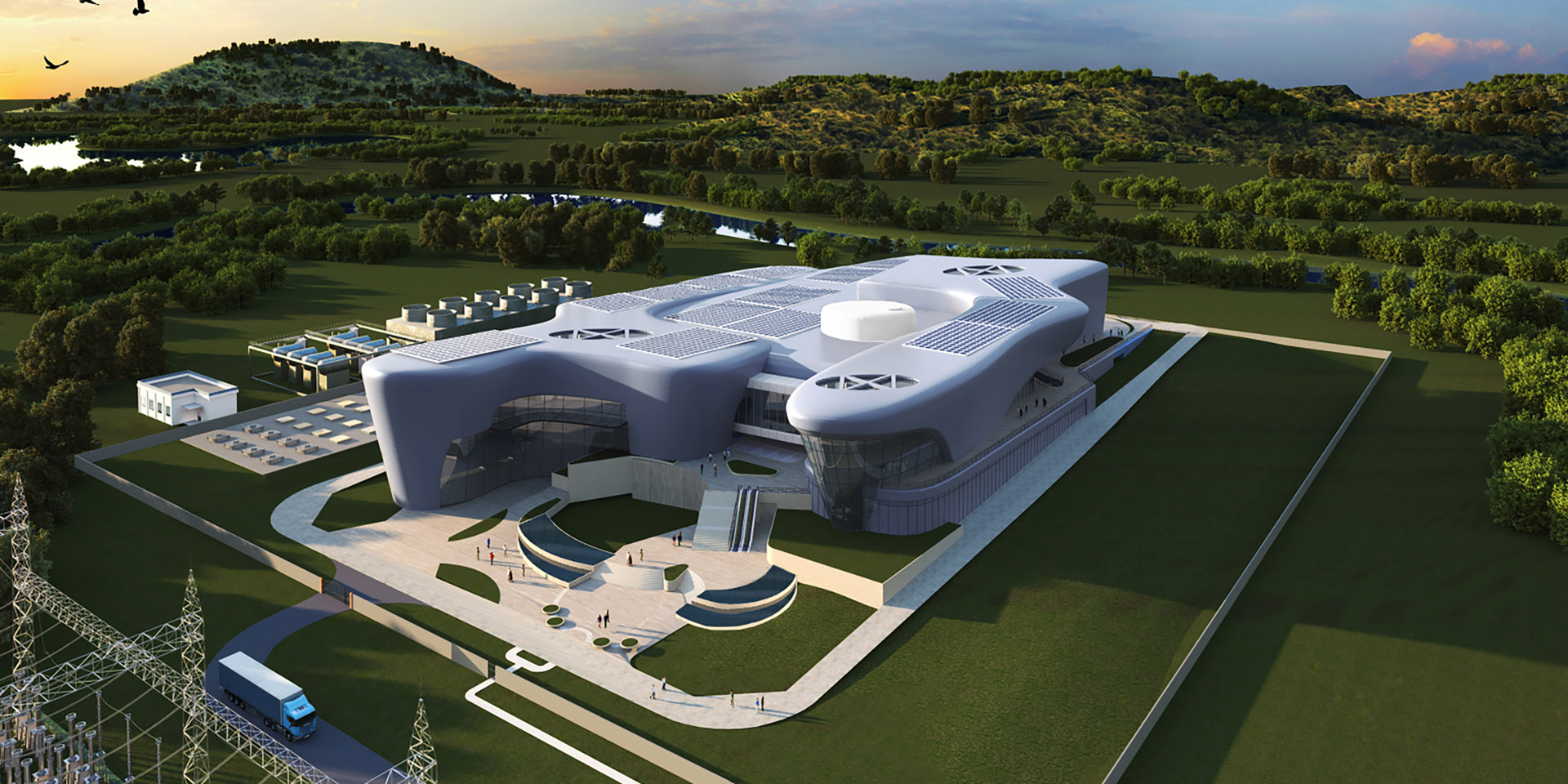
The cooling pipes that snake along the surface of the vacuum vessel thermal shield will be removed and replaced. Here, on a right-hand outboard panel, workers determine the impact of pipe removal on the surface of the component. (Photo: ITER Organization)
ITER’s machine assembly phase began about two and a half years ago. Now, staff are reversing some of that assembly work to make needed repairs. According to a news article published by the ITER Organization on January 9, ITER is “facing challenges common to every industrial venture involving first-of-a-kind components.” Over one year after problems were first detected and less than two months after they were made public in late November, tests and analysis are producing a clearer picture of necessary repairs to the tokamak’s thermal shield panels and vacuum vessel sectors.
“There is no scandal here,” said ITER director general Pietro Barabaschi. “Such things happen. I've seen many issues of the kind, and much worse.”
A rendering of Holtec’s SMR-160 plant. (Image: Holtec International)
Small modular reactor developers Holtec International and GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy (GEH) are both looking to the United Kingdom as a prime location for deployment of their units—the SMR-160 and BWRX-300, respectively.
On December 19, Holtec Britain announced that it is poised to enter the United Kingdom’s generic design assessment (GDA) process for the SMR-160 early in 2023, enabling the start of construction of the first U.K. unit as soon as 2028. (The GDA, developed by the Office for Nuclear Regulation and the Environment Agency, gauges the safety, security, and environmental protection aspects of a nuclear plant design. Successfully completing the assessment culminates in a design acceptance confirmation from ONR and a statement of design acceptability from the Environment Agency.)
The Human Systems Simulation Laboratory at INL allows researchers to simulate industrial control rooms to improve performance. (Photo: INL)
In the 1960s, nuclear energy established itself as a mainstay of the electrical grid for its ability to produce carbon-free, safe, and reliable power. Indeed, nuclear energy currently provides about 50 percent of carbon-free electricity in the United States, but a major challenge is its cost.