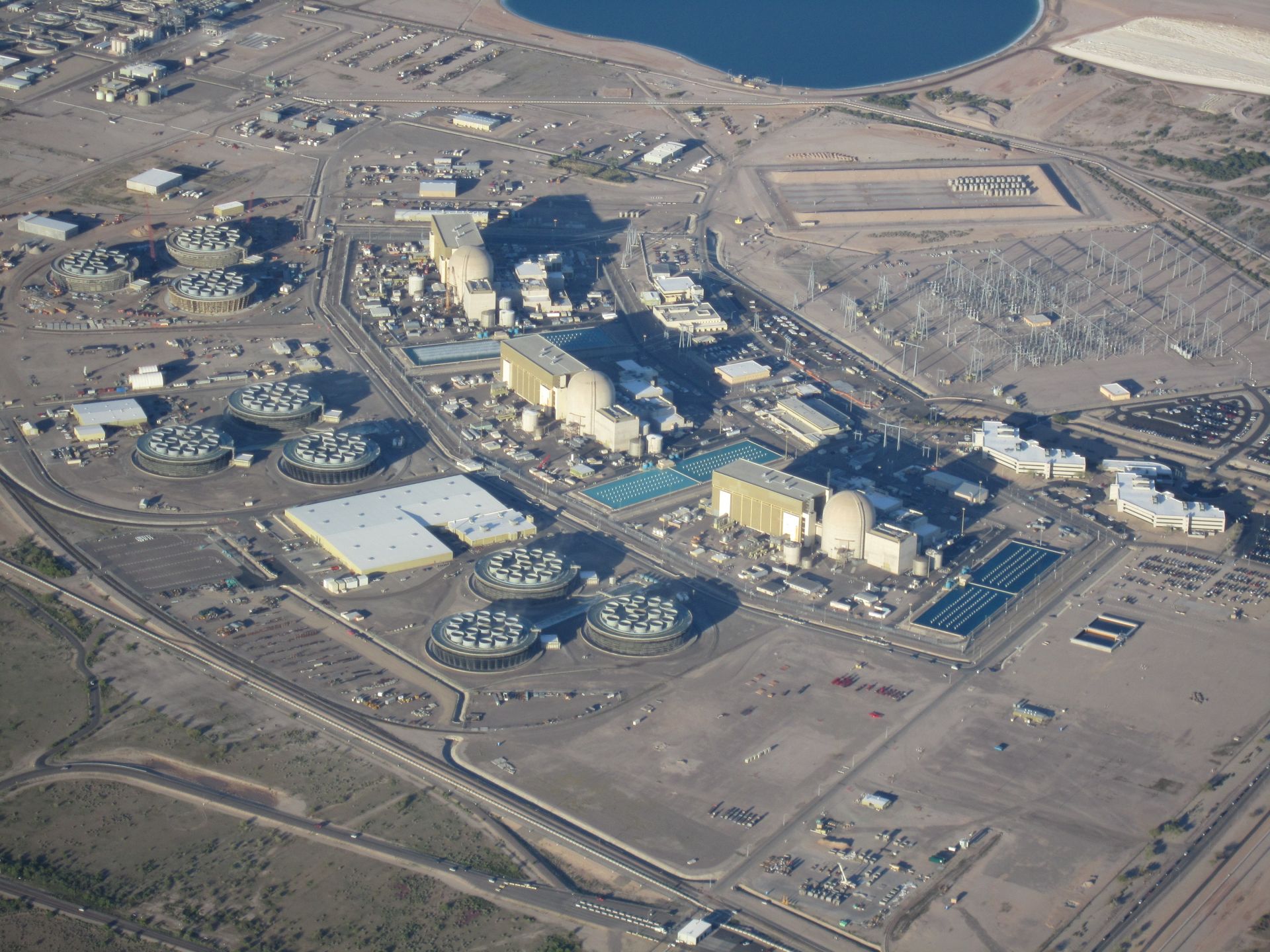
A depiction of an electrolyzer from Bloom Energy. (Photo: Bloom Energy)
Using nuclear power technology to produce clean hydrogen is getting a visibility boost as the Department of Energy hosts a virtual three-day (June 6–8) Annual Merit Review and Peer Evaluation Meeting on the agency’s efforts to accelerate clean hydrogen production. On June 6, the DOE announced a notice of intent (NOI) to fund the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law’s $8 billion program to develop regional clean hydrogen hubs (H2Hubs) and the launch of a new Hydrogen Shot Incubator Prize that seeks “disruptive technologies” to reduce the cost of clean hydrogen production. That same day, Westinghouse Electric Company and Bloom Energy Corp. (a maker of solid oxide electrolyzer technology) announced a letter of intent to develop electrolyzers for use in the commercial nuclear power market and said they are “well positioned to support the U.S. Department of Energy’s developing hydrogen hubs.”
The plant’s Program Engineering Department head has overseen significant new technology implementations for maintenance.
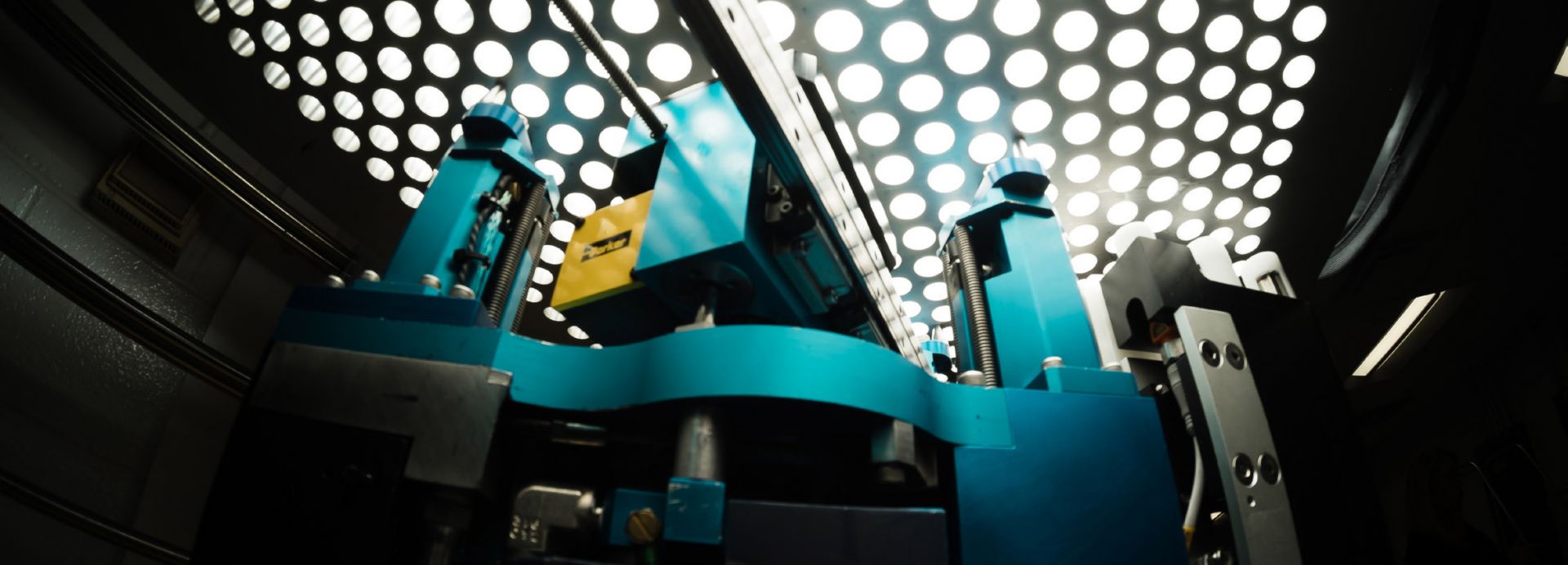

The Zephyr system uses probes for steam generator inspections. Photos: APS
The Palo Verde Nuclear Generating Station, a three-unit pressurized water reactor plant operated by Arizona Public Service Company, has started using an inspection technology relatively new to the nuclear industry. The technology, called smart pigs (an acronym for “piping inline gauges”), has previously been employed by oil and gas companies for inspecting and cleaning underground pipes. After testing and analyzing smart pig products from several companies, Palo Verde’s underground piping consultant, Dan Wittas, selected a smart pig suitable for navigating the tight-radius bends in the plant’s spray pond piping. The spray pond system consists of piping, a pump, and a reservoir where hot water (from the Palo Verde plant) is cooled before reuse by pumping it through spray nozzles into the cooler air. Smart pigs work by using the water’s flow through the piping to move an inspection tool within the pipe itself. The technology replaces the previous method of pipe inspection, in which various relatively small sections of piping were unearthed and directly inspected, and were considered to be representative examples of the overall piping condition. In contrast, the smart pigs obtain corrosion levels for the length of piping traveled through and allow a corrosion baseline to be established.





 The Fusion Energy Science Advisory Committee (FESAC), which is responsible for advising the Department of Energy’s Office of Science, on December 4 published the first public draft of
The Fusion Energy Science Advisory Committee (FESAC), which is responsible for advising the Department of Energy’s Office of Science, on December 4 published the first public draft of 
