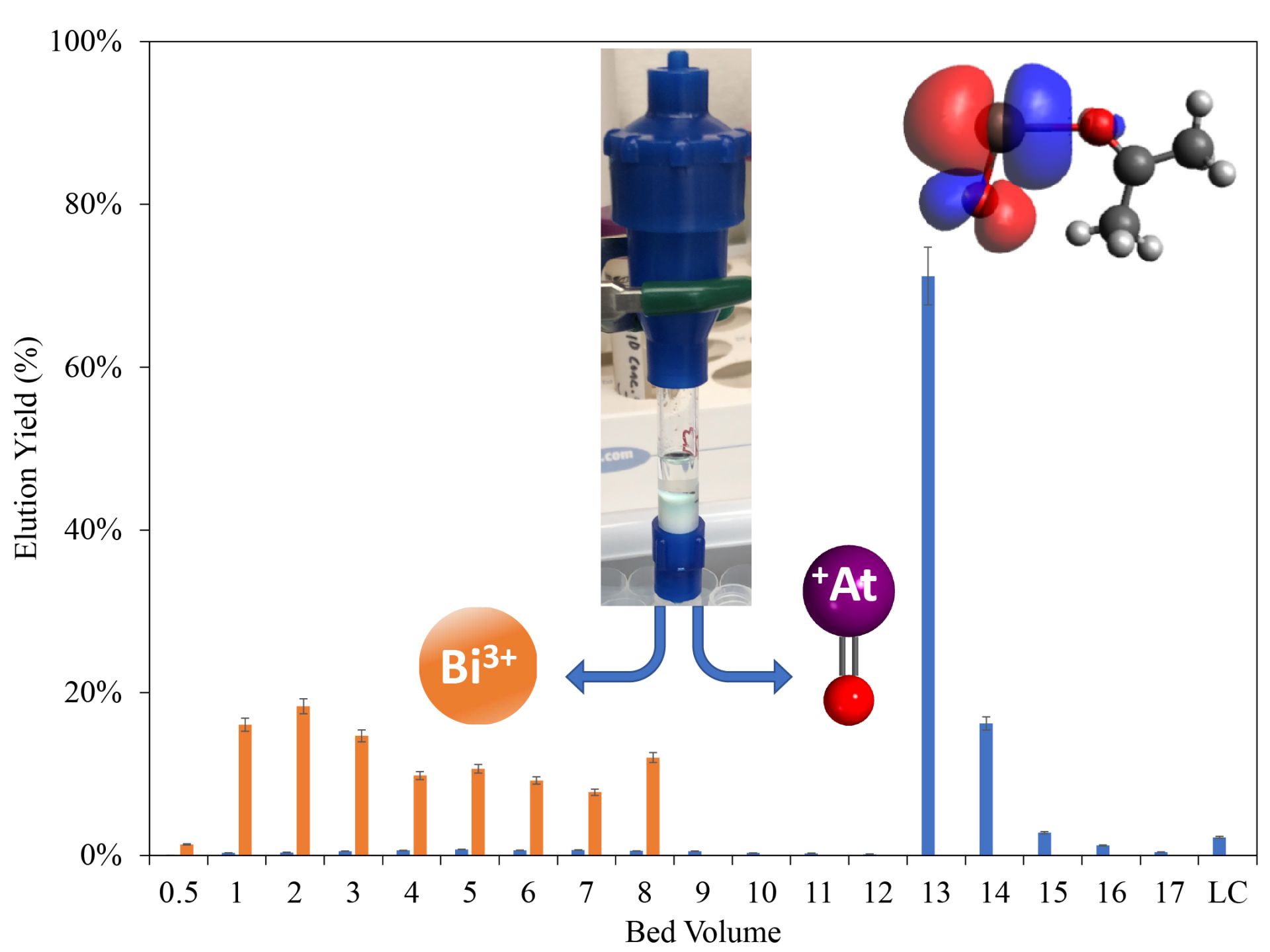
Simplifying steps: In an attempt to simplify the purification process, Burns and his colleagues sought to use nitric acid for extracting the astatine-211 from bismuth. For their experiments, they filled a chromatography column that is often used for separating mixtures with tiny porous beads infused with organic chemicals called ketones.
Next, the researchers made astatine-211 by bombarding bismuth with alpha particles at the Texas A&M University Cyclotron Institute. They then dissolved the bismuth in nitric acid. When they passed this solution through the chromatography column, the researchers found that only astatine-211 formed a chemical bond with the ketones. Furthermore, since the ketones are hydrophobic they were repelled away from nitric acid, sticking to the beads. The net effect was that bismuth passed through the column whereas pure astatine-211 remained collected within the beads.
This procedure, the researchers found, takes roughly 10 to 20 minutes, unlike other astatine purification processes that can take hours.
Already equipped: Although a cyclotron is needed in producing medical-grade astatine-211, Burns said many hospitals are already equipped with such a machine for producing other chemicals, like fluorodeoxyglucose F 18, which is needed for positron emission tomography. But even for hospitals that might rely on astatine-211 delivery from an off-site location, the short purification procedure offers more time for transportation.
“Texas A&M University, for example, is in a really nice geographical location; we're right in the middle of five of the top 20 largest cities in America and we're right next to one of the major cancer centers in the United States,” said Burns. “We are aiming to produce, purify, and ship astatine in batches large enough for preclinical and clinical trials. We are not there yet, but we have made significant progress through this elegant separation technique.”
Contributors: Other contributors to the research include Evgeny Tereshatov, Geoffrey Avila, Kevin Glennon, Andrew Hannaman, Kylie Lofton, Laura McCann, Mallory McCarthy, Lauren McIntosh, Steven Schultz, Gabriel Tabacaru, Amy Vonder Haar, and Sherry Yennello from the Cyclotron Institute at Texas A&M.
The research is funded by the DOE's Isotope Program, managed by the Office of Science; Texas A&M University through the Bright Chair in Nuclear Science; the Texas A&M System National Laboratories Office; and the DOE.
Vandana Suresh is a senior science writer for Texas A&M University.