A view through the 20-cm disk amplifiers of the OMEGA laser at the University of Rochester’s Laboratory for Laser Energetics. (Photo: University of Rochester/J. Adam Fenster)
Proponents of inertial fusion energy celebrated in December 2022, when researchers at the National Ignition Facility at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory achieved fusion ignition by subjecting a carefully crafted diamond cryogenic sphere containing frozen deuterium-tritium fuel to NIF’s laser energy. NIF has yet to repeat the feat, in part because that facility was not designed to produce fusion energy, and ignition requires near-perfect targets. For inertial fusion energy to serve as a reliable power source, it will require swift, reliable, and economic target production.
Portsmouth’s X-326 Process Building undergoes demolition in 2022. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management awarded a 10-year contract worth up to $5.87 billion to Southern Ohio Cleanup Company (SOCCo) of Aiken, S.C., for the decontamination and decommissioning of the DOE’s Portsmouth site in southern Ohio. SOCCo is a newly formed limited liability company comprising Amentum Environment and Energy, Fluor Federal Services, and Cavendish Nuclear (USA) Inc.
A ceremony was held in Seoul, South Korea, to launch the new SMR Alliance (Photo: SK Inc.)
The government of the Republic of Korea and the country’s industrial sector are teaming up to promote the development of small modular reactors. At a launch ceremony for the SMR Alliance, held July 4, the participants announced strategic plans and signed business agreements.
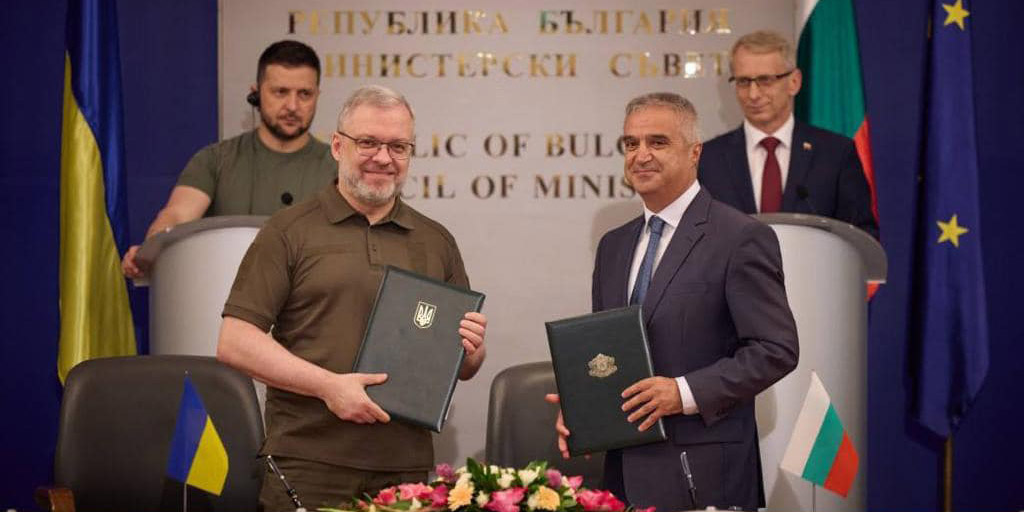
In the foreground, from left: Ukrainian energy minister German Galushchenko and Bulgarian energy minister Rumen Radev at the MOU signing ceremony in Sofia, Bulgaria. Looking on are (from left) Ukrainian president Volodymyr Zelenskyy and Bulgarian prime minister Nikolai Denkov.
The energy ministries of Bulgaria and Ukraine have announced the signing of a memorandum of understanding to expand collaboration in the energy sector, including the nuclear energy sector.
(Image: Kuk Cho/Pusan National University)
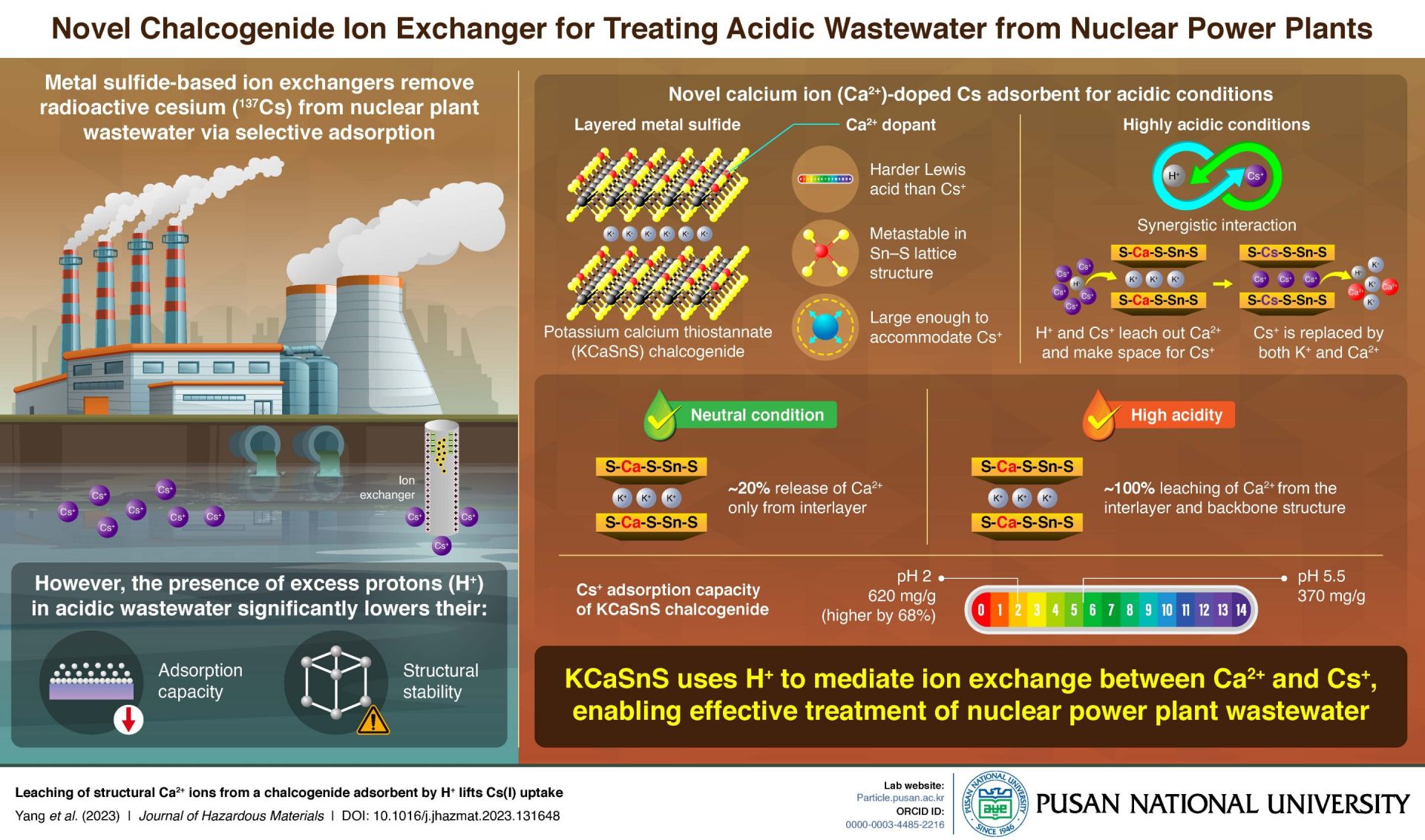
Researchers from the Pusan National University in South Korea have developed a new calcium-doped ion exchanger for the removal of radioactive cesium from acidic nuclear power plant wastewater. The findings have the potential for developing more efficient and effective methods of remediating radioactive contamination.


.jpg)