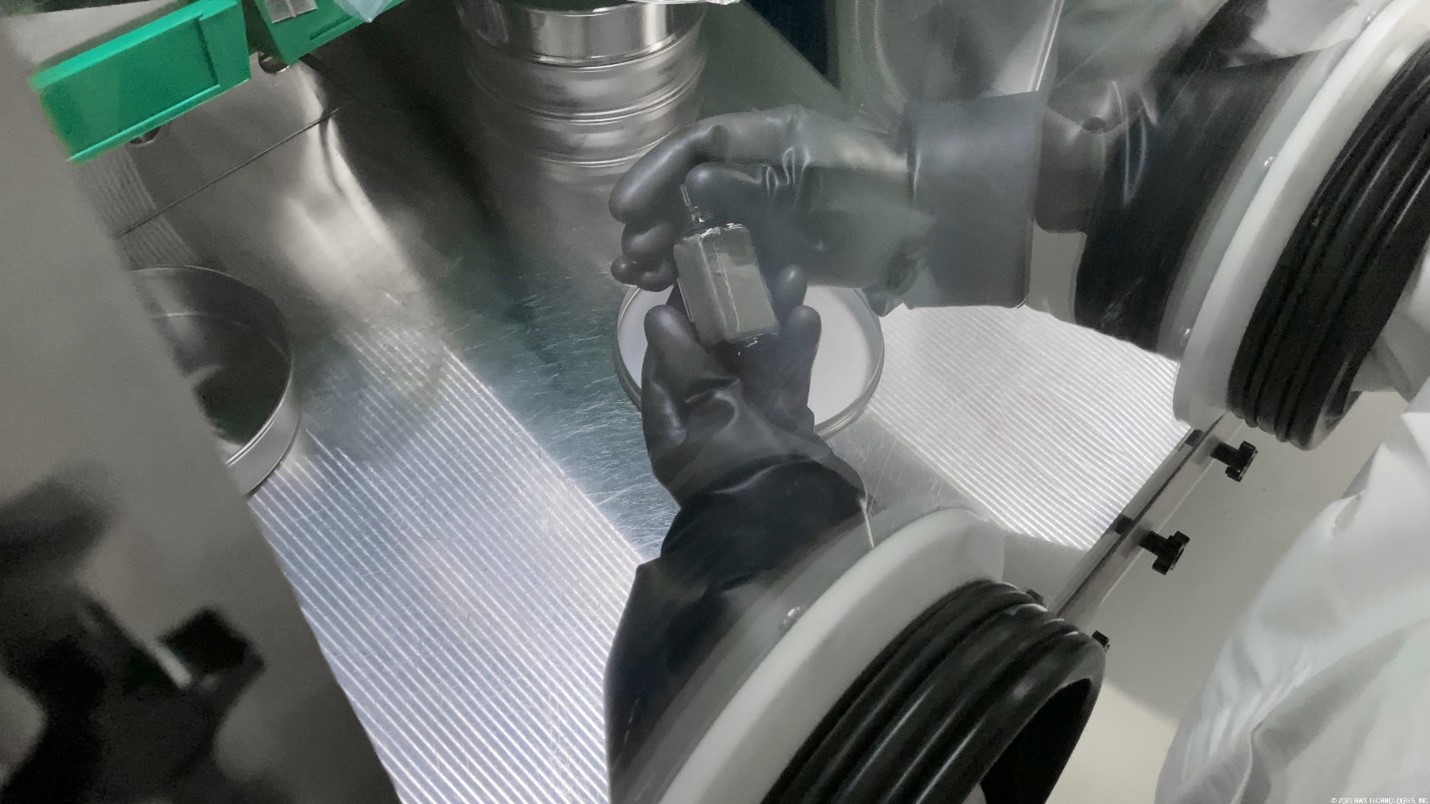
Coated uranium fuel kernels, as viewed through a glovebox. (Photo: BWXT)
Nuclear thermal propulsion (NTP) is one technology that could propel a spacecraft to Mars and back, using thermal energy from a reactor to heat an onboard hydrogen propellant. While NTP is not a new concept, fuels and reactor concepts that can withstand the extremely high temperatures and corrosive conditions experienced in the engine during spaceflight are being designed now.
BWX Technologies announced on December 13 that it has delivered coated reactor fuels to NASA for testing in support of the Space Technology Mission Directorate’s NTP project. BWXT is developing two fuel forms that could support a reactor ground demonstration by the late 2020s, as well as a third, more advanced and energy-dense fuel for potential future evaluation. BWXT has produced a videoof workers processing fuel kernels in a glovebox.
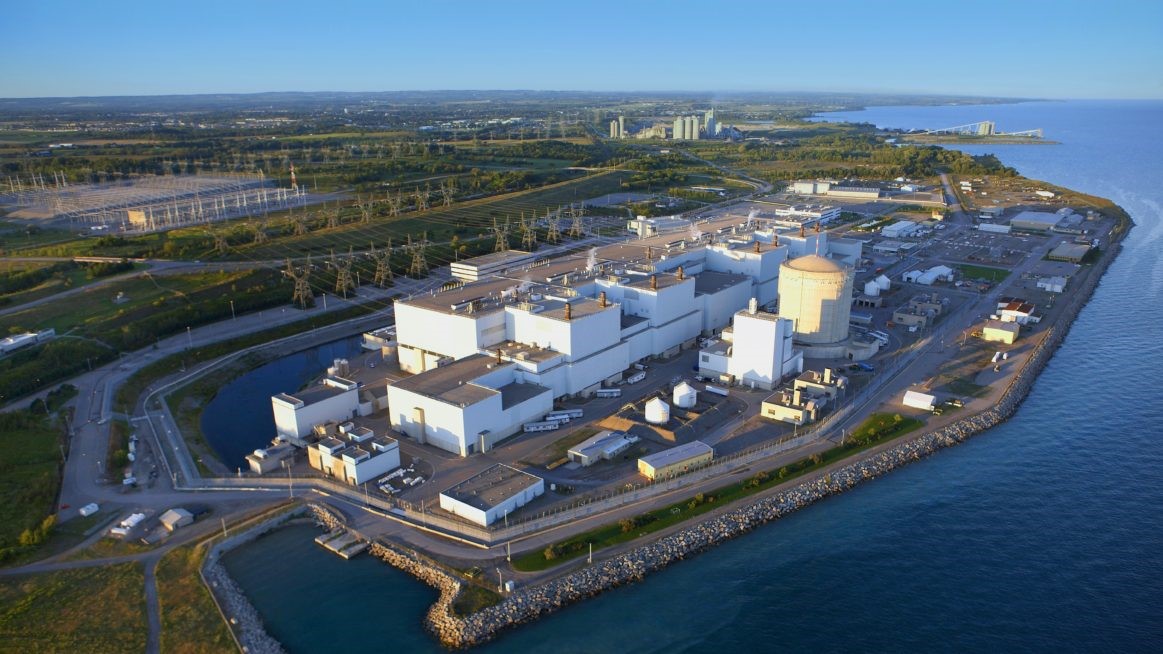
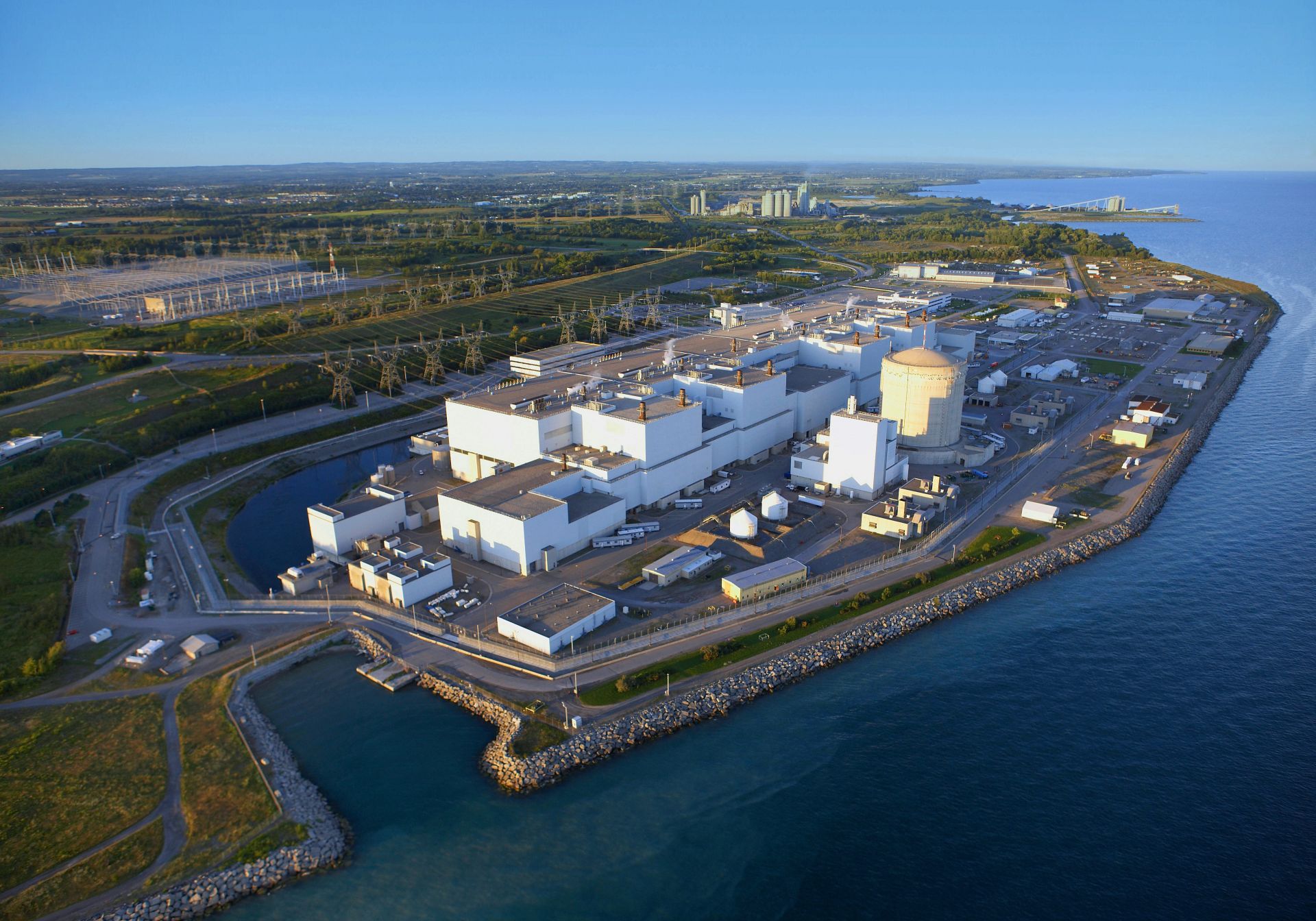
Darlington nuclear power plant. (Photo: OPG)
The Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission (CNSC) has amended Ontario Power Generation’s (OPG) operating license for its Darlington nuclear power station near Clarington, Ontario, allowing the company to produce the medical radioisotope molybdenum-99 using Darlington’s Unit 2 CANDU reactor. OPG subsidiary Laurentis Energy Partners, in conjunction with BWXT Medical, is leading the program to produce Mo-99 at Darlington.
The TRISO-X fuel pebble shown here contains TRISO particles—HALEU-bearing kernels of oxide and carbide in alternating layers of pyrolytic carbon and silicon carbide. (Image: X-energy)
X-energy and Centrus Energy announced last week that they have completed the preliminary design of the TRISO-X fuel fabrication facility and have signed a contract for the next phase of work. The planned facility would produce TRISO fuel particles and pack those particles into fuel forms, including the spherical graphite “pebbles” needed to fuel X-energy’s Xe-100 high-temperature gas reactor.
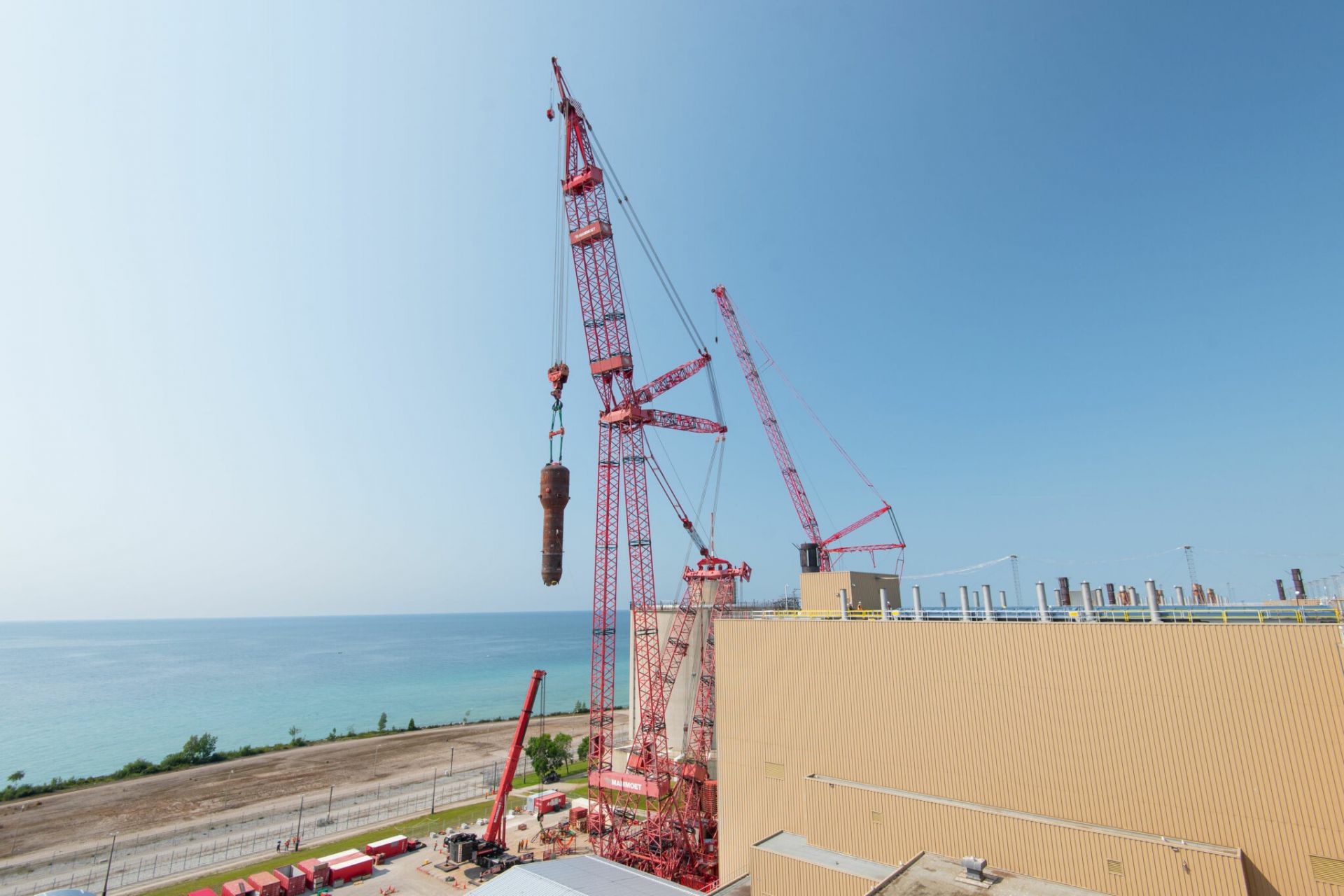
Bruce nuclear power plant in Ontario, Canada. (Photo: Bruce Power)
The first of eight 160-ton steam generators for Unit 6 at Canada’s Bruce nuclear power plant was installed last week as part of the facility’s major component replacement project. “Congrats to the MCR team and our partners, including @AeconGroup, @Framatome_CA, @UEandC, @mammoetglobal, @BWXT, and others who contributed to this historic moment,” Bruce Power tweeted on September 30.
The component was fabricated at BWXT Canada’s Cambridge, Ontario, location and was shipped to the Bruce site in late 2020, as shown in this video.
The vendor responsible for generator removal is the Steam Generator Replacement Team (SGRT), a 50-50 joint venture between Aecon and the Steam Generating Team, itself a partnership between Framatome and United Engineers & Constructors. In July, Framatome announced that SGRT had been awarded an approximately C$350 million (about $278 million) contract by Bruce Power to replace the steam generators at Units 3 and 4.
A crane removes the first of the Unit 6 steam generators on July 23. (Photo: Bruce Power)
Bruce Power has removed the first of eight steam generators from Unit 6 at the Bruce nuclear plant in Ontario, the company announced earlier this week. The work was done as part of the facility’s major component replacement (MCR) project.
Workers remove asbestos siding panels from a Portsmouth Gaseous Diffusion Plant building. Photo: Business Wire
Fluor-BWXT Portsmouth, a joint venture of Fluor and BWX Technologies, along with engineering company Jacob, have received a contract extension valued at up to $690 million, including options, from the Department of Energy. The contract, announced April 6, is for environmental management work at the former Portsmouth Gaseous Diffusion Plant near Piketon, Ohio.
BWX Technologies, Westinghouse, and X-energy will have two years for design engineering before one mobile reactor could qualify for demonstration.
Three reactor developers got a boost on March 9 when they were each awarded a contract from the U.S. Department of Defense (DOD) to design a reactor that can fit inside a standard shipping container for military deployment. The DOD’s Strategic Capabilities Office (SCO), in partnership with the Department of Energy, proposes to build and demonstrate a 1–10 MWe reactor within four years that, if successful, could be widely deployed to support the DOD’s domestic and operational energy demands.