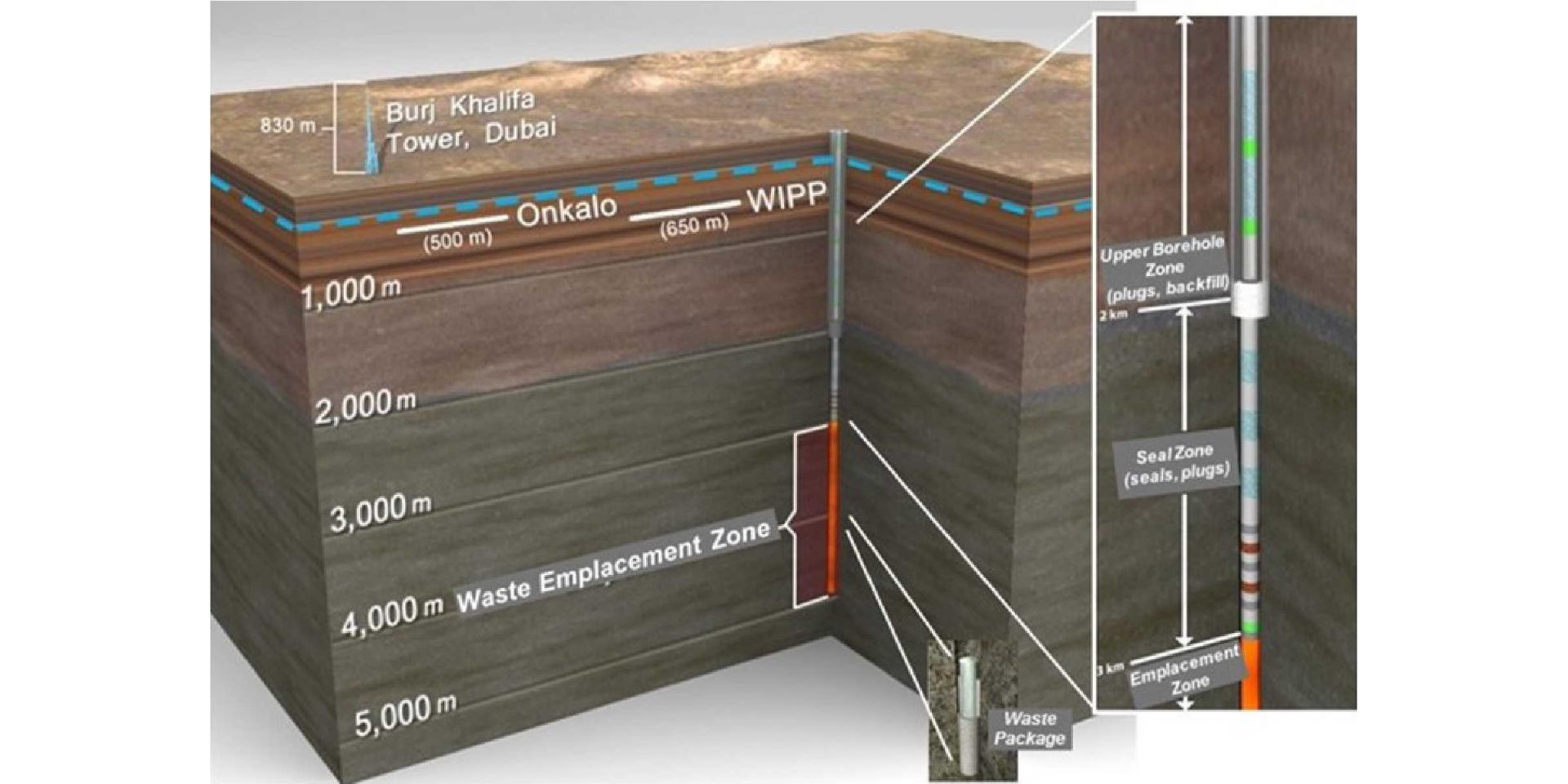
A schematic illustration of a deep borehole repository assuming disposal into a bedrock. (Image: Sandia National Laboratories via IAEA)
The International Atomic Energy Agency is launching a new Coordinated Research Project (CRP) to increase international knowledge and drive progress toward testing deep borehole disposal for intermediate- and high-level radioactive waste.
SRS reached a landmark achievement with the placement of 2,000 double-stacked canisters of vitrified HLW. (Image: DOE)
To expand interim storage of vitrified high-level radioactive waste at the Savannah River Site, the Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management and its liquid waste contractor Savannah River Mission Completion (SRMC) have double stacked 2,000 canisters in one of the site's two glass waste storage buildings (GWSB). GWSB 1 consists of a below-grade, seismically qualified concrete storage location containing support frames for the vertical storage of 2,262 10-foot-tall canisters.
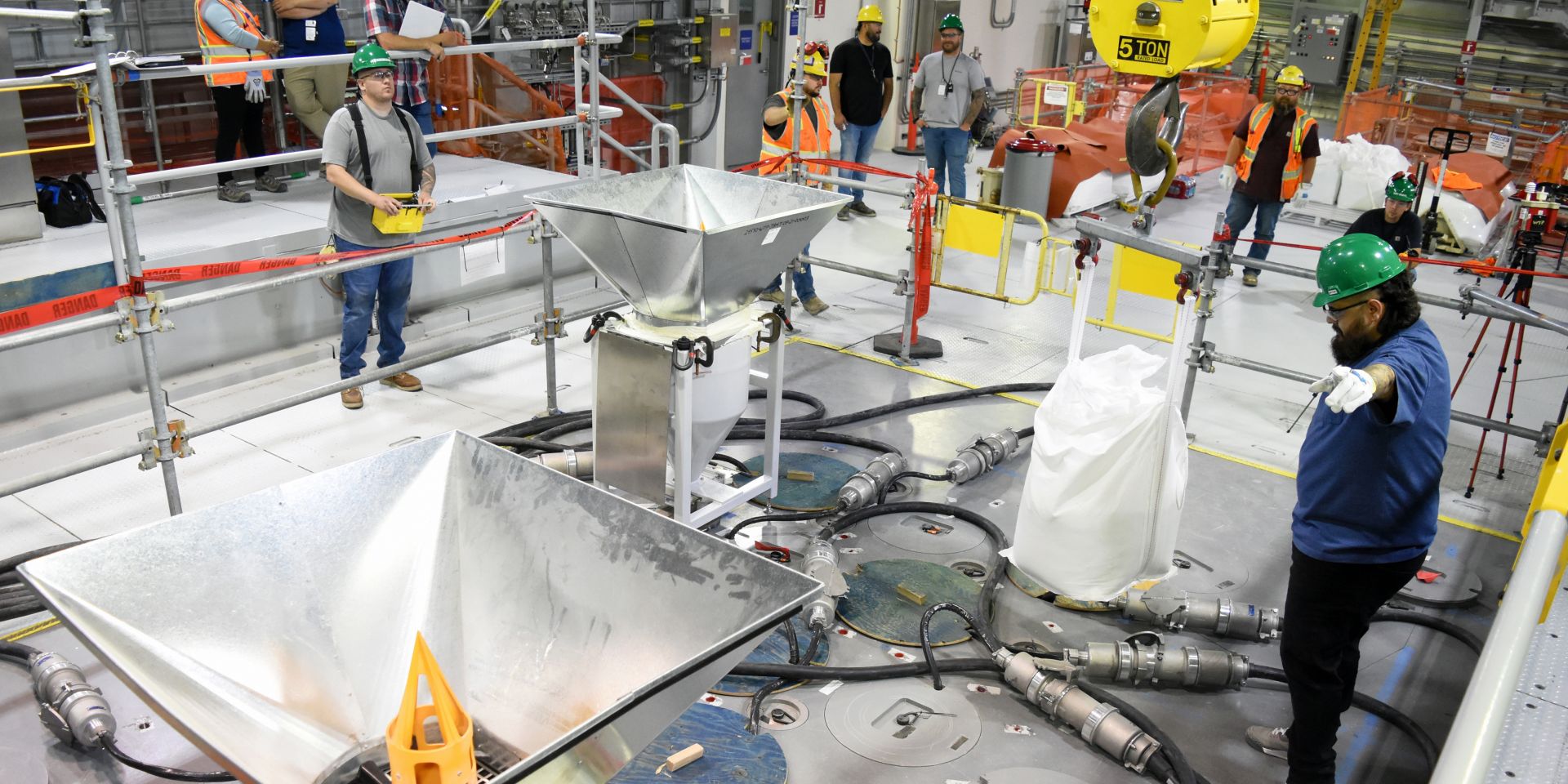
A 300-pound bag of frit is in position to be poured into the melter at Hanford’s LAW Facility. (Photo: Bechtel National)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management announced that the first batches of glass-forming beads, called frit, were poured last week into a melter at the Hanford Site’s Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant (WTP), also known as the Vit Plant. The melter, which has been heated to 2,100ºF, will be used to immobilize Hanford’s radioactive and chemical tank waste, turning it into a stable glass form through vitrification.
Some of the participants of the recent SRNL-Hanford Analytical Knowledge Sharing Workshop pause for a photo. (Photo: DOE)
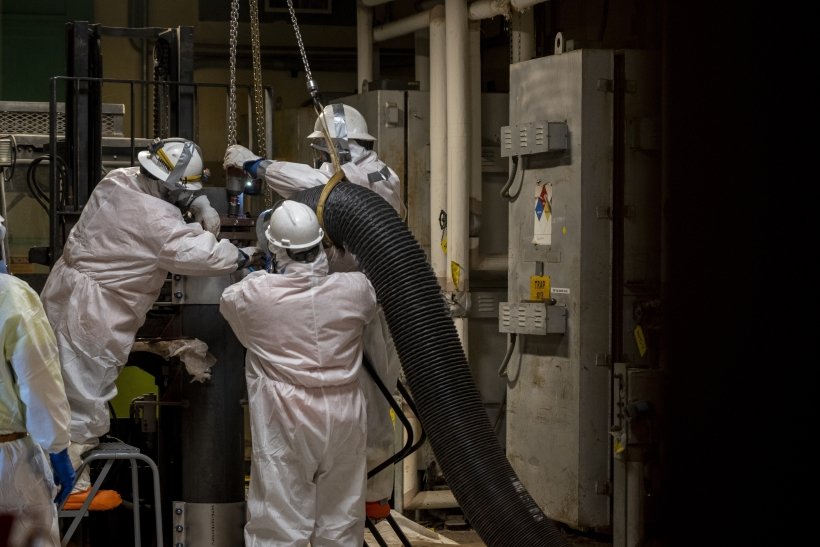
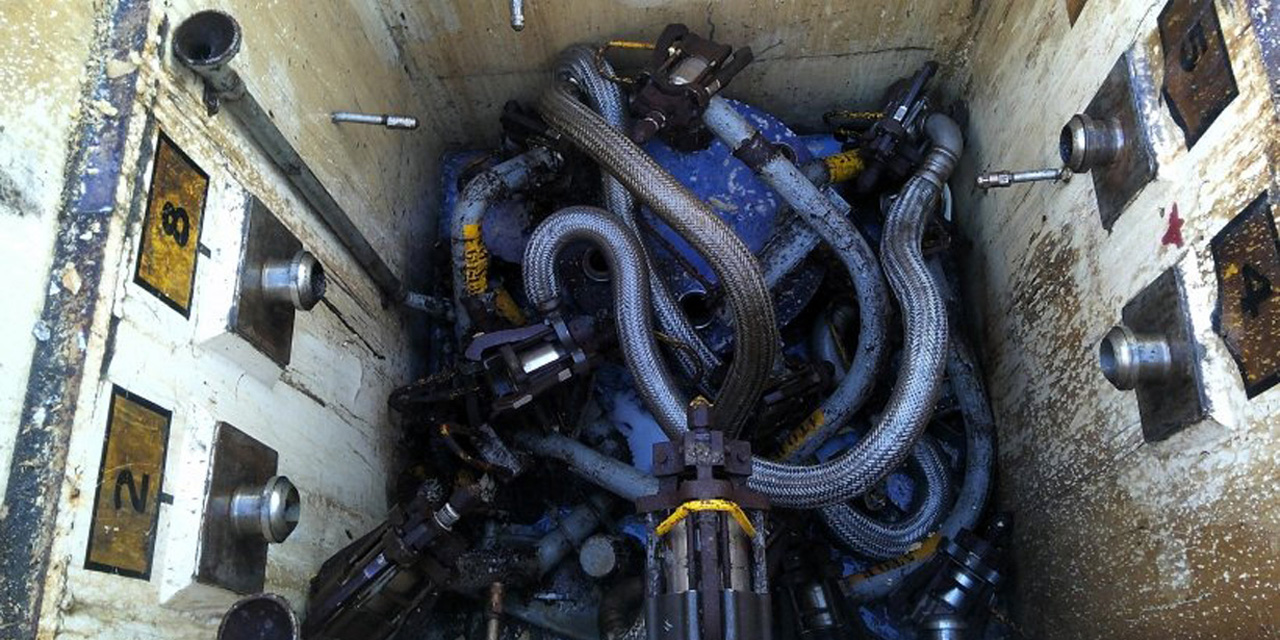
Workers at the Hanford Site dubbed this network of waste tank connections “Medusa” because it looked like a head covered with snakes. (Photo: DOE)
Workers at the Department of Energy’s Hanford Site in Washington state recently removed a complex piece of equipment that had been standing in the way of future tank waste retrieval.
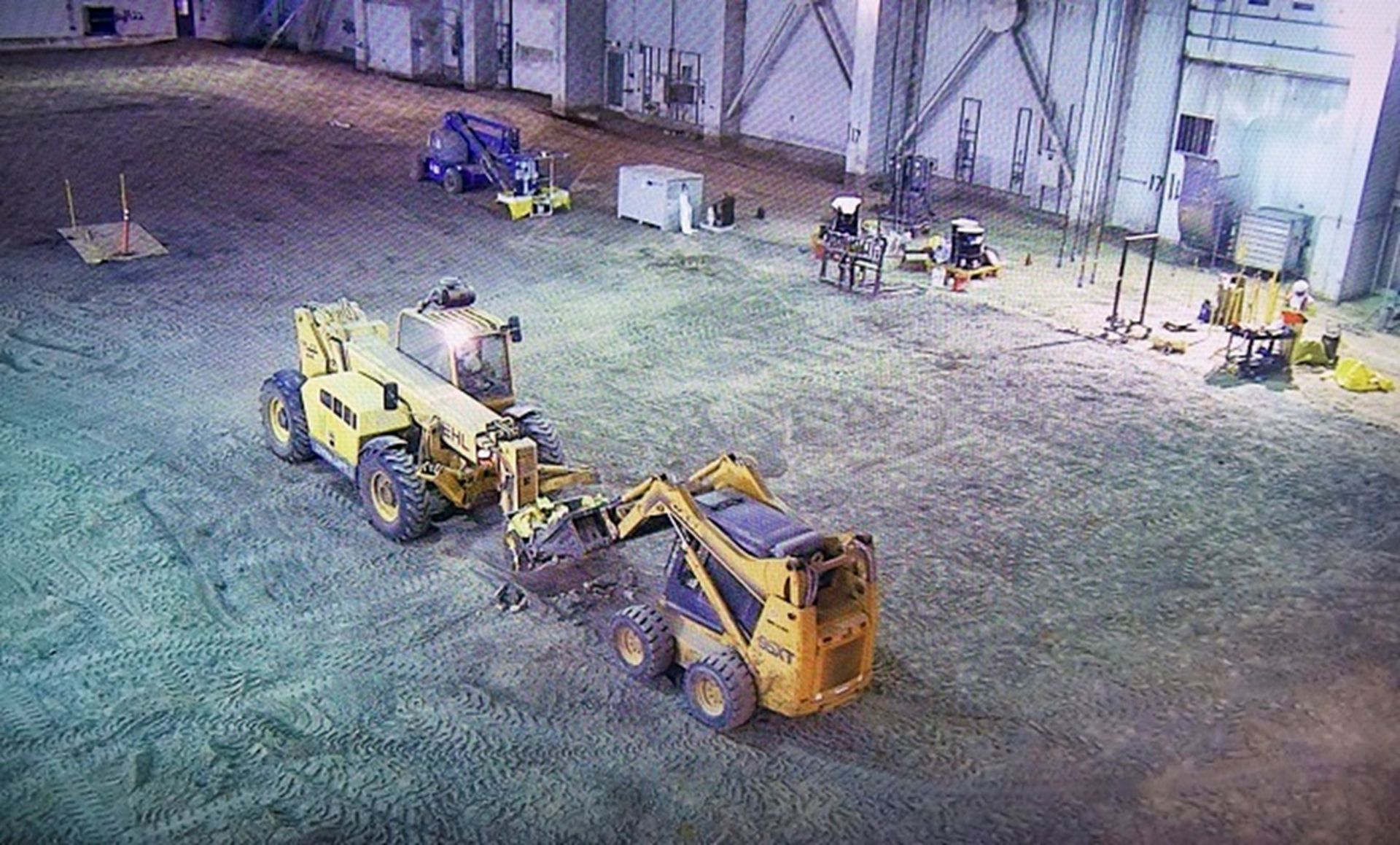
Work crews use light construction equipment to remove the final pieces of asphalt from one of the pads at the TSA-RE at INL. (Photo: DOE)
The Idaho National Laboratory is moving closer toward closing its largest building—which, at more than 316,000 square feet, could comfortably house a modern U.S. aircraft carrier, according to the Department of Energy.
Savannah River National Laboratory employee Vernon Bush, center, and SRNL summer intern Jadrion Huell, standing at right, of Claflin University, conduct a job shadowing activity with students Tredarius Lassiter, seated at left, and Tommy Applewhite. (Photo: DOE)
A three-day Minority Serving Institutions Partnership Program (MSIPP) event, led by Savannah River National Laboratory researcher Simona Hunyadi Murph, was held recently at the South Carolina site, according to a release by the Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (DOE-EM). The event included a collaborative workshop, job shadowing, and a tour of the laboratory and Savannah River Site field activities.
Portsmouth’s X-326 Process Building undergoes demolition in 2022. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management awarded a 10-year contract worth up to $5.87 billion to Southern Ohio Cleanup Company (SOCCo) of Aiken, S.C., for the decontamination and decommissioning of the DOE’s Portsmouth site in southern Ohio. SOCCo is a newly formed limited liability company comprising Amentum Environment and Energy, Fluor Federal Services, and Cavendish Nuclear (USA) Inc.
A photo from 2021 of the Fukushima nuclear power station with the more than 1,000 water storage tanks on site. (Photo: TEPCO)
We’ve all seen the headlines such as “Should Japan Dump Fukushima's Radioactive Water into the Ocean?” along with “Japan Set to Pour Fukushima Waste into Pacific, Irking China” and “Japan Is Slowly but Surely Releasing Wastewater from the Fukushima Nuclear Plant into the Pacific Ocean.” The most recent spate of fearmongering was triggered by the IAEA’s July 4 announcement that the agency had finished its independent assessment of Japan’s plans to release the treated wastewater stored at the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power station and found the plan “consistent with IAEA Safety Standards.”
Paducah Site deactivation crews use negative air machines to open sodium fluoride traps. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management recently shipped for off-site disposal 14 sodium fluoride traps, or exchange vessels, from the C-310 Product Withdrawal facility at the DOE’s Paducah Gaseous Diffusion Plant site in Kentucky. DOE-EM said it has also eliminated the site’s entire inventory of chlorine gas cylinders.
The Waste Isolation Pilot Plant, near Carlsbad, N.M. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management and the New Mexico Environment Department (NMED) have negotiated a settlement on terms to renew the 10-year operating permit for the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant near Carlsbad, N.M. The DOE, along with WIPP’s operating contractor, Salado Isolation Mining Contractors, and the NMED negotiated the settlement with New Mexico stakeholders.
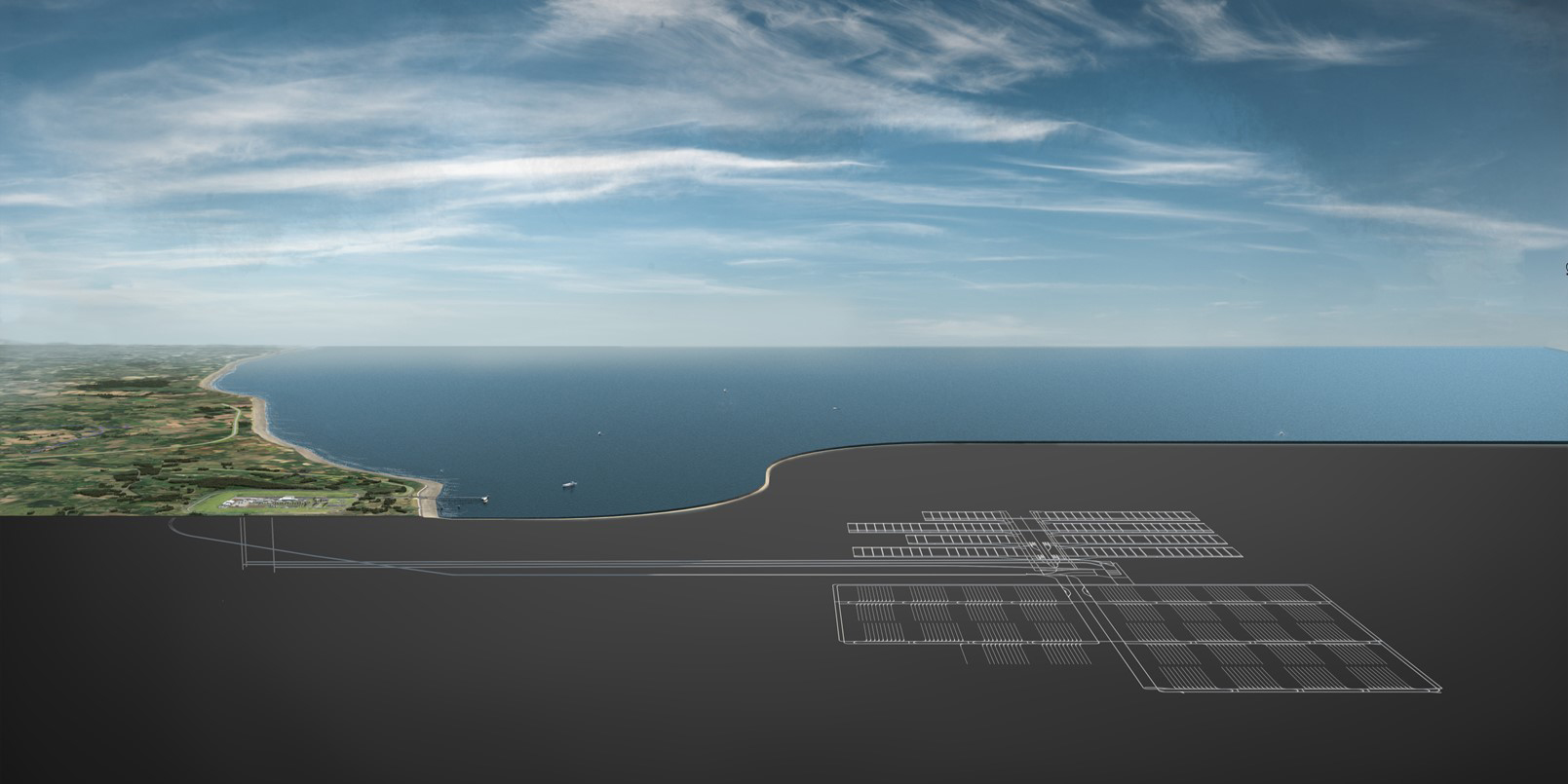
Concept art showing a geological disposal facility with tunnels and vaults in deep underground rock, under the seabed. (Image: NWS)
Nuclear Waste Services, the United Kingdom’s radioactive waste management organization, launched in January 2022, has begun a wide range of studies to evaluate sites that could be suitable to host a geological disposal facility (GDF).
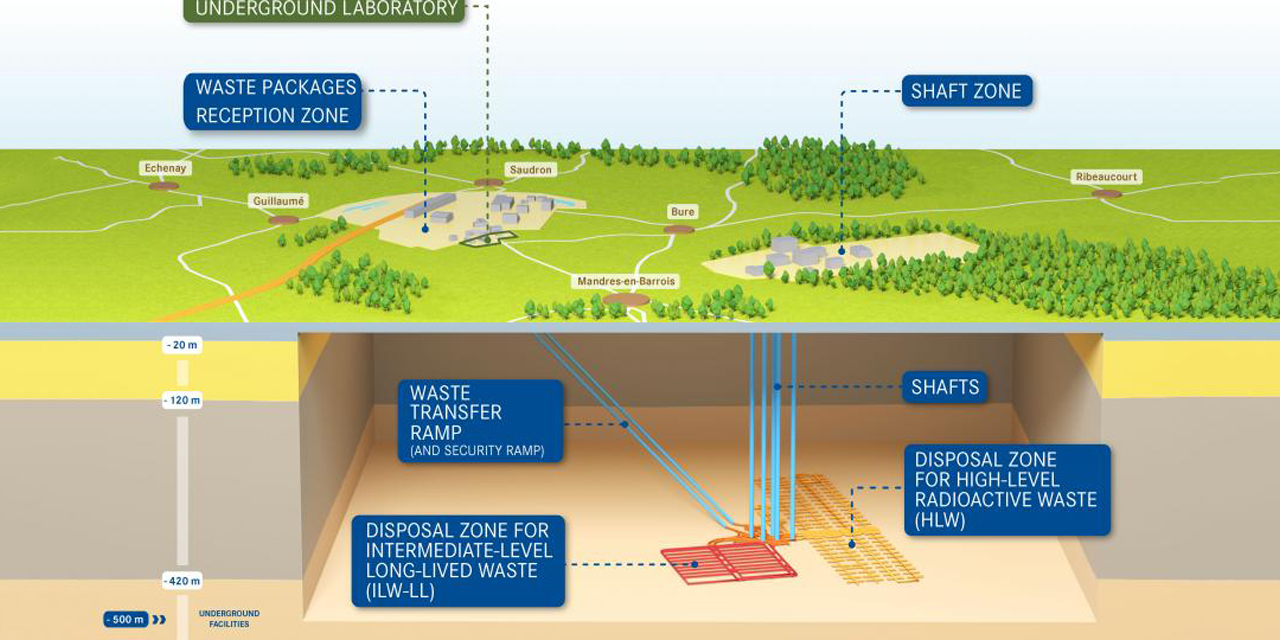
Diagram of the Cigéo repository in France. (Image: Andra)
Having deemed the application admissible, France’s nuclear safety authority, Autorité de sûreté nucléaire (ASN), will undertake a technical appraisal of Andra’s application to construct the Cigéo deep geological disposal facility for radioactive waste.


 (002) 2x1.jpg)








.jpg)