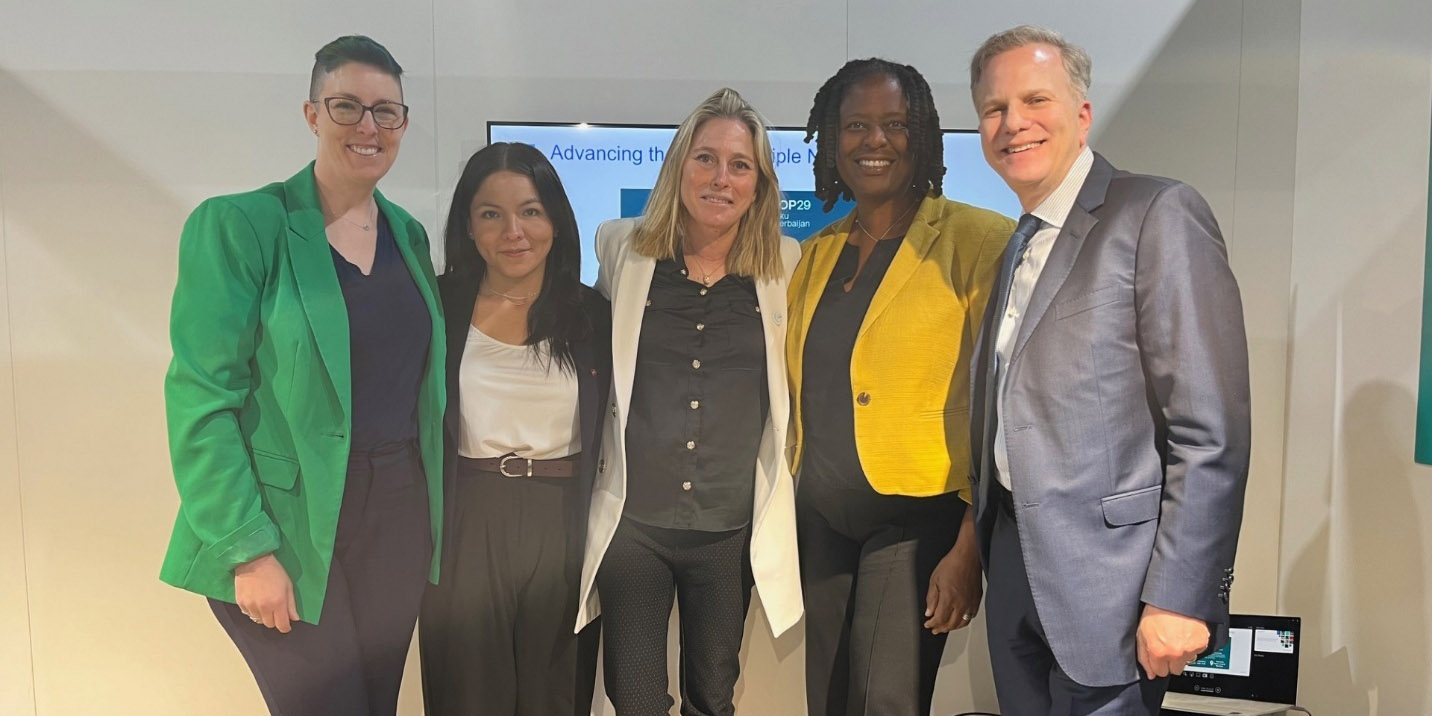
ANS’s COP29 Week 1 delegation were, from left, Gale Hauck, Shirly Rodriguez, Lisa Marshall, and Seth Grae, pictured here with WNA director general Sama Bilbao y León (center). (Photo: Seth Grae)
COP29 was good for nuclear energy, but not so good for anything else.
That was one of Seth Grae’s takeaways from this year’s Conference of the Parties—or, United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC)—held for two weeks in November in Baku, Azerbaijan. Grae, chief executive of Lightbridge Corporation and chair of the American Nuclear Society’s International Council, attended with four other ANS delegates: ANS President Lisa Marshall, Gale Hauck, Shirly Rodriguez, and Andrew Smith.
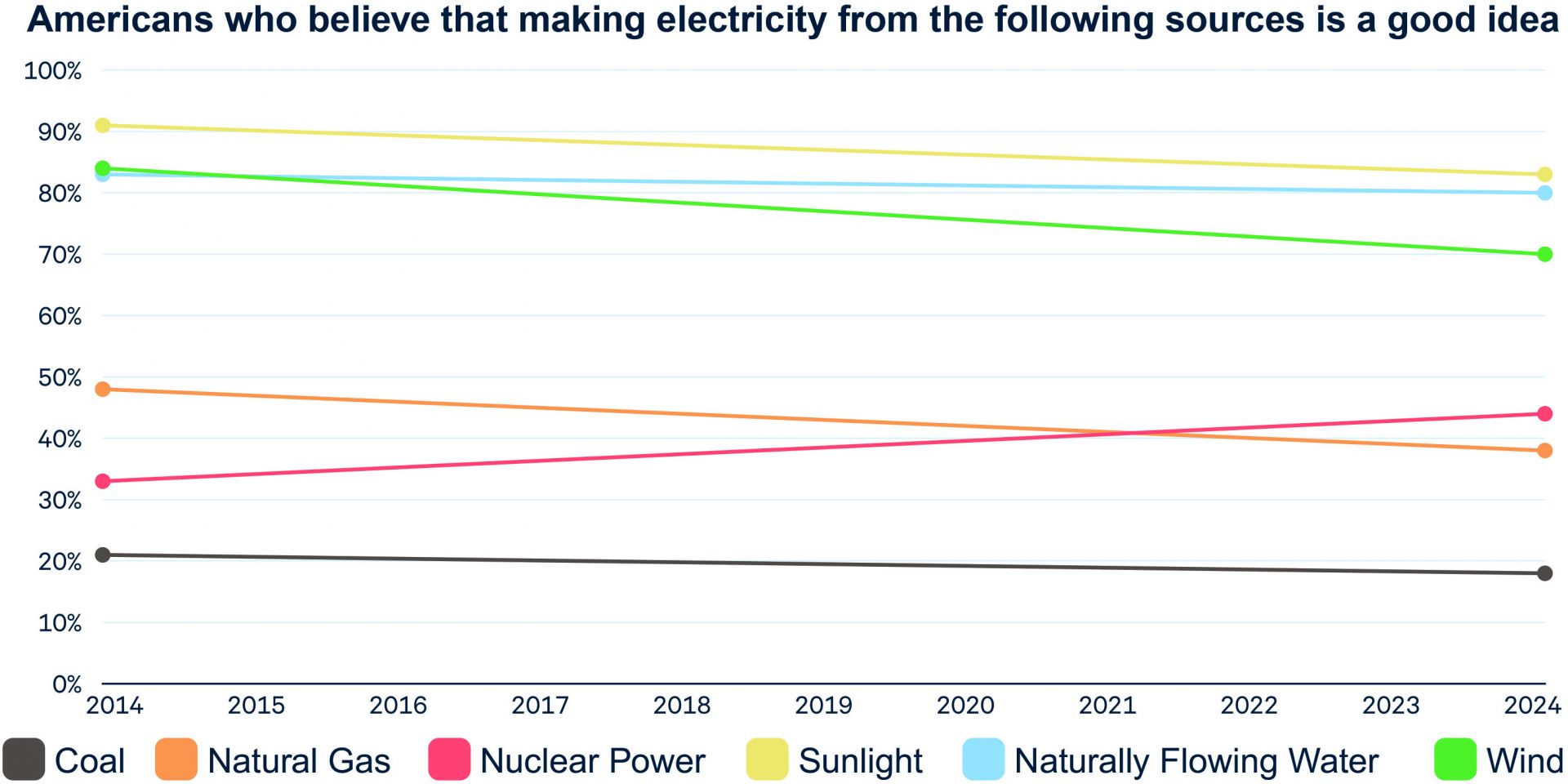
Nuclear was the only energy source to show a boost in public opinion over the past decade. (Graph: Jon A. Krosnick and Bo MacInnis, Climate Insights 2024: American Understanding of Climate Change; Washington, DC: Resources for the Future; 2024.)
A new report based on what its authors call “the definitive American public opinion surveys on climate change and the environment” has found a statistically significant increase in the percentage of survey respondents who think nuclear power is a good way to generate electricity, relative to a survey that asked the same question in 2013. That’s despite evidence that “Americans’ views on climate change have remained remarkably steady.” The new report, Climate Insights 2024: American Understanding of Climate Change, is the product of a 27-year polling partnership led by the Political Psychology Research Group at Stanford University and Resources for the Future (RFF), and it was released July 15.
Final COP28 text calls on countries to accelerate nuclear energy and other zero-carbon technologies
DUBAI, UNITED ARAB EMIRATES — Statement from American Nuclear Society (ANS) Executive Director and CEO Craig Piercy on the finalized text of the first global stocktake of the 28th Conference of the Parties (COP28) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC):
“On behalf of our 10,000 members around the world, the American Nuclear Society applauds the nuclear-inclusive climate deal reached at COP28. This historic climate agreement urges countries to forge ahead on climate progress by accelerating the deployment of zero-carbon technologies, notably embracing nuclear energy, and transitioning away from fossil fuels.
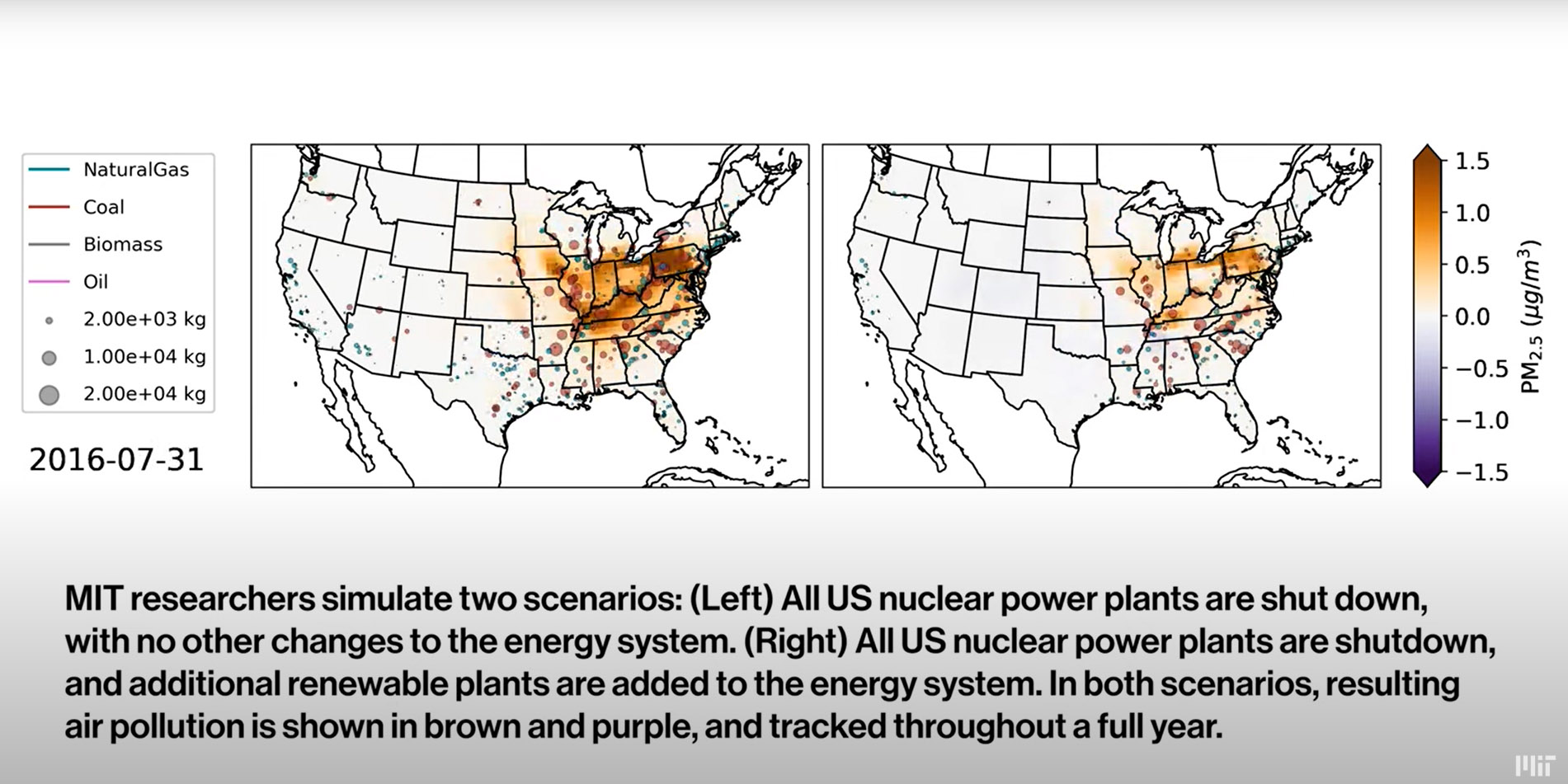
A still from a video posted by MIT that illustrates the air pollution that would be generated over one year by a grid with no nuclear power. (Credit: MIT)
Nuclear power is the single largest source of clean energy in the United States, but how can the value of “clean” be measured? Two recent reports by researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, respectively, measured the clean energy benefits of nuclear energy in different ways: the benefits to human health from the air pollution avoided and the future economic value of avoided carbon emissions.
The ministers representing their respective nations as the statement on civil nuclear fuel cooperation was announced were (from left) Jonathan Wilkinson, minister of natural resources of Canada; Yasutoshi Nishimura, Japan’s minister of economy, trade, and industry; Jennifer Granholm, U.S. energy secretary; Grant Shapps, U.K. energy security secretary; and Agnes Pannier-Runacher, French minister for energy transition.
A civil nuclear fuel security agreement between the five nuclear leaders of the G7—announced on April 16 on the sidelines of the G7 Ministers’ Meeting on Climate, Energy and Environment in Sapporo, Japan—establishes cooperation between Canada, France, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States to flatten Russia’s influence in the global nuclear fuel supply chain.
Gabriela Hearst (Photo: gabrielahearst.com)
One doesn’t typically come across nuclear fusion in a fashion magazine, but a recent issue of Vanity Fair profiled the creative director of a famous luxury fashion house who has made nuclear fusion a conceptual focus of her clothing creations. According to the article, Gabriela Hearst, the creative director at the New York City office of Paris-based Chloé, has designed a spring-summer 2023 collection “inspired by site visits to labs in the Pacific Northwest, New England, and southern France, where hundreds of scientists and engineers are working to develop technology that will produce a net energy gain through fusion.”
The Byron nuclear power plant
(This story has been updated from yesterday's post about the Illinois energy package.)
With only days remaining before the scheduled retirement of Exelon Generation’s Byron nuclear plant, the Illinois House has approved a comprehensive energy package (S.B. 2408) that would save the plant, as well as the state’s similarly struggling Braidwood and Dresden facilities.