Constellation offers first-ever corporate green bonds
In a bid to generate up to $900 million in additional funding for nuclear energy projects, Constellation Energy announced this week that it will issue corporate green bonds in the United States.

A message from Electrical Builders, Ind.
America’s Top Performing Nuclear Plants Rely on Electrical Builders, Industries to Expand and Extend the Life of Their Critical Electrical Assets
In a bid to generate up to $900 million in additional funding for nuclear energy projects, Constellation Energy announced this week that it will issue corporate green bonds in the United States.
![]() Here is a recap of industry happenings from the recent past:
Here is a recap of industry happenings from the recent past:
PPPL awards contract for fusion development
The Department of Energy’s Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory has awarded an engineering support services contract for the development of fusion energy to a consortium of business partners led by AtkinsRéalis that includes Jacobs Technology and Longenecker and Associates. The contract has a base period of three years with two optional years and a ceiling value of $50 million. Services to be provided under the agreement include design of future upgrades for the National Spherical Torus Experiment–Upgrade (NSTX-U, the main fusion experiment at PPPL); design and fabrication of plasma diagnostic and heating subsystems for ITER (the international fusion facility being constructed in France); conceptual design of electricity-generating fusion plants; and development of physics and technology advances for improving the economics of fusion plants. Another partner that will support this contract is the United Kingdom Atomic Energy Authority, for which AtkinsRéalis has been working on stage 1 of the Spherical Tokamak for Energy Production (STEP) program.

X-energy has opened a regional operations and training center aimed at supporting future deployment of its advanced modular nuclear reactor fleet and the operators who will run it.
In March 1949—75 years ago this month—the 25-kilowatt reactor known as Clementine reached full power. As an experimental reactor, it had a rather long and successful run. It was the world’s first fast neutron (high-energy) reactor and operated from initial criticality in 1946 to final shutdown in 1952.
By a narrow vote of 9–7, the 5th Circuit Court of Appeals denied a petition to rehear the court’s 2023 decision to vacate Interim Storage Partners’ (ISP’s) license to build and operate a consolidated interim storage facility for commercial spent nuclear fuel in Andrews County, Texas.

Staff and researchers at Penn State’s Radiation Science and Engineering Center (RSEC) will work this year to install a small angle neutron scattering (SANS) device and become the first and only U.S. university research reactor to host SANS capability. The $9.8 million device, donated by Helmholtz Zentrum Berlin (HZB) in Germany, will help researchers determine the structure of organic materials such as polymers, complex fluids, and biomolecules.
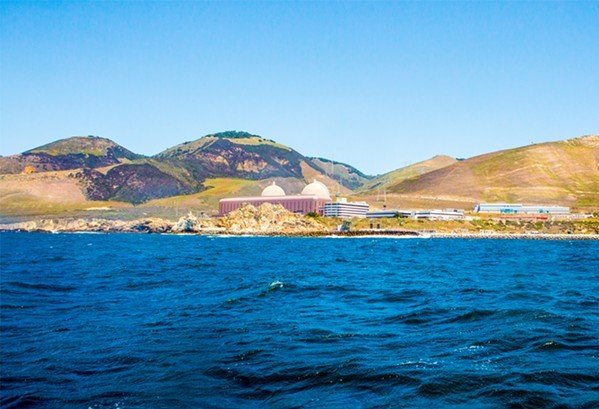

The owners of the Diablo Canyon nuclear power plant plan to dredge a massive buildup of shoaled sediment from its seawater intake cove.
Pacific Gas and Electric spokesperson Suzanne Hosn said, “The dredging project in the Diablo Canyon marina will remove approximately 70,000 cubic yards of sediment to prevent circumstances that could impact the power plant’s cooling system. Dredging will take place for the first time since operations began because of a rapid increase in sediment.”

Lightbridge Corporation announced today that it has reached “a critical milestone” in the development of its extruded solid fuel technology. Coupon samples using an alloy of zirconium and depleted uranium—not the high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU) that Lightbridge plans to use to manufacture its fuel for the commercial market—were extruded at Idaho National Laboratory’s Materials and Fuels Complex.

The American Nuclear Society is hosting an online event this week that will look at how women are making history in nuclear science and technology trade careers. The webinar is scheduled for Thursday, March 21, from 6:00 p.m. to 7:00 p.m. (EDT).
Registration is required.
The American Nuclear Society election for 2024 is now open, and members can vote for the Society’s next vice president/president-elect as well as four U.S. members-at-large and one young member for the Board of Directors.
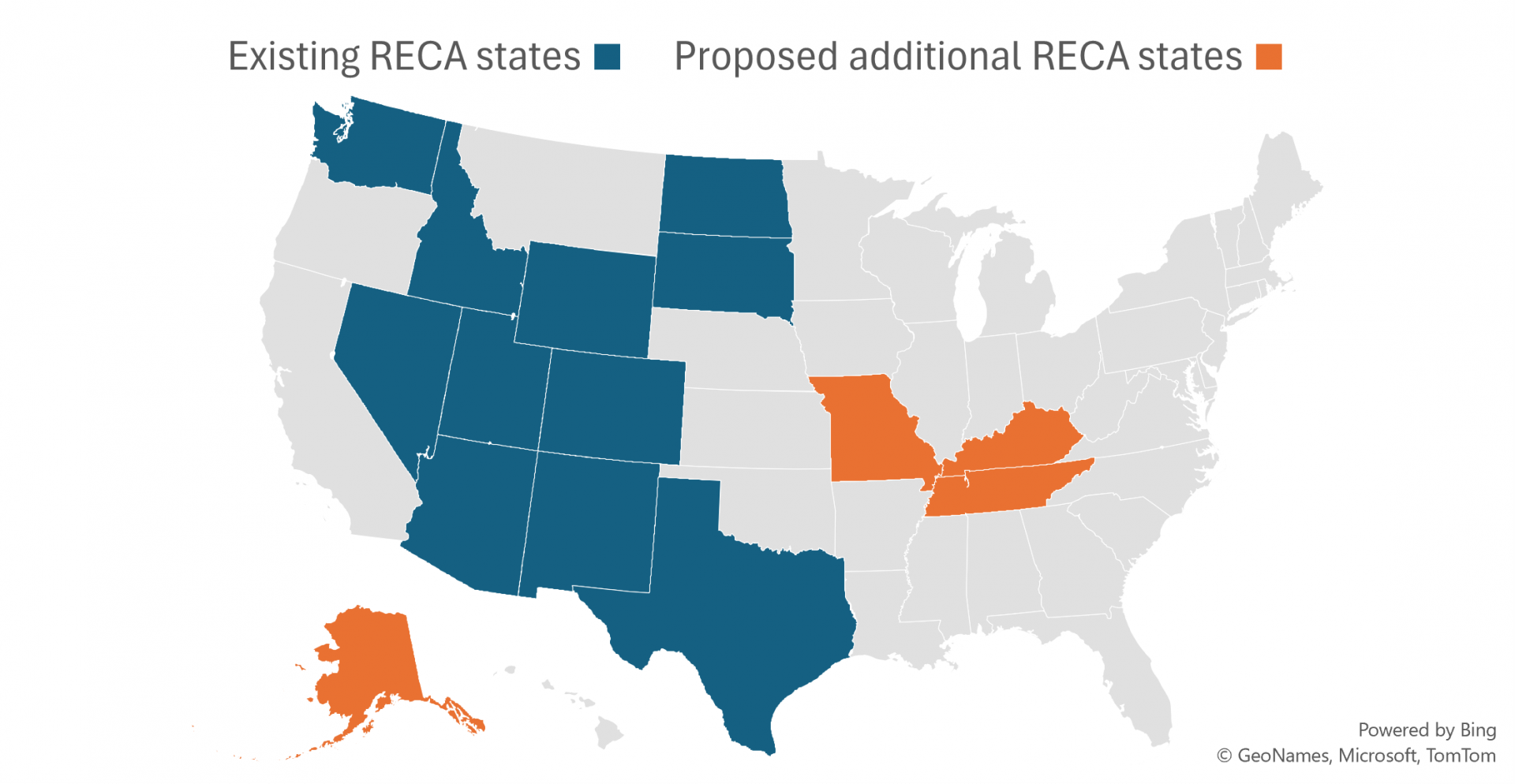
The Manhattan Project may have begun more than 80 years ago, but it’s still in the news—and not just because of Oppenheimer’s recent haul at the Academy Awards. On March 7, the Senate passed S. 3853, the Radiation Exposure Compensation Reauthorization Act, by a vote of 69 to 30, sending the bill to the House. It’s Sen. Josh Hawley's (R., Mo.) second attempt to reauthorize the Radiation Exposure Compensation Act (RECA)—which was first enacted in 1990 to address the legacy of U.S. nuclear weapons production—before it expires in June. The bill would extend the deadline to claim compensation by five years and expand it from the dozen states now covered to include individuals exposed to radiation in certain regions of Missouri, Alaska, Kentucky, and Tennessee.

After decades of false starts, U-turns, and stasis, the United States has arrived at a de facto solution for its high-level nuclear waste: Leave it in storage where it was produced, no matter how many tens of billions of dollars it costs, what impediments it raises for nuclear expansion, or what burdens it creates for the reuse of old reactor sites.
Dumb as it sounds, this is keeping all the major players happy. And it avoids alternative pathways, each of which has problems.
The American Nuclear Society has hosted workshops for teachers for years, but the latest Educator Workshop and Research Reactor Tour, which took place in November at the 2023 Winter Conference and Expo, was especially successful. ANS partnered with the University of Maryland for the event, which was part of the Society’s Powering Our Future initiative, sponsored by the Department of Energy.
The U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission, the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission, and the U.K. Office for Nuclear Regulation have signed a memorandum of cooperation to collaborate on technical reviews of advanced reactor and small modular reactor technologies.
The newest edition of the Nuclear News Buyers Guide will be out soon, marking the 55th year of the most comprehensive goods and services publication in the nuclear industry. The American Nuclear Society invites all companies that perform or seek nuclear-related work to participate by identifying areas of expertise and providing contact information.
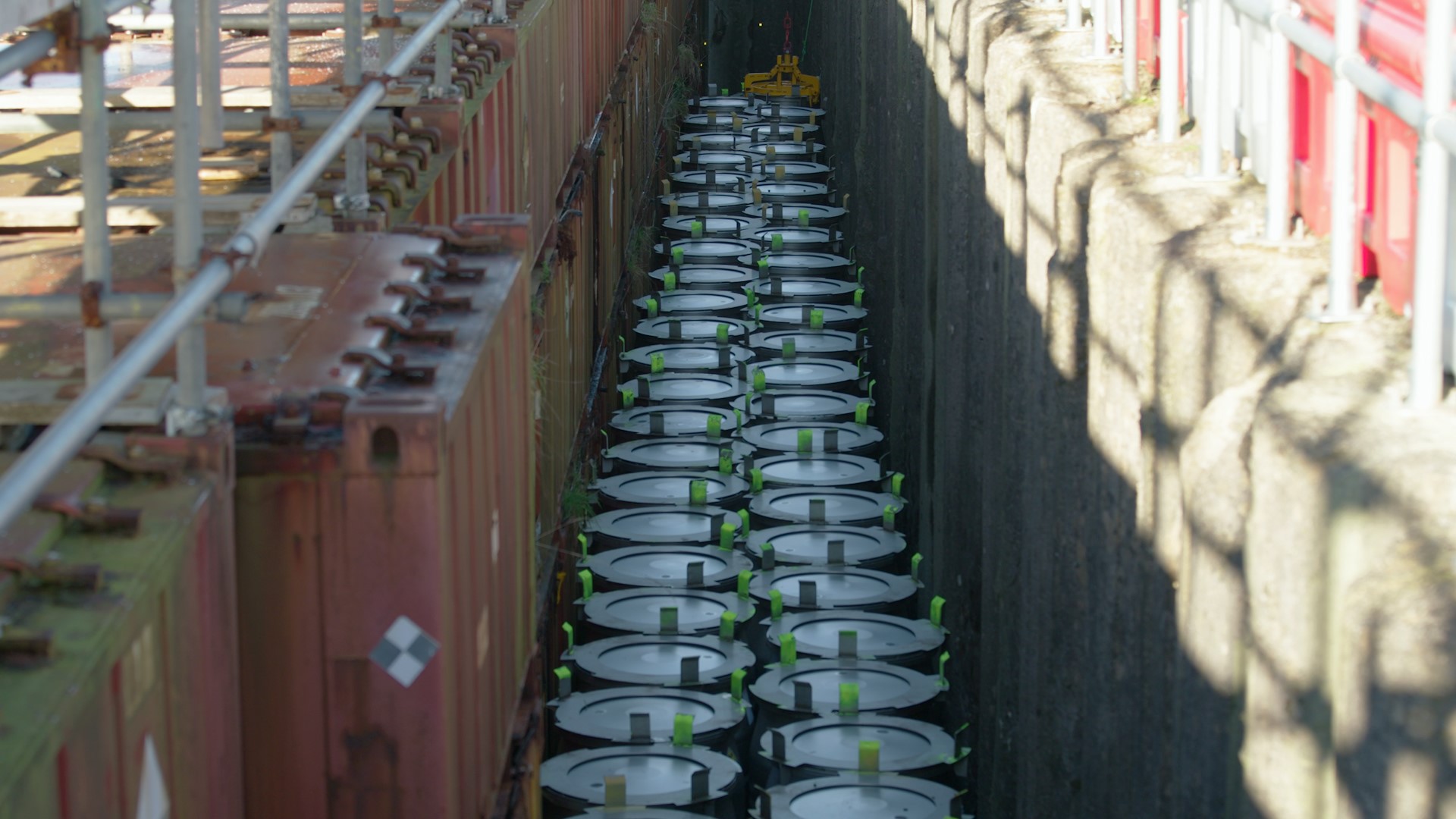

More than 1,000 drums of low-level radioactive waste in the United Kingdom have been safely disposed of earlier than expected. The project was completed through the collaborative work of Nuclear Waste Services (NWS), Nuclear Restoration Services (NRS), and Nuclear Transport Solutions (NTS).
Contracts valued up to a combined $1 billion have been awarded by the National Nuclear Security Administration’s Office of Nuclear Smuggling Detection and Deterrence to SeaTech Global Security Solutions of Richland, Wash., and Parsons Government Services International Inc. of Pasadena, Calif.

Craig Piercy
cpiercy@ans.org
Spoiler alert: America has one more nuclear reactor on line.
It’s been a long, hard slog for the Vogtle reactor expansion project, and the news coverage has been tough. I would describe it as the “standard media fare” of late—a steady flow of click-inducing “breaking news” alerts on cost overruns and schedule delays. Sure, it’s all fair game in a world with press freedom, but I had hoped for more substance along with the “horse race” reporting from our Fourth Estate.
Nuclear is hard—but it’s not just nuclear. In the United States, big groundbreaking projects of all sorts veer over budget and behind schedule frequently these days, resulting in unpleasant headlines along the way. Then, when they are up and running, these facilities tend to fall out of the public spotlight, and we all start taking them for granted. But this narrative arc hides a larger truth. When Vogtle Unit 4 joins Unit 3 in commercial operation later this year, the two units together are tipped to churn out over 17 million megawatt-hours of steady 24/7 power on an annual basis. That’s more energy per year than all the windmills in California—enough to feed one million homes and businesses. It will do this for the next 60, 80, maybe even 100 years. Talk about a buried lede!
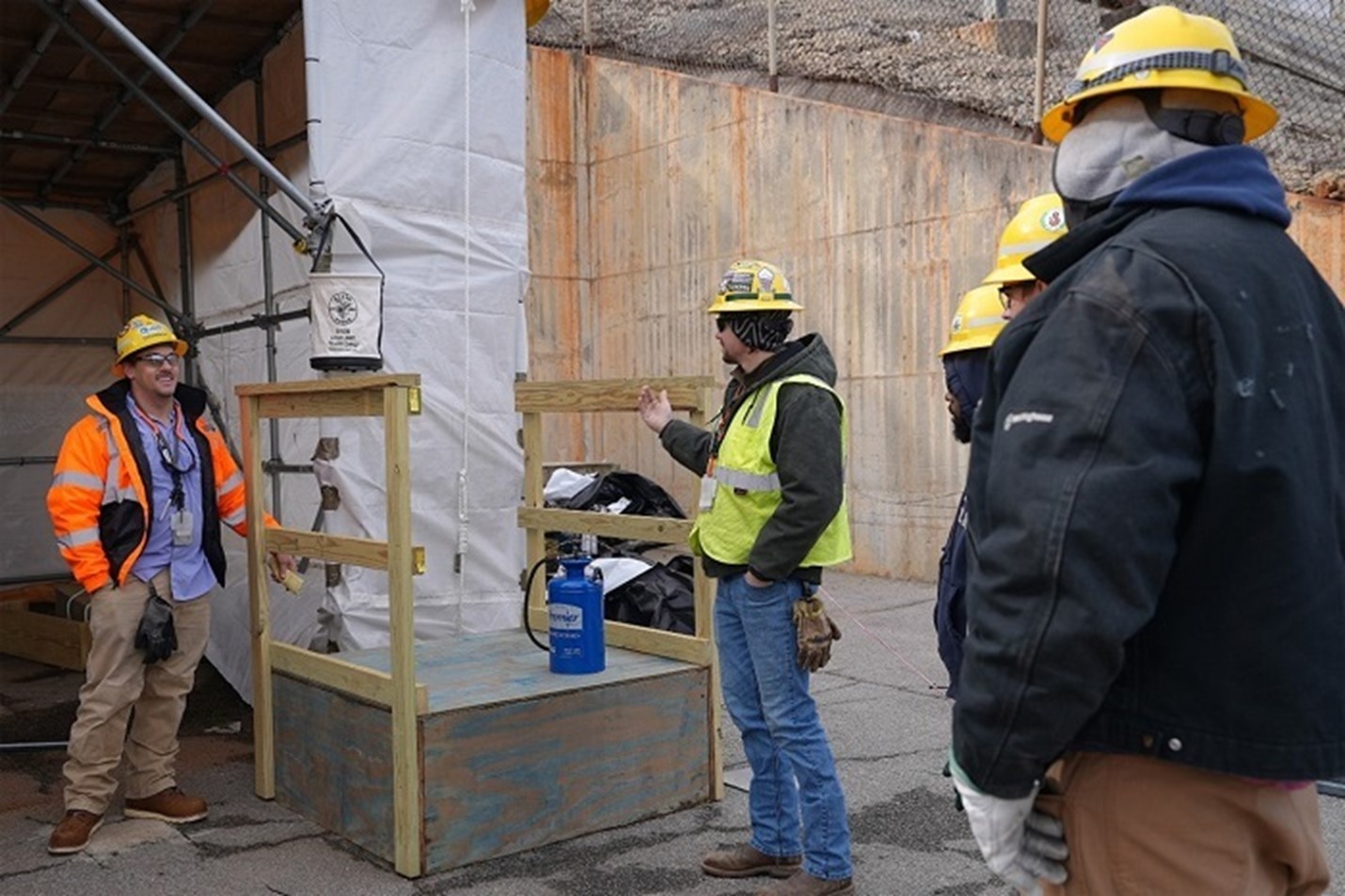

A new program at the Savannah River Site is educating workers on everyday workplace hazards through a new hands-on, peer-led mobile field course.
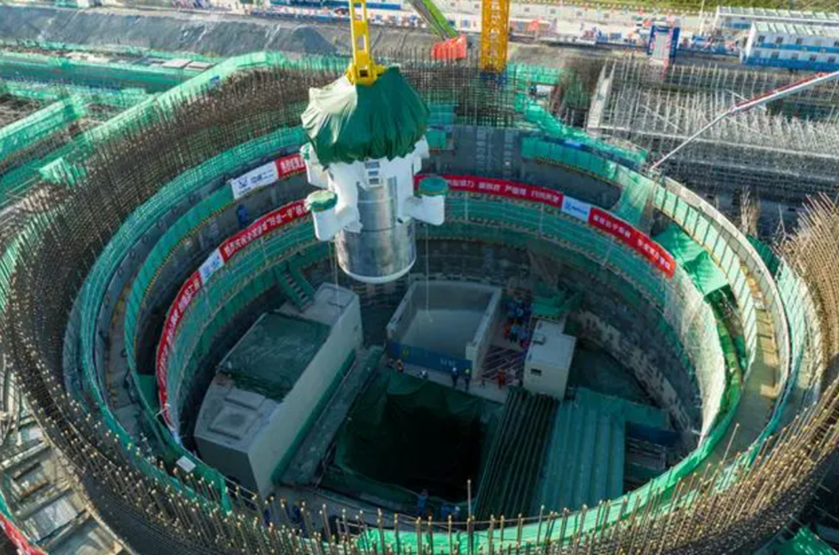

China is on pace to add as many as 10 reactors a year and may surpass the United States’ total nuclear capacity by 2030.
As part of this growth, construction is wrapping up this month on the world’s first onshore commercial modular pressurized water reactor—Linglong One, which is located in the Hainan province. That’s according to China Metallurgical News, an established news unit reporting on China’s industrial chain.