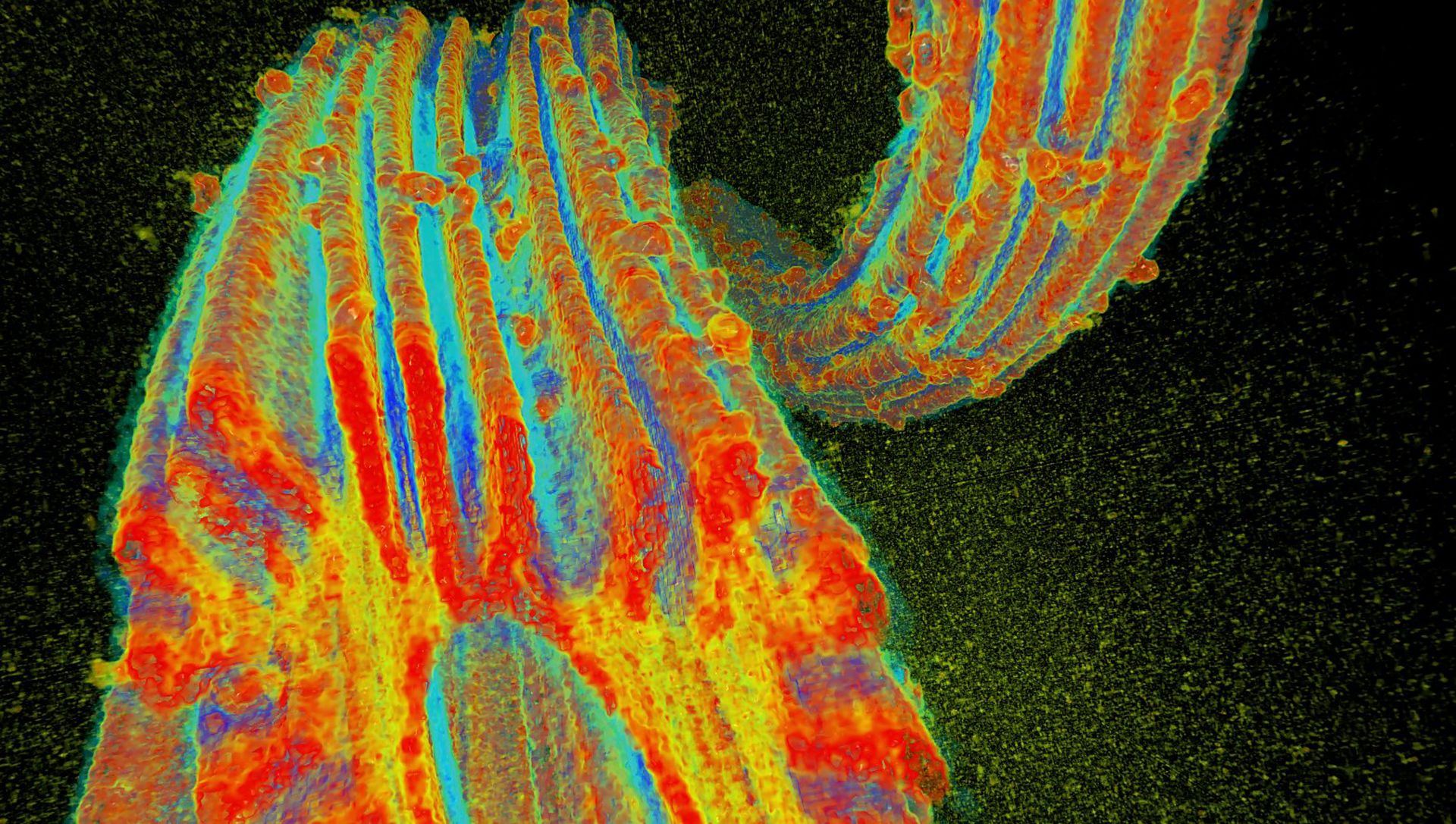
Researchers have been working frantically to develop an array of materials and fibers to economically extract uranium from seawater—and they have succeeded. PNNL scientists exposed this special uranium-sorbing fiber developed at ORNL to Pseudomonas fluorescens and used the Advanced Photon Source at Argonne National Laboratory to create a 3-D X-ray microtomograph to determine microstructure and the effects of interactions with organisms and seawater. (Image: PNNL)
America, Japan, and China are racing to be the first nation to make nuclear energy completely renewable. The hurdle is making it economical to extract uranium from seawater, because the amount of uranium in seawater is truly inexhaustible.
While America had been in the lead with technological breakthroughs from the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest and Oak Ridge National Laboratories, researchers at Northeast Normal University in China have sprung ahead. But these breakthroughs from both countries have brought the removal of uranium from seawater within economic reach. The only question is when will the source of uranium for our nuclear power plants change from mined ore to seawater extraction?
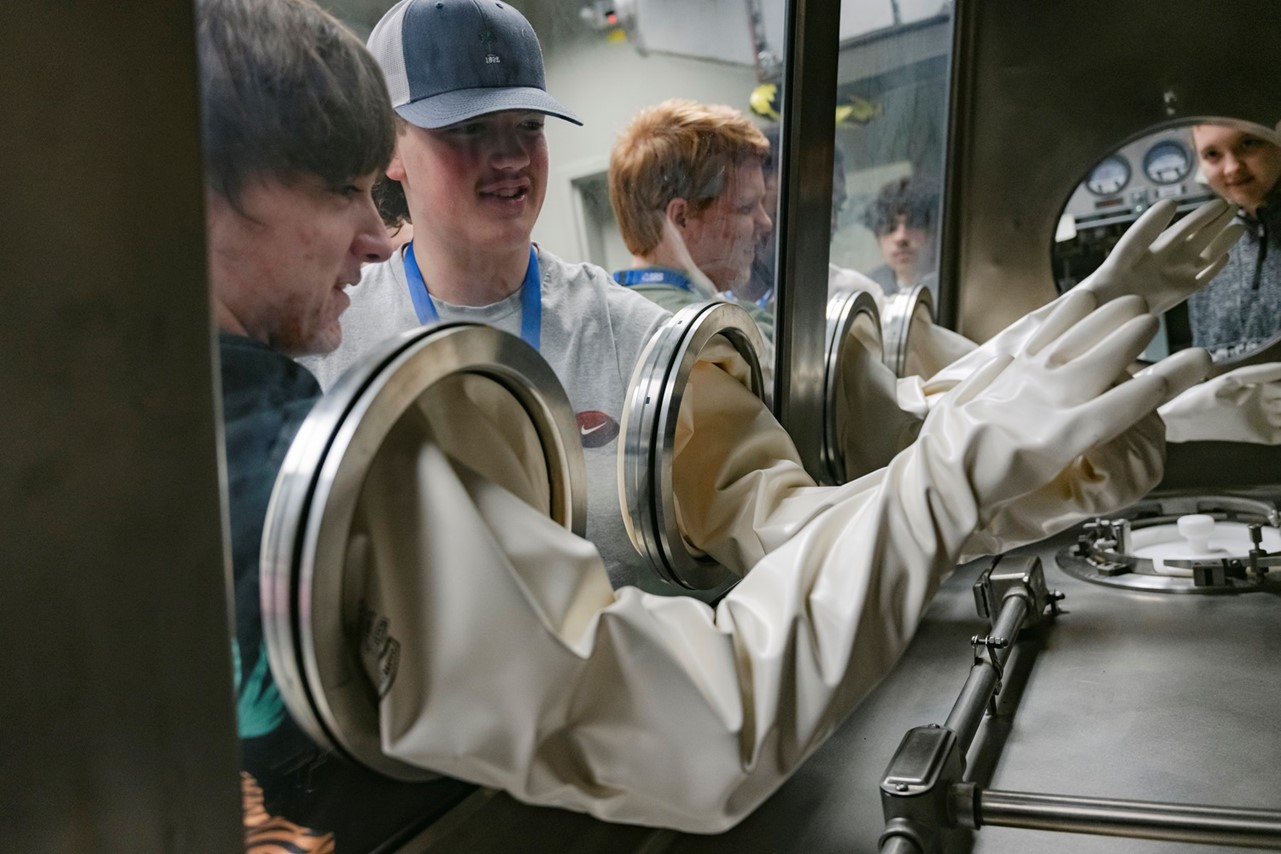
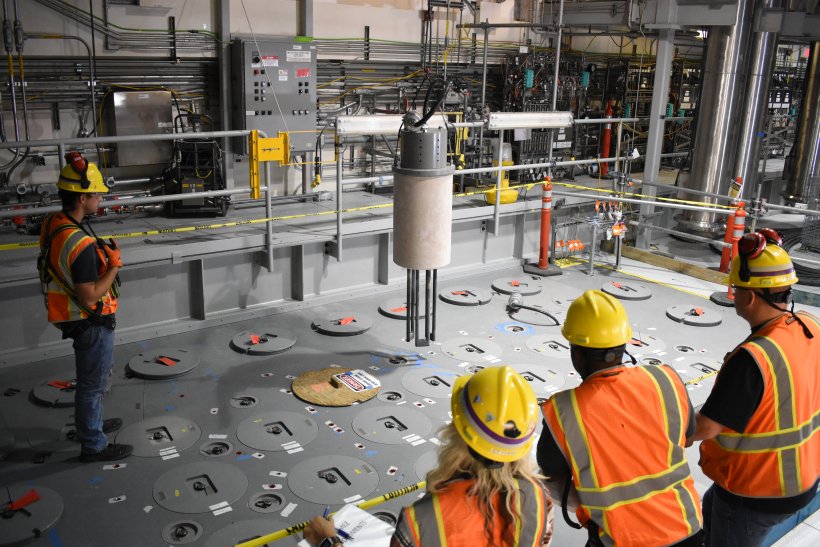
Aiken County Public School District students test out a mock glovebox during a tour of the Savannah River Site’s Waste Solidification Building. (Photo: SRNS)
Fifteen area high school students recently completed job shadow experiences with leaders, engineers, and education outreach personnel at the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site in South Carolina, according to Savannah River Nuclear Solutions (SRNS).
Clinton nuclear power plant, located near Clinton, Ill. (Photo: Constellation)
Constellation Energy is asking the Nuclear Regulatory Commission for an initial license renewal for its Clinton nuclear plant in Illinois, which would allow the facility to operate through 2047.
This move is not unexpected from Constellation, the largest producer of nuclear power in the United States. The vast majority of nuclear plants in the United States have already been approved for their first 20-year renewal term. Clinton, which came on line in 1987, is one of the nation’s “newer” plants.
Radioisotopes target cancer, improve imaging, and have myriad other medical uses
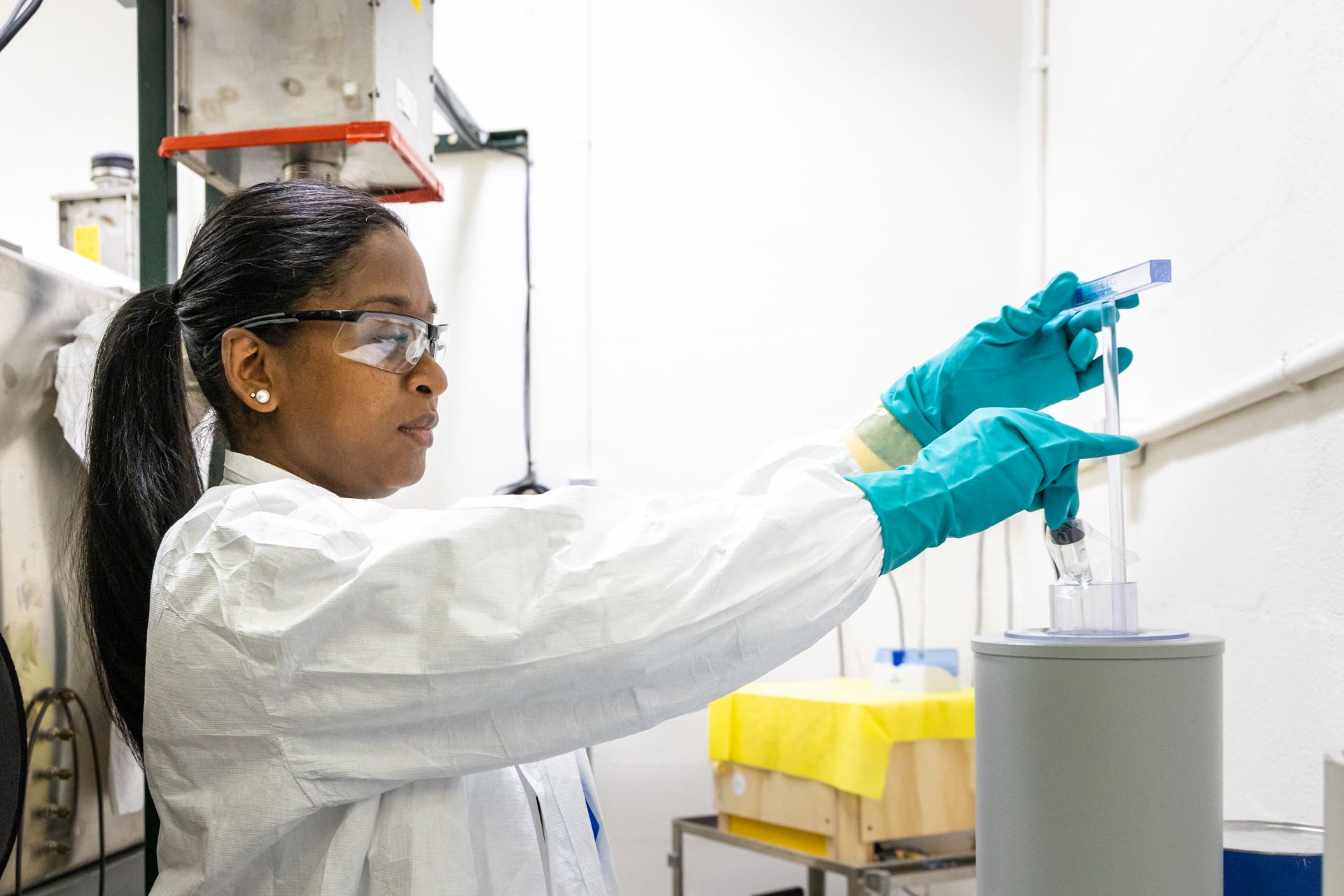
ORNL radioisotope manufacturing coordinator Jillene Sennon-Greene places a shipment vial of actinium-225 inside the dose calibrator to confirm its activity is within customer specifications. (Photo: Carlos Jones/ORNL, DOE)
On August 2, 1946, 1 millicurie of the isotope carbon-14 left Oak Ridge National Laboratory, bound for the Barnard Free Skin and Cancer Hospital in St. Louis, Mo.
That tiny amount of the radioisotope was purchased by the hospital for use in cancer studies. And it heralded a new peacetime mission for ORNL, built just a few years earlier for the production of plutonium from uranium for the Manhattan Project.
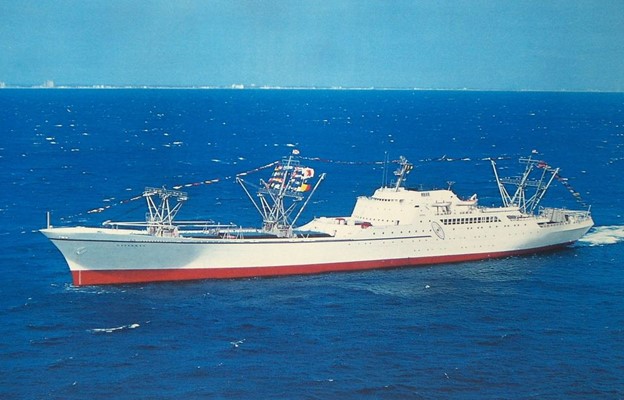
The N.S. Savannah. (Photo: N.S. Savannah Association)
What will happen to the retired nuclear-powered merchant ship, the N.S. Savannah? The Maritime Administration (MARAD) of the Department of Transportation is investigating possibilities for the vessel’s future, whether it be in disposition, transportation, or preservation.
Assistant energy secretary for international affairs Andrew Light (seated, left) and Bulgarian energy minister Rumen Radev (seated, right) sign the new agreement in Bulgaria. (Photo: U.S. Embassy in Bulgaria)
Officials from the United States and Bulgaria inked a deal this week to cooperate as Bulgaria further develops its civil nuclear power program.
A working group will explore plans to design, construct, and commission two new units at Bulgaria’s Kozloduy nuclear power plant. The two countries will also “explore collaboration on research and training programs and developing Bulgaria's nuclear supply chain resilience,” according to reports.
One of 18 startup heaters is installed in Hanford’s second melter, which will be used to vitrify liquid waste. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management announced that crews at the Hanford Site’s Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant, also known as the Vit Plant, recently installed 18 temporary startup heaters in the second of two melters in the plant’s Low-Activity Waste Facility.
Vogtle-4, pictured in August 2023. (Photo: Georgia Power)
Georgia Power’s Vogtle-4, located near Waynesboro, Ga., reached initial criticality this week, hitting a major milestone in the start-up of the reactor.
The company announced the news on February 14. Initial criticality demonstrates that operators have safely started the nuclear reactor, or, in other words, the fission reaction within the unit is now self-sustaining and the nuclear reactor is ready to produce heat.
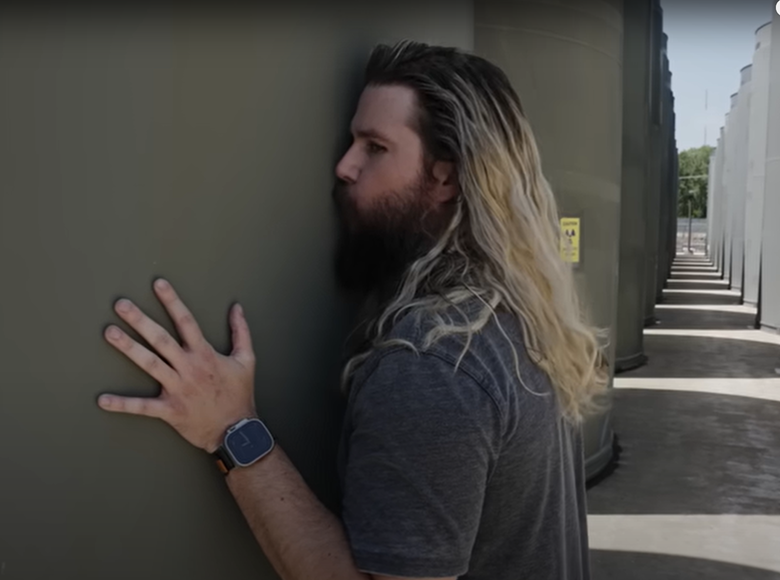
Kyle Hill appreciates a Dresden nuclear waste cask. (Photo: Kyle Hill)
On this holiday that celebrates all things love, here’s a look at the love affair that Kyle Hill has with nuclear energy—even its waste.
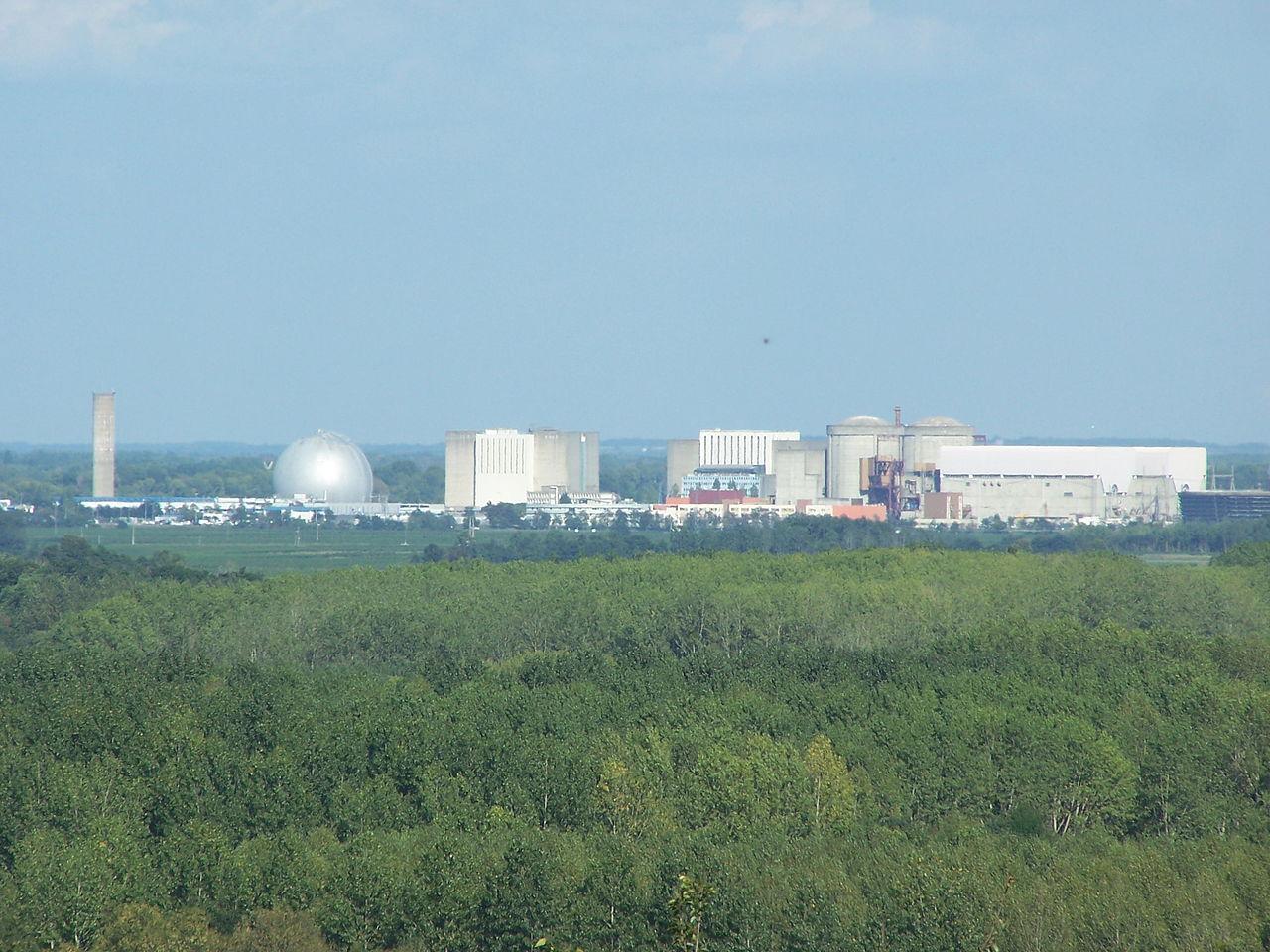
Chinon nuclear power plant in France. (Photo: Wargus/Wikimapia)
A fire this past weekend at Chinon nuclear power plant in France forced two reactors to be shut down. According to initial reports, a transformer in a nonnuclear sector of Unit 3 caught fire.
The incident occurred February 10 in the early morning hours, local time, and the fire was quickly extinguished.
The U.S. Treasury Department building in Washington, D.C.
Two weeks remain for public comments on the proposed language in the new federal rules proposed for hydrogen production tax credits. A public hearing on the regulations is scheduled for March 25, 2024.
While the federal proposal is largely popular among environmentalists and some pronuclear advocates, there are concerns from others that it would cut out opportunities for existing legacy nuclear plants that are well-equipped to convert part of their operations to hydrogen production. The proposed rules require hydrogen to come from newly built resources—the largest obstacle for legacy nuclear sites but further incentive to deploy new reactors—and would permit using natural gas if employed with carbon capture and sequestration.
















.jpg)