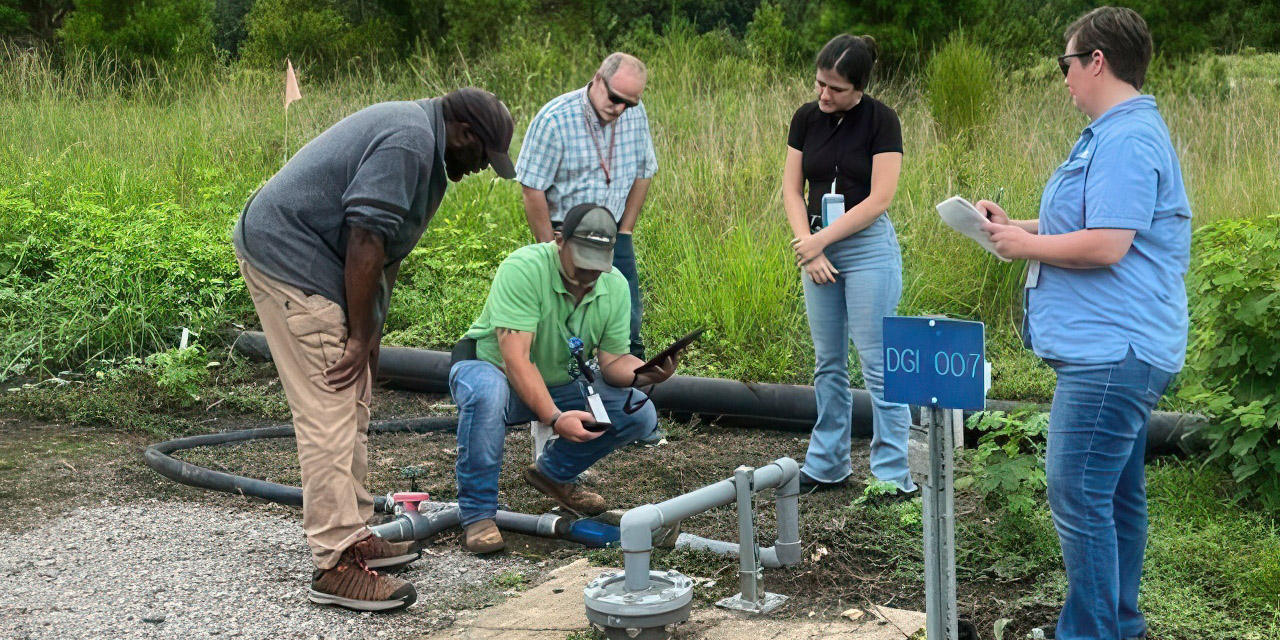
This series of photos shows the grouting of the K West Reactor spent fuel storage basin. Workers removed nearly 1 million gallons of contaminated water before filling the 16-foot-deep basin with about 6,500 cubic yards of grout—enough to fill two Olympic-size swimming pools. (Images: DOE)
Workers at the Department of Energy’s Hanford Site in Washington state recently finished filling the last large concrete basin at the K Reactor Area with cement-like grout. The basin stored reactor fuel rods from historic plutonium production in the 1950s.
Representatives of Urenco, the United Kingdom, the United States, Germany, the Netherlands, and the IAEA gathered at Urenco’s Capenhurst site. (Photo: Urenco)
Uranium enricher Urenco welcomed representatives from the International Atomic Energy Agency to an August 19 event to mark the creation of an IAEA Centre of Excellence for Safeguards and Non-Proliferation at its Capenhurst, England, site. Representatives of the three nations with ownership stakes in Urenco—the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, and Germany—were joined by representatives from the United States, where Urenco also operates an enrichment plant. Urenco expects the new center to be fully operational in 2025.
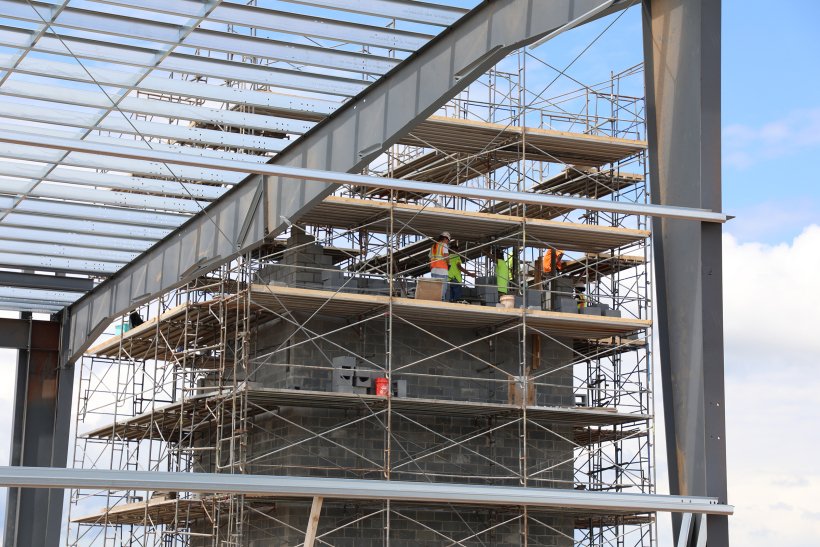
Construction crews work to erect the platform’s structural framework. (Photo: DOE)
Crews are making significant progress on the construction of the K-25 viewing platform at the Oak Ridge Reservation in Tennessee, the Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management announced on August 20. When completed next year, the elevated platform will offer a sweeping panoramic view of the massive 44-acre footprint of the K-25 Building, which once produced enriched uranium used in the weaponry that ended World War II.
The Sellafield nuclear site in Cumbria, England. (Photo: Simon Ledingham)
The Nuclear Decommissioning Authority (NDA), the government agency charged with cleaning up the United Kingdom’s nuclear sites, has awarded three contracts totaling £30 million (about $39 million) for research into new decommissioning techniques.
When consumers buy food, they cannot always detect food fraud. (Infographic: Mariia Platonova/IAEA)
The adulterating of food products for financial gain, either through dilution, substitution, mislabeling, or other action, has become a lucrative industry. And because food fraud is designed to avoid detection, gauging its financial impacts can be difficult. Experts estimate that food fraud affects 1 percent of the global food industry at a cost of about $10 billion to $15 billion a year, with some estimates putting the cost as high as $40 billion a year, according to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
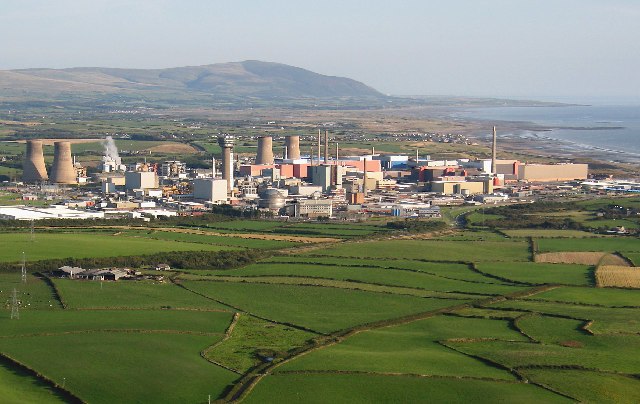
The San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station. (Photo: SCE)
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission noted two low-level regulatory violations during a recent inspection of the San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station, which is currently undergoing decommissioning in Southern California. The violations involved the shipment of two reactor pressurizers from San Onofre to EnergySolutions’ disposal facility in Clive, Utah.
The Donald C. Cook nuclear power plant. (Photo: ANS Michigan-Ohio Section)
Federal regulators began an investigation this week at the Donald C. Cook nuclear plant around the circumstances of multiple diesel generator failures. The facility continues to operate safely.
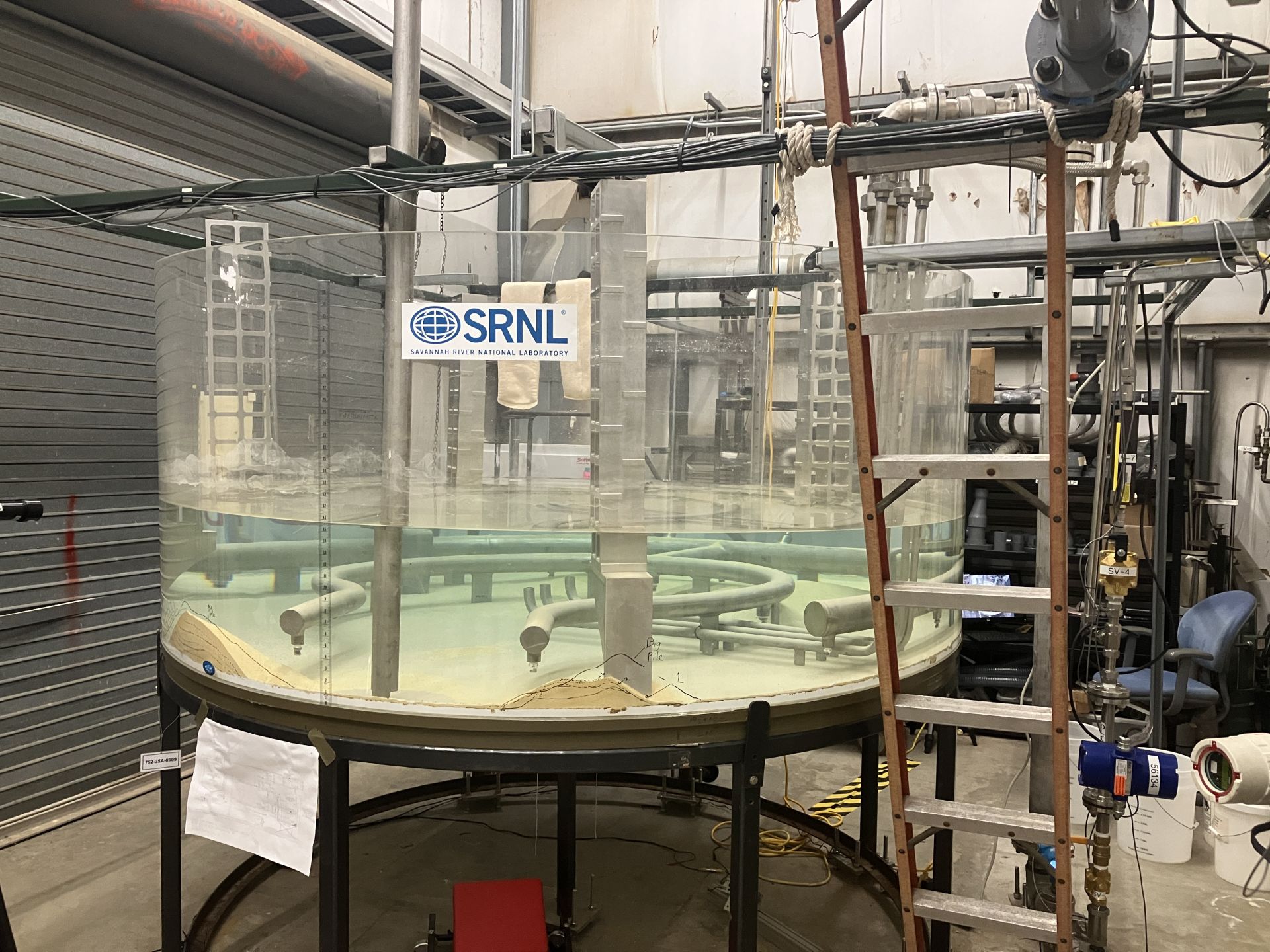
A mock-up model at SRNL was used to demonstrate a full-scale jet cleanout system to remove undissolved material from the H Canyon electrolytic dissolver. (Photo: DOE)
A collaboration between Savannah River Nuclear Solutions (SRNS) and Savannah River National Laboratory (SRNL) is making progress toward processing non-aluminum spent nuclear fuel (NASNF) as part of the site’s accelerated basin de-inventory mission. SRNL is the managing and operating contractor at the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site in South Carolina.
The D Area Groundwater Treatability Study project team assesses artesian flow into injection well at the Savannah River Site. (Photo: SRNS)
Savannah River Nuclear Solutions (SRNS), the management and operations contractor for the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site, announced that it has injected more than 100 million gallons of clean artesian well water to neutralize shallow groundwater contamination underneath 33 acres of a former coal storage yard and the associated runoff basin at the site in South Carolina. According to Ashley Shull, senior scientist for the project, “100 million gallons is nine times more water than [is] contained in the Georgia Aquarium in Atlanta.”
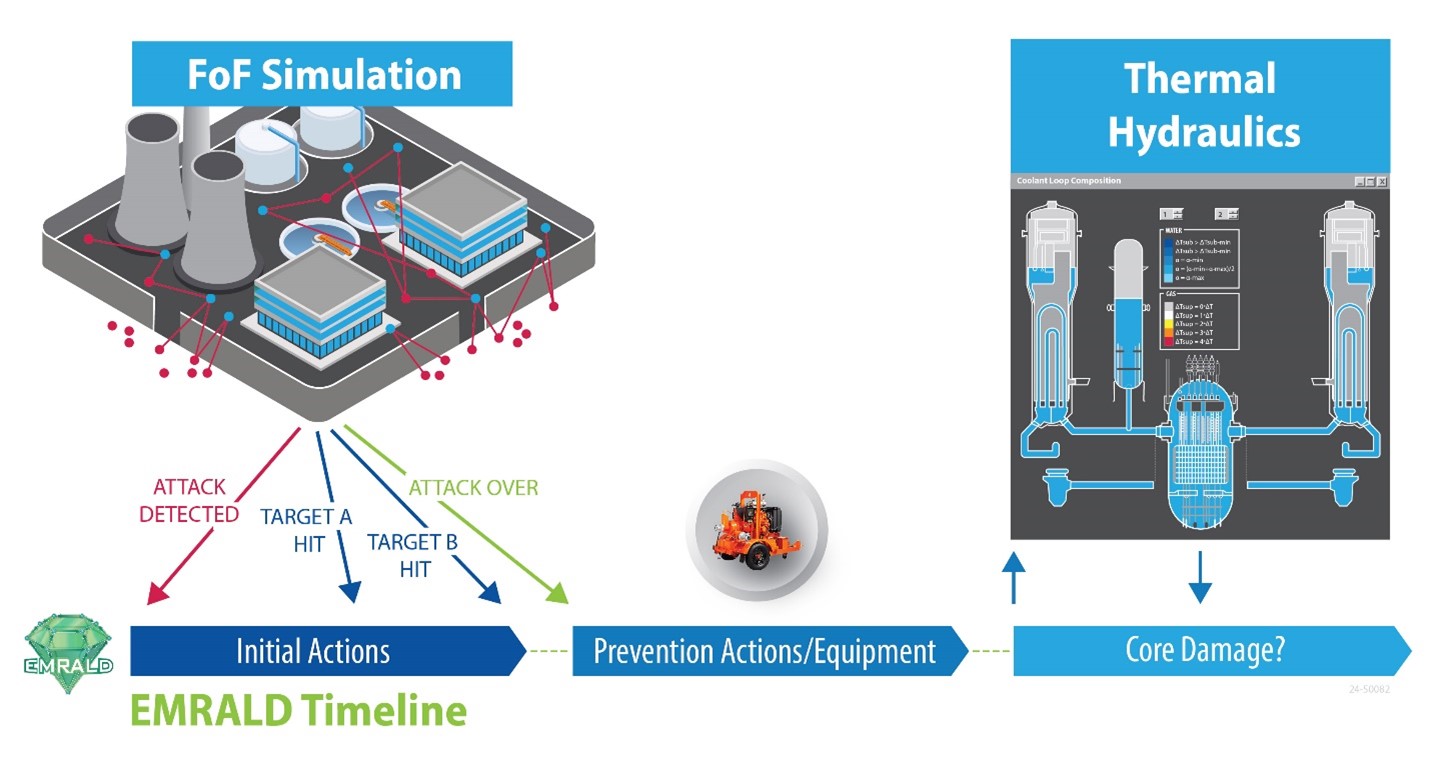
The MASS-DEF framework with prevention actions and timelines modeled in EMRALD software interacting with force-on-force (FoF) simulation and thermal hydraulics models. The risk-informed modeling in the MASS-DEF framework integrates physical security effectiveness analysis with safety measures, such as time to core damage. (Graphic: INL)
Today’s nuclear power plants are the nation’s largest source of carbon-free energy, but they come with high operating and maintenance costs.
Competition from other sources, especially natural gas, coupled with low electricity prices, has resulted in the closure of some plants in the last decade due to economic reasons.
One way to alleviate these economic pressures is to reduce the cost of operating nuclear power plants, including the costs associated with physical security.
Up-front requirements can enhance the ability to support maintenance and operations from start-up through long-term operation
It may seem counterintuitive, but the best time to enhance the ability to support operations and maintenance for a new plant is before construction starts. This is one of many lessons learned by the currently operating nuclear fleet. As construction and startup of many nuclear facilities was completed, it quickly became evident that the ability to efficiently support operations and maintenance was limited. Most of the information necessary to establish and manage procurement of spare and replacement items, maintenance, and configuration of the facilities was unavailable and had to be gathered on a case-by-case, “on-demand” basis. Absence of necessary information and the associated challenges resulted in the need for staff augmentation and multiyear-long projects to develop equipment bills of material and maintenance programs and to perform technical evaluations for the huge quantities of spare and replacement items being requested.