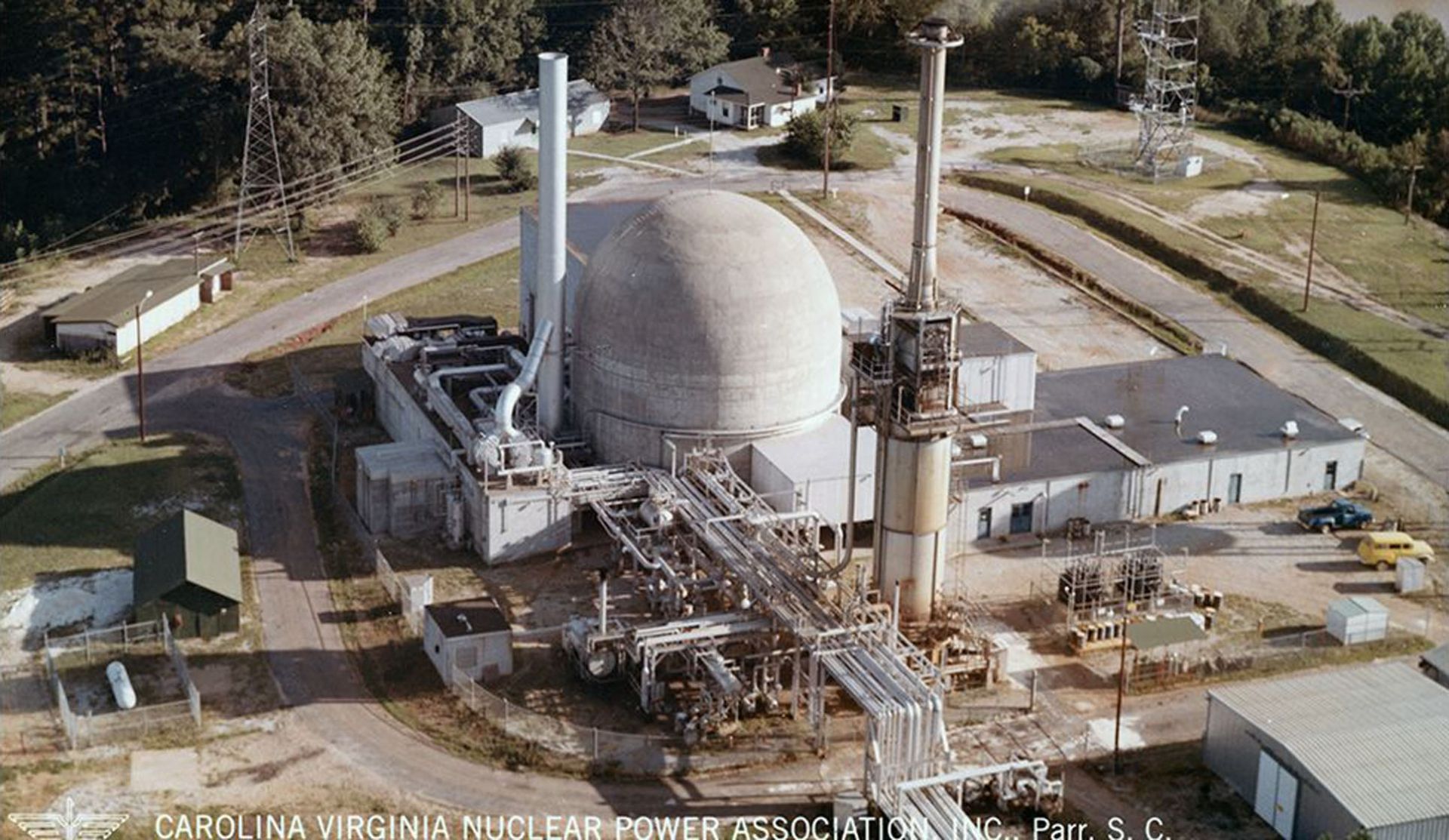
The Carolinas-Virginia Tube Reactor site, circa 1963. (Photo: Duke Energy)
The Carolinas-Virginia Tube Reactor (CVTR), also known as Parr due to its location in Parr, S.C., was a 65-MWt (17-MWe) pressurized tube reactor. Construction began in January 1960, and the reactor reached initial criticality in March 1963. Commercial operation commenced in December 1963, and the reactor was permanently shut down in January 1967 after the test program was complete.
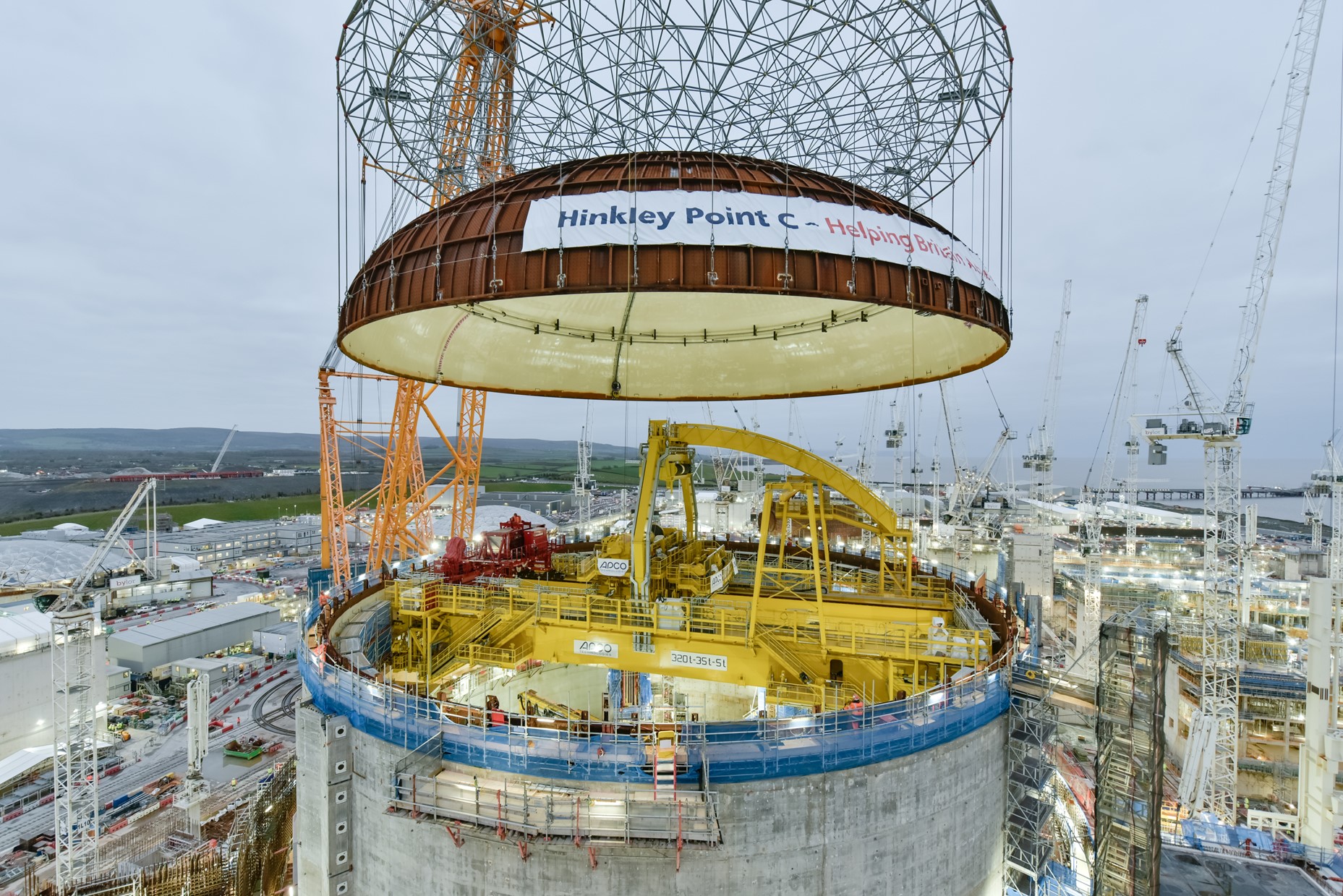
Workers place the dome atop Hinkley Point C’s first reactor building on December 15. (Photo: EDF Energy)
EDF Energy’s new nuclear build megaproject at Hinkley Point C last Friday moved forward—or, more literally, upward then downward—when workers, with a substantial assist from Big Carl, the world’s largest crane, successfully lifted the C1 reactor building’s 47-meter-wide, 245-ton steel dome into place.
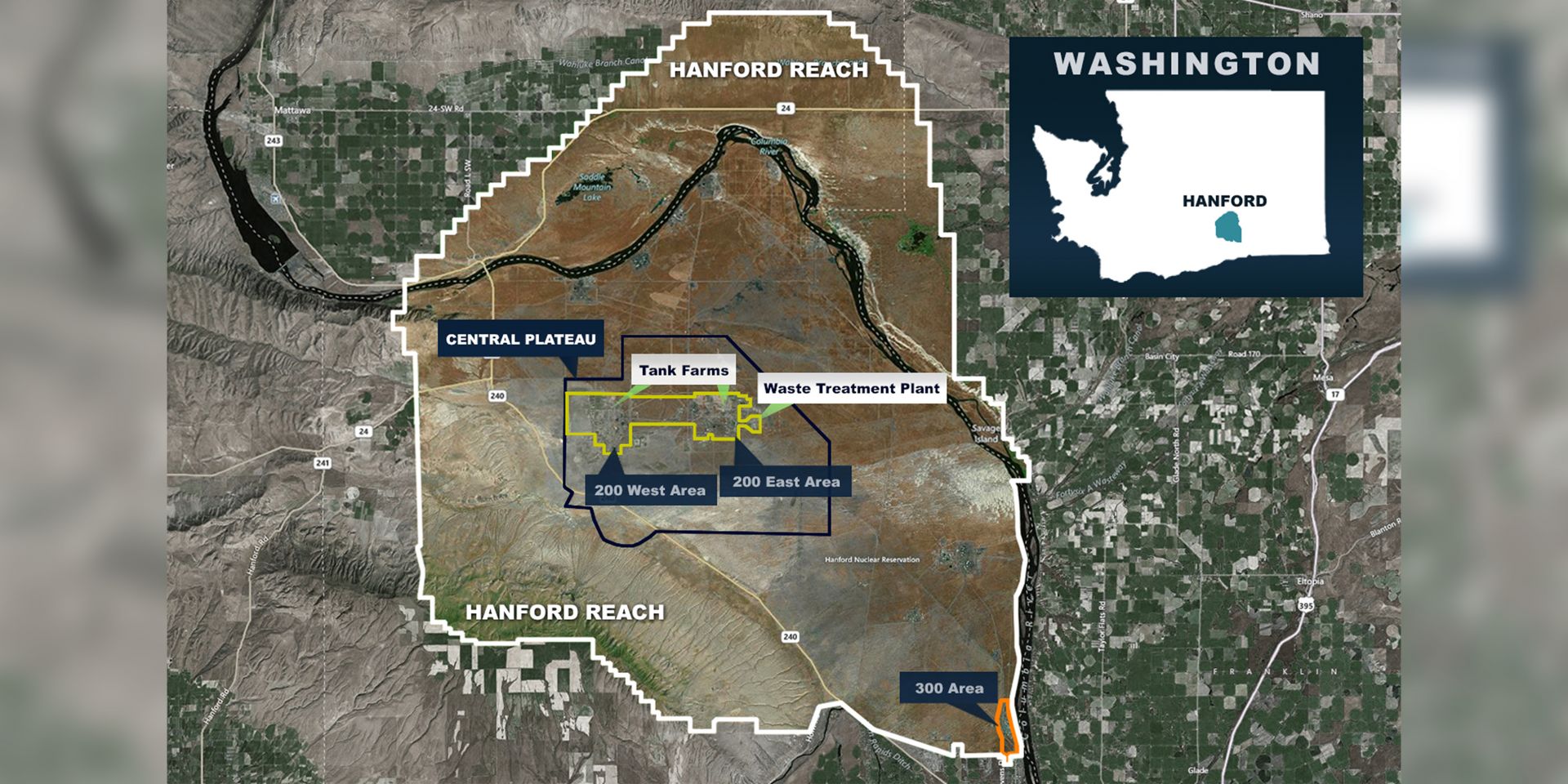
The DOE’s Hanford Site. (Image: Washington River Protection Solutions)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management issued for public comment the first request for qualifications (RFQ) related to the department’s Cleanup to Clean Energy initiative, which aims to increase energy production by making DOE land available for the potential development of carbon-free energy (CFE) electricity generation through leases.
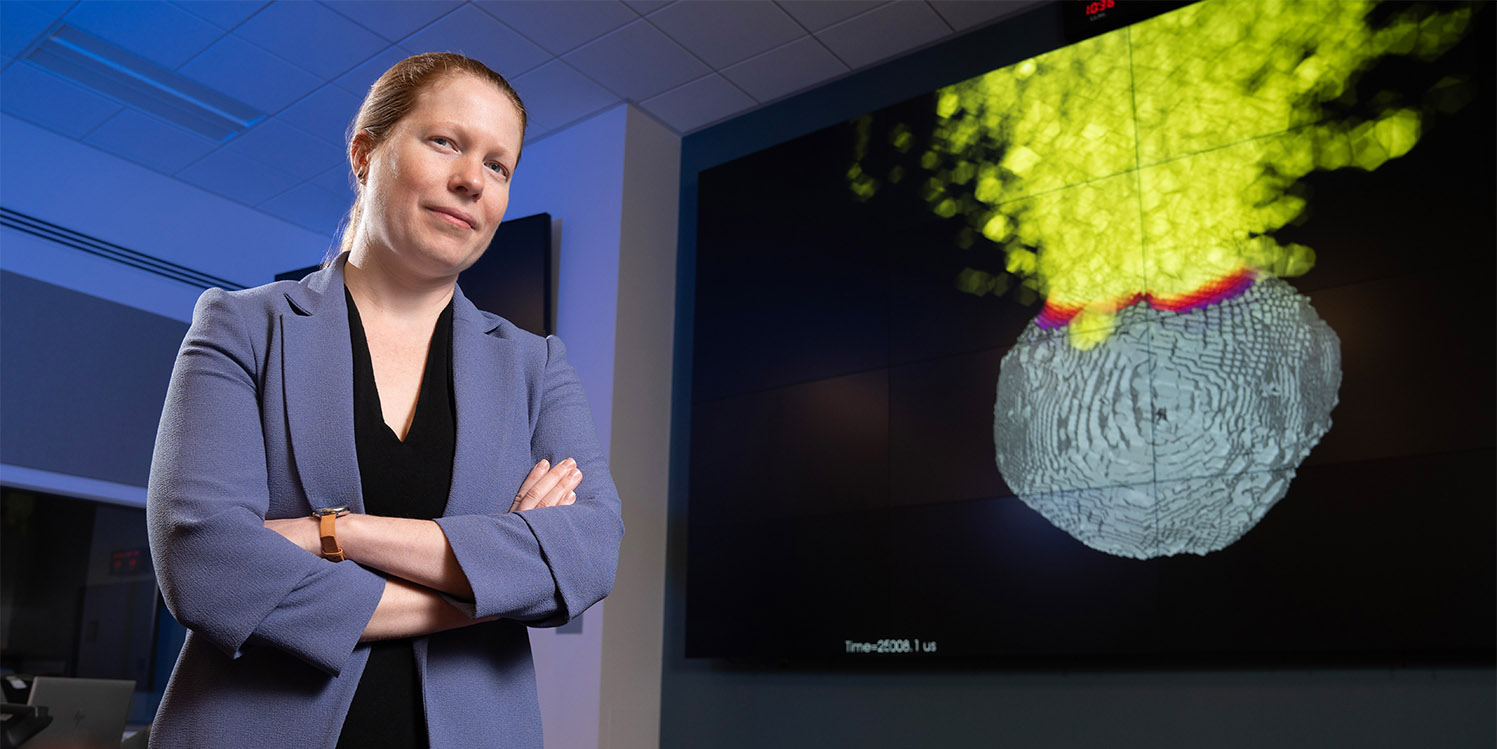
LLNL physicist Mary Burkey developed a novel approach to simulating the energy deposition from a nuclear device on an asteroid’s surface. (Photo: LLNL)
The same high energy density that makes nuclear energy a clean and efficient source of power could make it a good alternative to defend the planet against catastrophic asteroid impacts. NASA demonstrated the world’s first planetary defense technology in September 2022 by deliberately crashing a “kinetic impactor”—a heavy, box-like spacecraft—into an asteroid. Now, researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory have developed a new tool to model how a nuclear device could deflect—or even destroy—an asteroid threat to Earth in a more efficient and controlled way.
A slide from the DOE-FES’s recent presentation to the Fusion Energy Sciences Advisory Committee. (Image: DOE)
The Office of Fusion Energy Sciences (FES) in the Department of Energy’s Office of Science introduced a new plan—"Building Bridges: A Vision for the Office of Fusion Energy Sciences”—during a Fusion Energy Sciences Advisory Committee (FESAC) hearing on December 13, and announced that news December 14. What’s included? A plan for the DOE to “establish the steps needed to help advance fusion energy, including addressing key science and technology gaps in the supply chain and industry.” The vision is less a guiding document than a preview of DOE-FES’s near-term intentions, which include drafting a fusion science and technology road map in 2024 to shape investments for the coming decade.
Homer at his work station. (Artwork from The Simpsons used with the permission of 20th Century Studios)
In the episode “Duffless” in season 4 of The Simpsons, Homer is deep in the bowels of the Springfield Nuclear Power Plant when he encounters a gigantic mutant spider. He turns to a map that says, “To overcome the spider’s curse, simply quote a Bible verse.” Homer starts with, “Uh, thou shalt not . . .” but then, unable to remember anything from the Bible, he instead brains the spider with a rock. This sort of nuttiness is often how we’ve depicted the power plant on the show, where I’ve been a writer and producer for 20 seasons.
DOE-LM’s Taylour Whelan interviews DOE-LM director Carmelo Melendez for one of four podcasts produced for the office’s 20th anniversary celebration. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Legacy Management, which oversees department legacy sites that have been cleaned of radioactive waste and environmental contamination, debuted its first podcast on December 15. Launched in honor of the office’s 20th anniversary, the podcast series includes four episodes, each featuring a different member of the DOE-LM team.
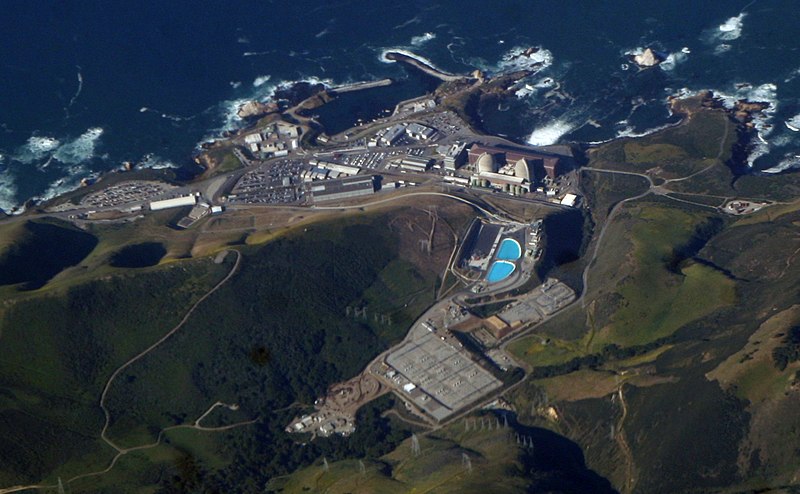
The Diablo Canyon nuclear power plant. (Photo: Doc Searls)
The California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) voted last Thursday to extend the life of Diablo Canyon an additional five years. The decision was the final step in the extension of the state's last remaining nuclear power plant, whose two reactors will now operate until at least 2029 and 2030, respectively, instead of closing in 2024 and 2025.
Africa is home to 1.5 billion people in 54 countries living on 12 million square miles. The economies of many of these countries are hobbled by a general dearth of energy that nuclear could solve without adding to the harm of global warming.
The World Nuclear Association and the African Commission on Nuclear Energy (AFCONE) last year signed a memorandum of understanding to encourage the use of nuclear energy in support of economic growth and sustainable energy development in Africa.






 The Department of Energy, in its
The Department of Energy, in its  A new report from the Emirates Nuclear Energy Corporation (ENEC) and the Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI) describes the use of nuclear energy to decarbonize some activities normally powered by oil and gas.
A new report from the Emirates Nuclear Energy Corporation (ENEC) and the Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI) describes the use of nuclear energy to decarbonize some activities normally powered by oil and gas.