Hanford’s Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant, also known as the Vit Plant. (Photo: Bechtel National)
Researchers at the Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory are investigating the details of plutonium chemistry with the goal of aiding the cleanup of the Hanford Site in Washington state. For more than 40 years, reactors located at Hanford produced plutonium for America’s defense program, resulting in millions of gallons of liquid radioactive and chemical waste.
ITER’s 10 cooling cells in the background have 11-meter-long 12-blade fans rotating at 92 rpm to induce an upward draft, which is reason for the yellow-vested assemblage in front to give a thumbs up. (Photo: ITER Organization)
Steam from one of ITER’s ten induced-draft cooling cells offers visual confirmation of a successful cooling system test, the ITER organization announced April 30. ITER’s cooling system features 60 kilometers of piping with pumps, filters, and heat exchangers that can pull water through at up to 14 cubic meters per second. Once fully operational, two cooling loops—one to remove the heat generated by the plasma in the ITER tokamak and one for its supporting infrastructure—will be capable of extracting up to 1,200 MW of heat.
Illustration by Ana Kova for U.S. Fusion Outreach
Fusion is riding a surge of attention that began in December 2022 when researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s National Ignition Facility achieved fusion ignition. The organizers of Fusion Energy Week—a group called the U.S. Fusion Outreach Team—on the other hand, trace fusion development back 100 years to the doctoral research of Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin, who discovered that stars, including our Sun, are mostly made of hydrogen and helium, which in turn led to the understanding that those elements are the “fuel” of potential fusion energy systems on Earth. In recognition of Payne-Gaposchkin’s birthday—May 10—the U.S. Fusion Outreach Team plans to hold a “grassroots celebration of fusion energy” May 6–10, 2024, and annually during the second week of May.
(Or how to test a nuclear thermal rocket without turning it on)
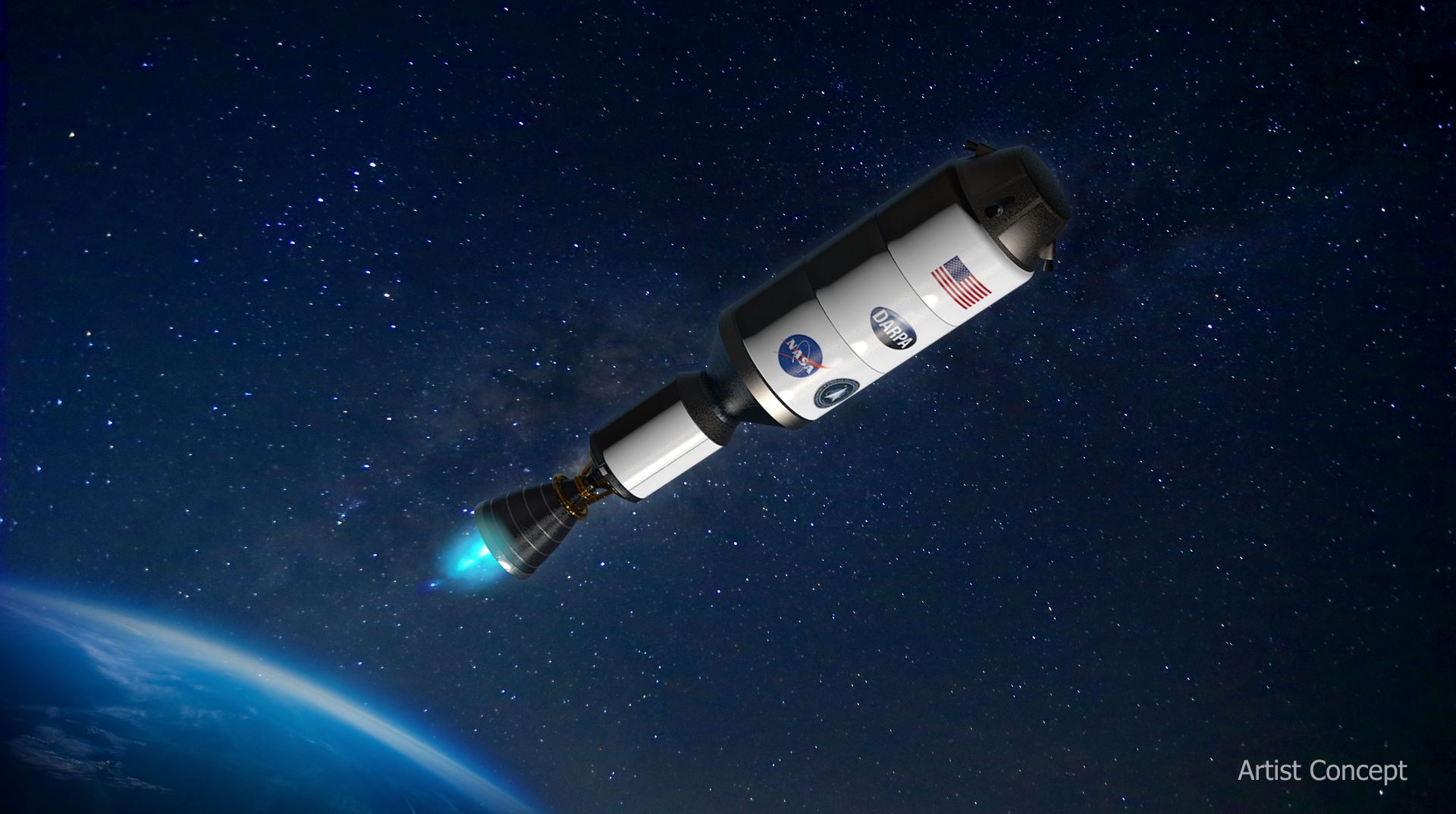
Artist’s concept drawing of DRACO. (Image: DARPA)
The United States is now closer than it has been in over five decades to launching the first nuclear thermal rocket into space, thanks to DRACO—the Demonstration Rocket for Agile Cislunar Orbit.
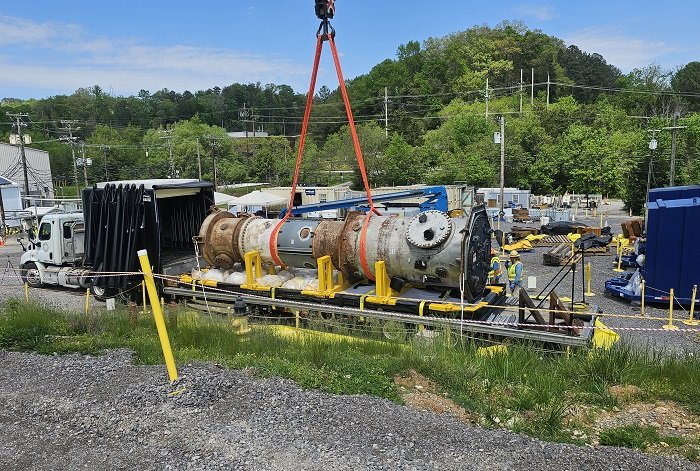
UCOR employees use a crane to load the Low Intensity Test Reactor vessel for transport to its final disposition location in Clive, Utah. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management announced that the 30-foot-long, 37,600-pound reactor vessel from Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s Low Intensity Test Reactor was shipped to EnergySolutions’ low-level radioactive waste facility in Clive, Utah, in late April.
ORNL’s High Flux Isotope Reactor, where Sr-89 and other radioisotopes are produced, photographed during a 2015 refueling. (Photo: ORNL)
The Department of Energy’s Isotope Program (DOE IP) announced last week that it would end its “active standby” capability for strontium-82 production about two decades after beginning production of the isotope for cardiac diagnostic imaging. The DOE IP is celebrating commercialization of the Sr-82 supply chain as “a success story for both industry and the DOE IP.” Now that the Sr-82 market is commercially viable, the DOE IP and its National Isotope Development Center can “reassign those dedicated radioisotope production capacities to other mission needs”—including Sr-89.
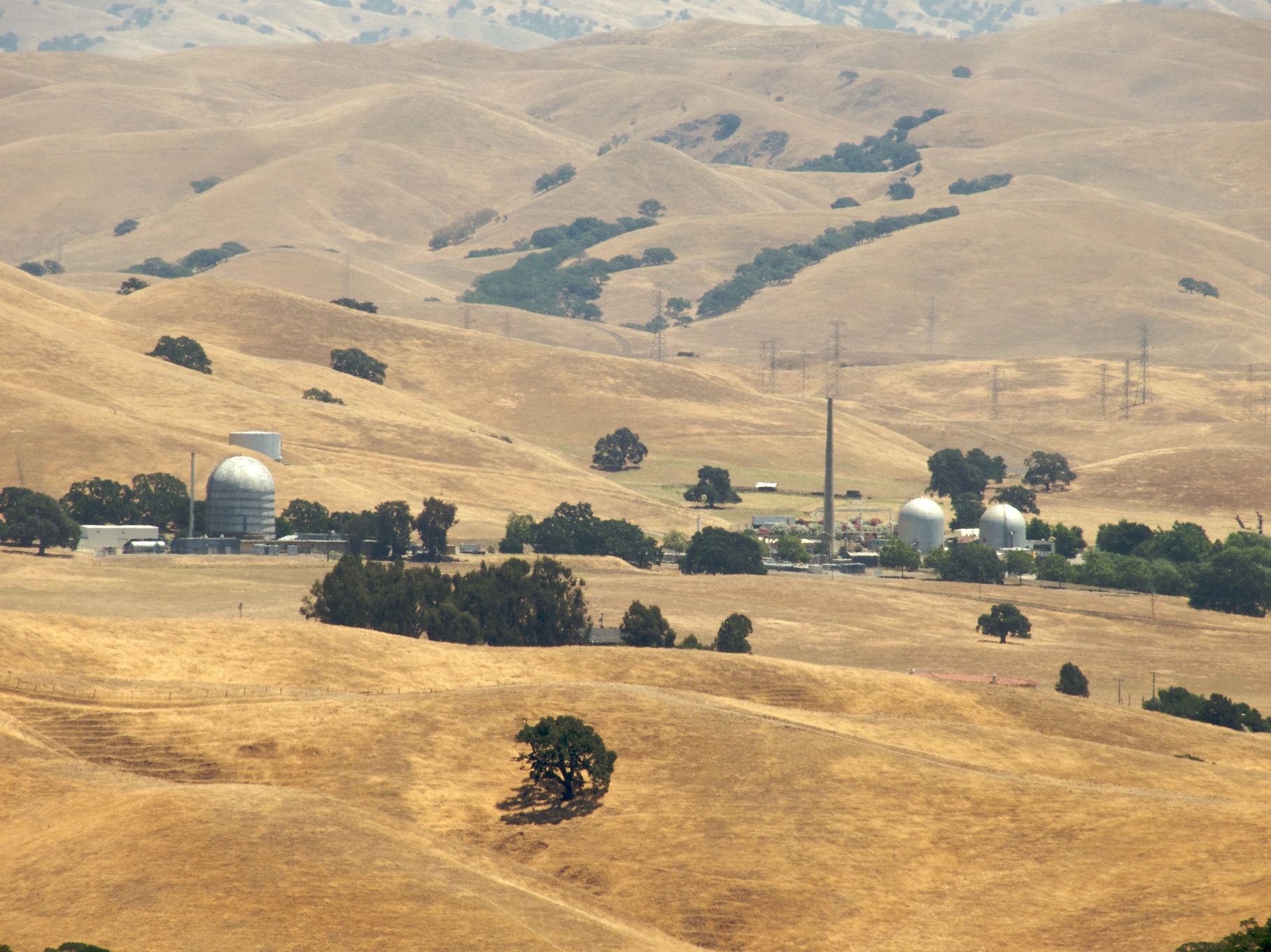
The Vallecitos Nuclear Center site in northern California. (Photo: Wikimedia Commons)
By an order dated April 25, the Nuclear Regulatory Commission has approved the transfer of ownership of Vallecitos Nuclear Center from GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy to NorthStar Group Services for nuclear decontamination, decommissioning, and environmental site restoration.
Energy Fuels’ White Mesa Mill in southeastern Utah is the only operating conventional uranium mill in the United States. (Photo: Energy Fuels)
The U.S. Senate approved April 30—by unanimous consent—a bill banning the importation of Russian uranium. The House of Representatives passed the bill, House Resolution 1042, last fall, and now President Biden is expected to sign it into law.
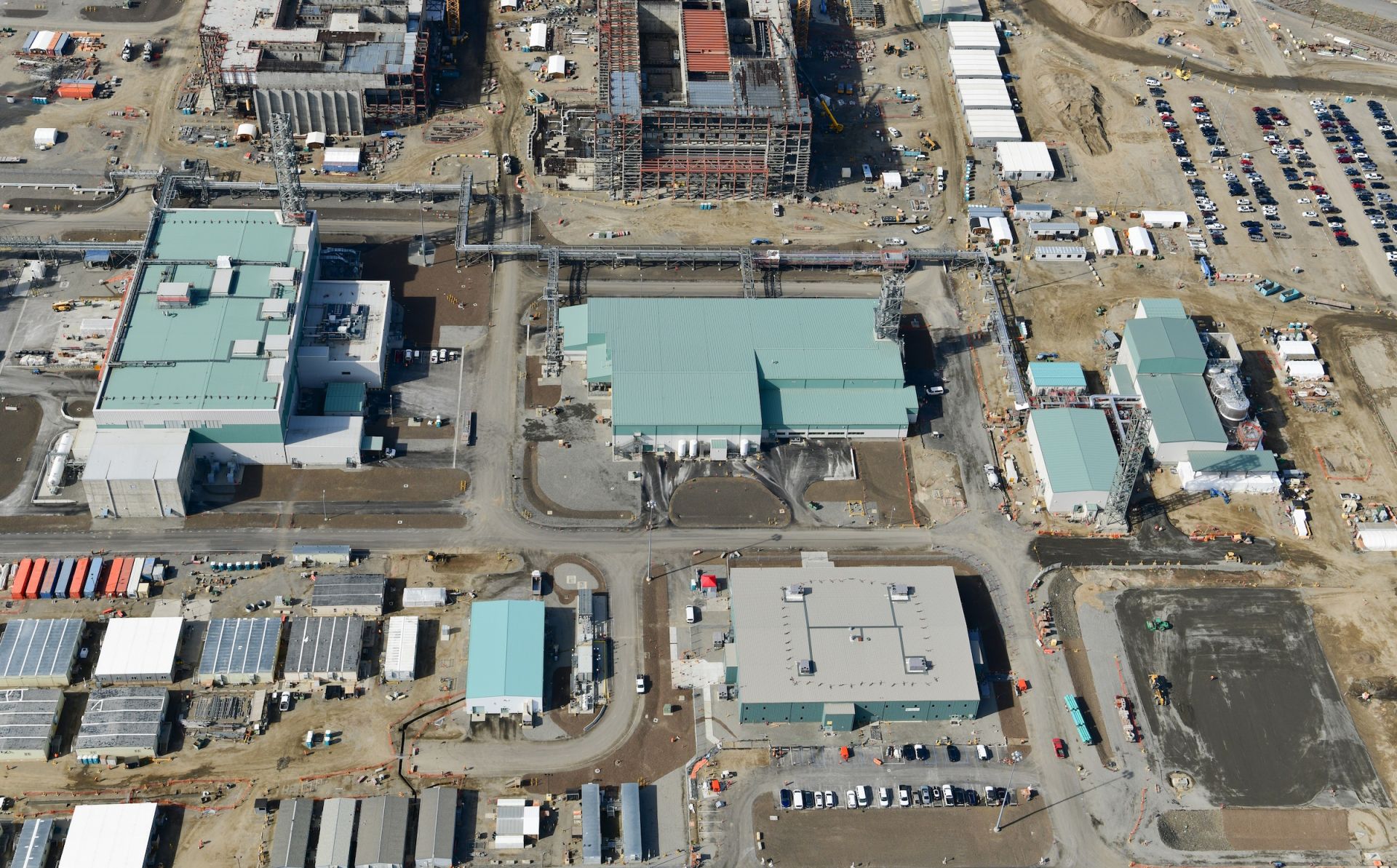
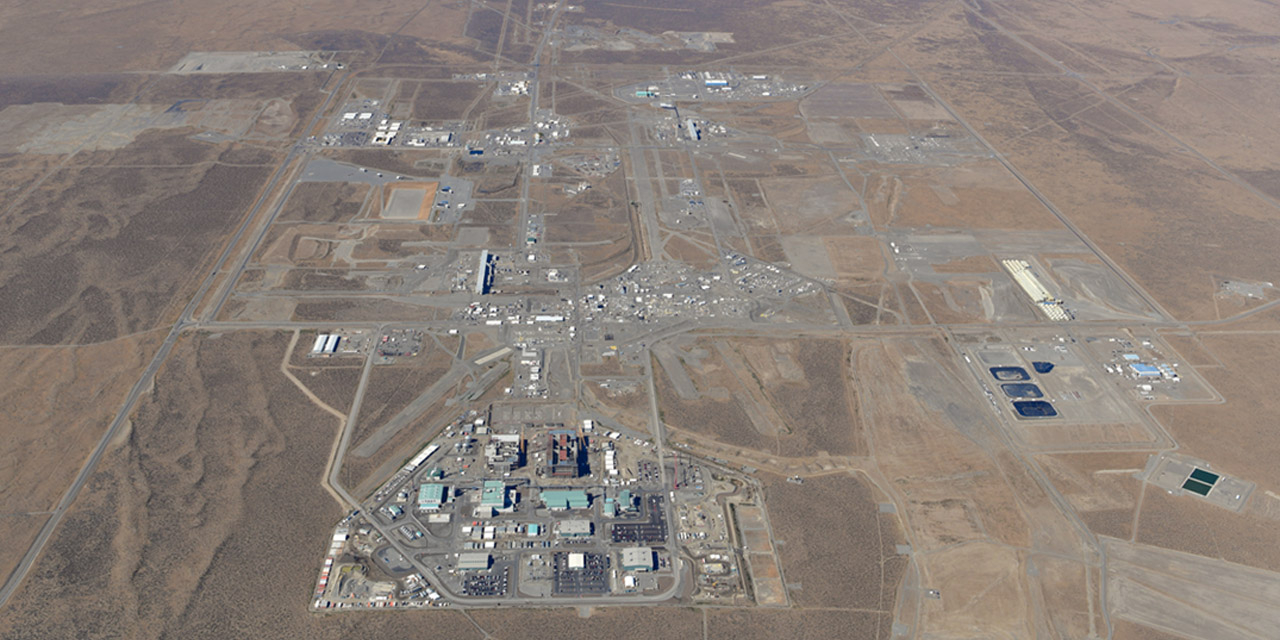
An aerial view of the Hanford Site’s 200 Area and the Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant, also known as the Vit Plant. (Photo: DOE)
The U.S. Department of Energy, Washington State Department of Ecology, and U.S. Environmental Protection Agency have reached an agreement on revised plans for managing millions of gallons of radioactive and chemical liquid waste stored in 177 underground tanks at the Hanford Site near Richland, Wash.
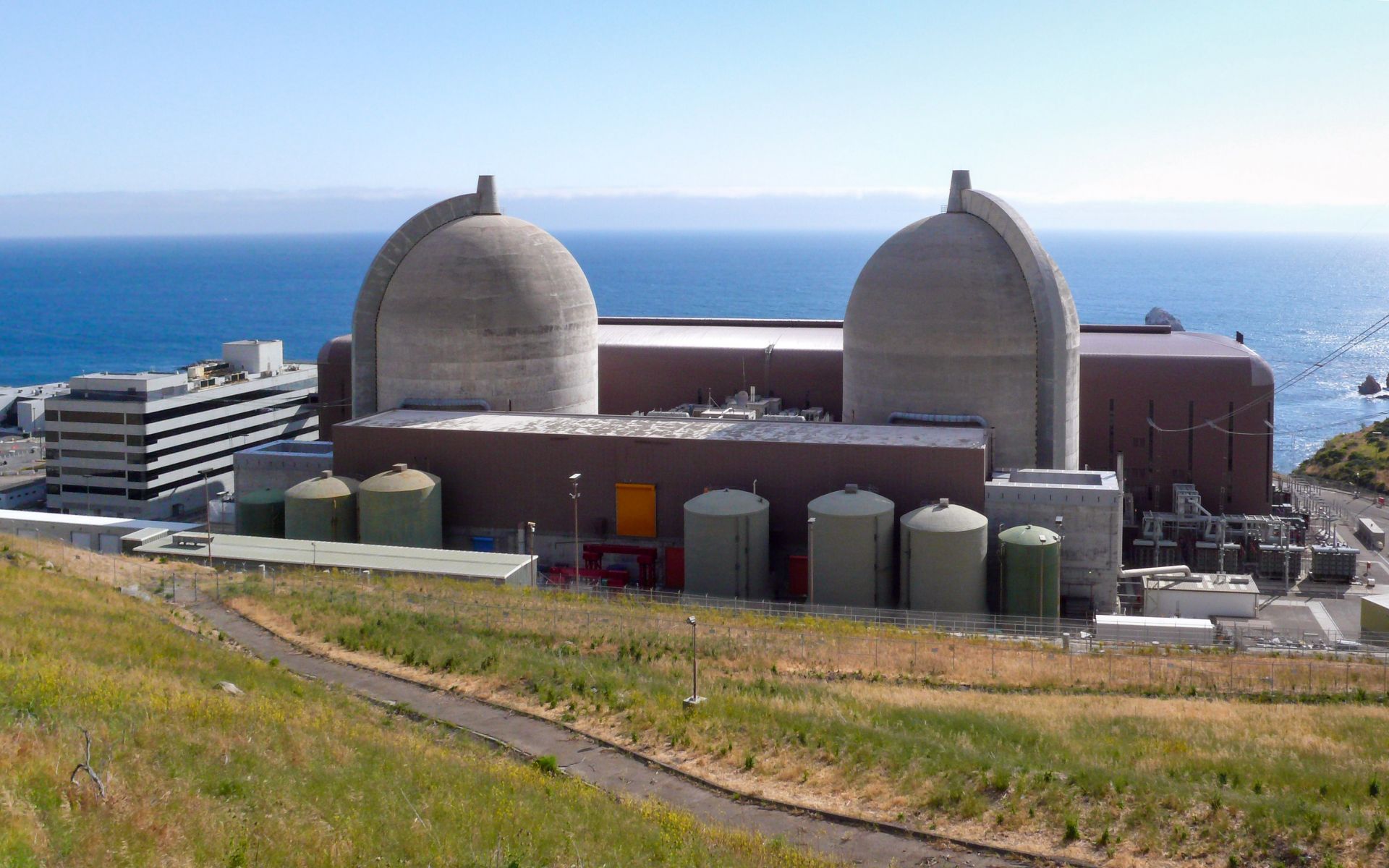
Diablo Canyon nuclear power plant. (Photo: PG&E)
A review from the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals this week denied a challenge to the Diablo Canyon nuclear plant’s license renewal application extension granted by the federal government.
In late 2023, the Nuclear Regulatory Commission agreed to formally docket the California plant’s request to extend plant operations beyond the current license expiration dates of 2024 and 2025 for the two respective units.