Savannah River Remediation workers double-stack HLW canisters in an underground vault in Savannah River’s Glass Waste Storage Building 2 using a one-of-a-kind shielded canister transporter. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) has demonstrated the capability to expand the double-stacking of high-level waste canisters at the Savannah River Site in South Carolina. That approach will save the site’s cleanup program millions of dollars, according to the DOE.
The Sodium Pump Test Facility was the last DOE building to be demolished at the Energy Technology Engineering Center site in California. (Photo: DOE)
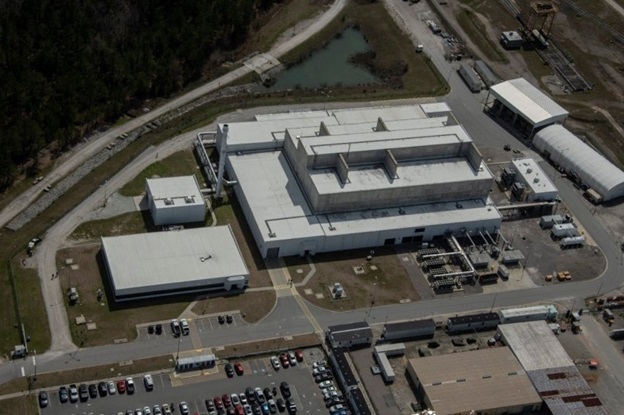
The demolition of the final of 18 DOE-owned buildings at the Energy Technology Engineering Center (ETEC) has been completed, according to the DOE. The ETEC is the former liquid metals research facility located at the Santa Susana Field Laboratory (SSFL), northwest of Los Angeles.
U.S. Forest Service employees Secunda Hughes (left) and Andrew Thompson inspect irrigation piping and sprinkler heads, part of a 62-acre pine plantation used to safely disperse tritium at the Savannah River Site.
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) is managing the release of tritiated water using a 62-acre plantation of pine trees and other natural resources to limit radioactively contaminated groundwater from reaching waterways on the Savannah River Site in South Carolina.
An archive photo of the Nevada National Security Site’s Test Cell C complex, which is being prepared for demolition and closure. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy is preparing to demolish two large, complex facilities at the Nevada Nuclear Security Site with ties to historical nuclear propulsion rocket development and testing programs. The DOE’s Environmental Management (EM) Nevada Program and its environmental program services contractor, Navarro Research and Engineering, have begun characterization and hazard reduction work on the site’s Engine Maintenance, Assembly, and Disassembly (EMAD) and Test Cell C (TCC) complexes.
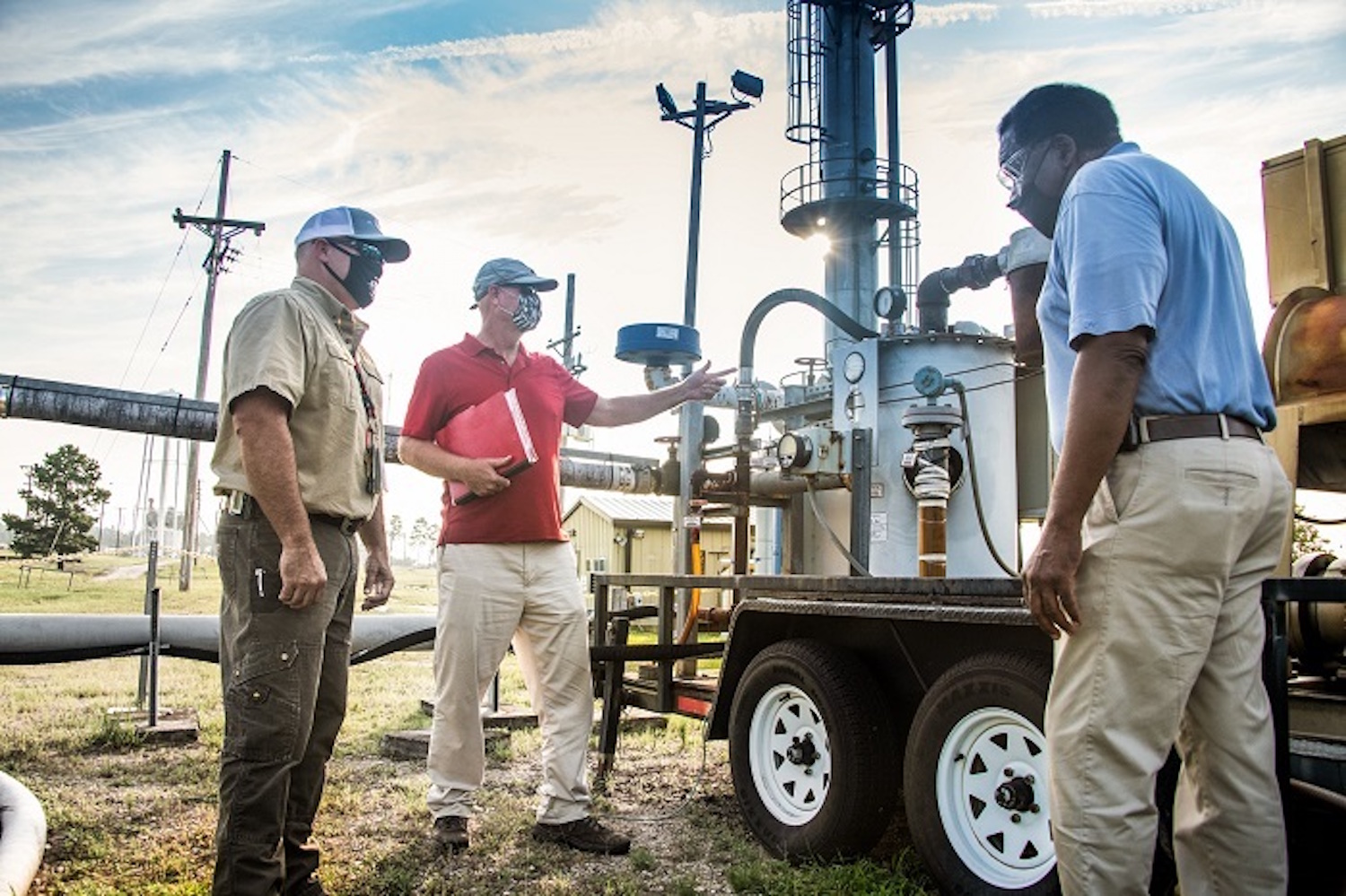
F Area operator Thomas Harman (left) and SRNS scientist Kevin Boerstler check the pumps, sensors, and piping that blend a base concentrate to inject into acidic groundwater at the Savannah River Site. (Photo: DOE)
The Savannah River Site is reducing the flow of hazardous and radioactive metal contaminants to South Carolina’s rivers and streams by injecting a mix of clean water and baking soda into the site’s groundwater. The base mix neutralizes groundwater that has become acidic as a result of SRS’s chemical separations work, helping restrict the flow of contaminants.
An artist’s rendition of the K East Reactor safe-storage enclosure. (Image: DOE)
DGR Grant Construction will construct a safe-storage enclosure over the K East Reactor building at the Department of Energy’s Hanford Site in Washington state. Two construction subcontracts, worth about $9.5 million, were awarded to the Richland, Wash.–based company by Central Plateau Cleanup Company, the DOE’s Richland Operations Office site cleanup contractor.
A shipment of transuranic waste approaches WIPP in New Mexico. (Photo: DOE)
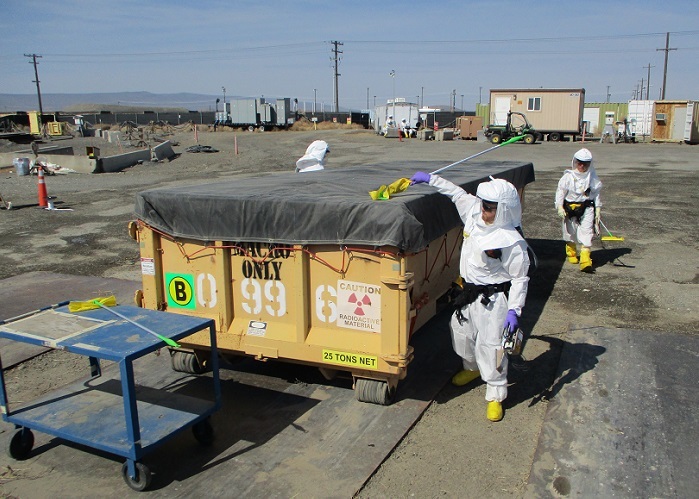
According to the Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM), shipments of transuranic waste to the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant in New Mexico are back to pre-pandemic levels, with the deep underground repository receiving 12 shipments in one week this summer.
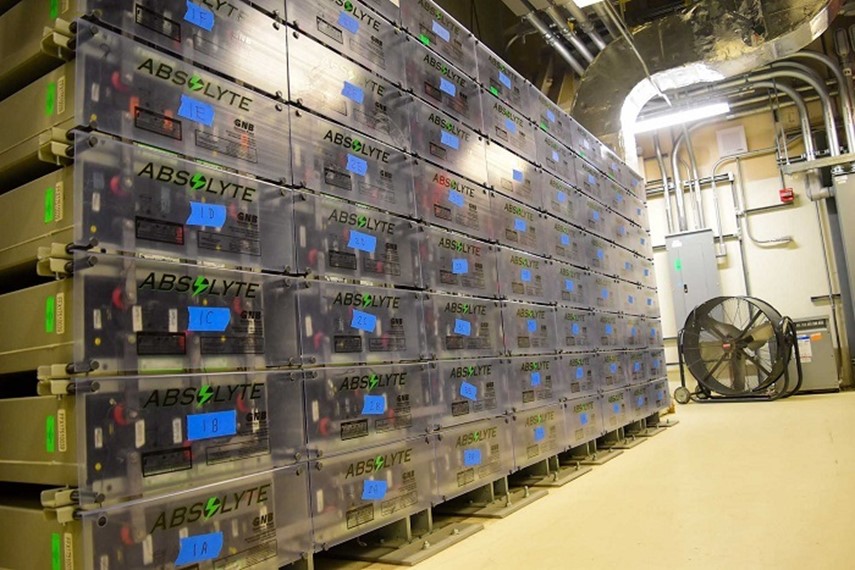
The DOE recently completed startup testing on the uninterruptable electrical power system for Hanford’s Low-Activity Waste Facility.
Department of Energy workers recently finished startup testing of a battery-powered backup electrical system for the Low-Activity Waste (LAW) Facility at the Hanford Site near Richland, Wash. According to the DOE’s Office of Environmental Management (EM), the uninterruptable electrical power system is vital to safeguarding the facility, part of Hanford’s Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant, in the unlikely event of a temporary power loss to the plant.
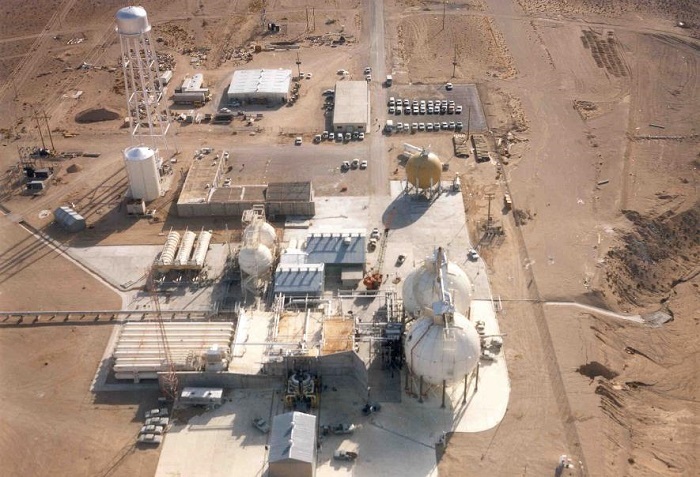
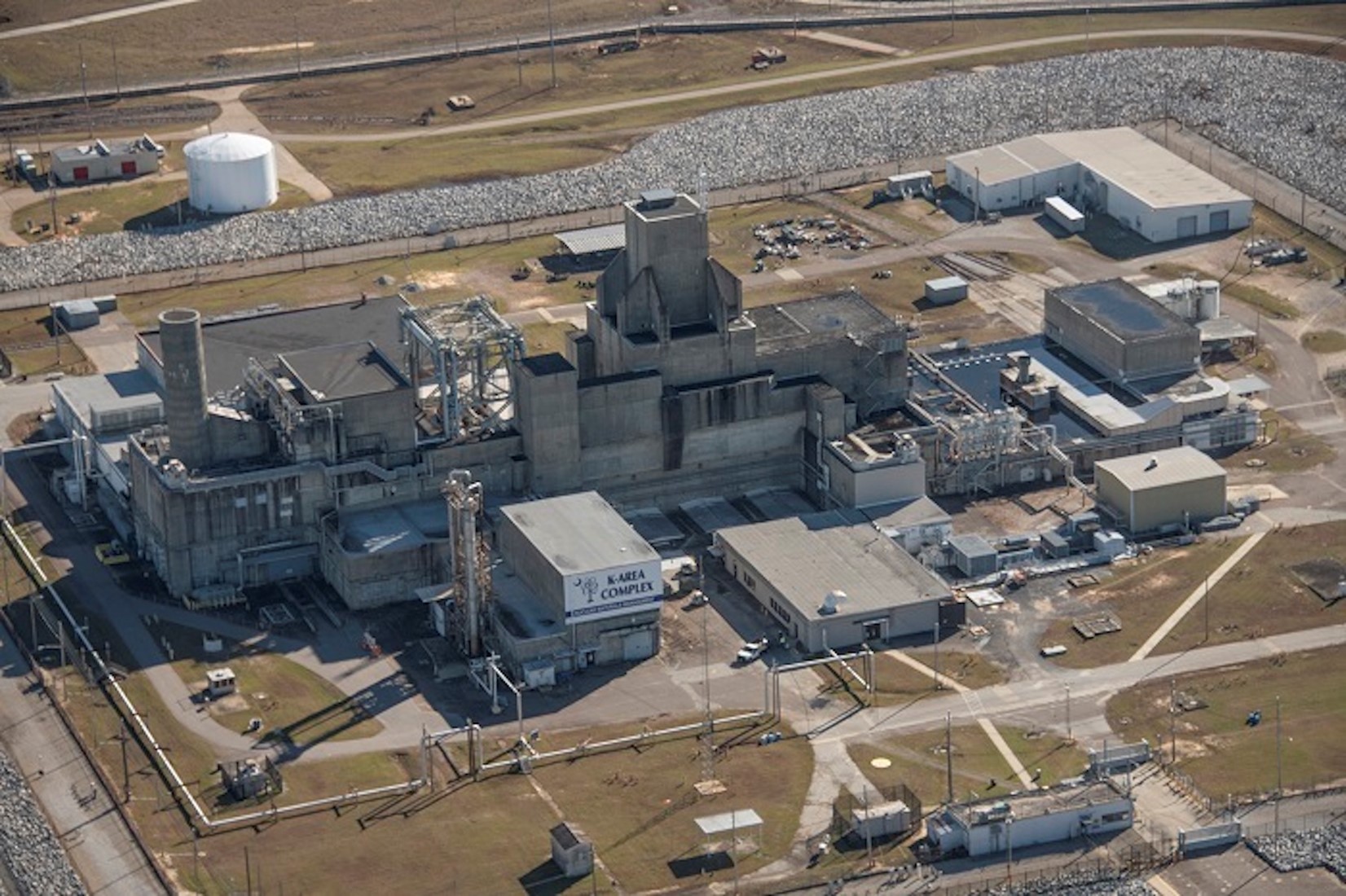
A view of Savannah River’s K Area Complex, where plutonium downblending operations take place. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management has doubled the number of work shifts for employees in glove box operations at its Savannah River Site in South Carolina. The increased work pace will help the department meet its commitment to South Carolina to remove surplus plutonium from the state, the DOE said.
From left, SRNS mechanic Todd Cockrell, engineer John Bradley, and project manager Joao Cardoso-Neto plan the removal of a vapor extraction unit at the Savannah River Site. (Photo: DOE)
Department of Energy site contractors Savannah River Nuclear Solutions and Savannah River Remediation received high marks from a recent independent audit of their environmental management work at the Savannah River Site in South Carolina.
The Waste Isolation Pilot Plant in southeastern New Mexico.
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management has issued a final request for proposals for a transportation services contract for the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant in southeastern New Mexico. The current WIPP transportation services contract, held by CAST Specialty Transportation, expires on May 27, 2022.
Demolition of the last of 11 structures at the former Y-12 Biology Complex at Oak Ridge was completed in June, and the removal of the building’s slab foundation is scheduled to be completed this fall. (Photo: DOE)
Crews with the Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) have completed the demolition of Building 9207, the largest and final building at the former Biology Complex at the Y-12 National Security Complex in Oak Ridge, Tenn., the DOE announced this week. Removal of the massive six-story, 255,000-square-foot building ushers in a new chapter of transformation at Y-12, the DOE said.
A view of the Savannah River Site’s Salt Waste Processing Facility. (Photo: DOE)
The Salt Waste Processing Facility at the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site has performed largely as expected, processing more than one million gallons of radioactive waste during its first eight months of operation, the DOE reported on June 8. The SWPF is being used to treat the majority of the site’s remaining liquid radioactive waste, generated from the production of nuclear materials.
The Waste Isolation Pilot Plant in southeastern New Mexico.
The Department of Energy has issued a final request for proposals for a 10-year, $3 billion management and operating contract for the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant near Carlsbad, N.M. The current M&O contract, held by Nuclear Waste Partnership, expires on September 30.
A loaded waste container at the site of the former Plutonium Finishing Plant is surveyed to ensure that it is safe for transfer to Hanford’s on-site disposal facility. (Photo: DOE)
Final cleanup activities at the Hanford Site’s demolished Plutonium Finishing Plant have resumed following a pause in work prompted by the COVID-19 pandemic, the Department of Energy announced. Crews with the DOE’s Richland Operations Office and site contractor Central Plateau Cleanup Company will remove, package, and dispose of rubble remaining from the demolition of the plant’s plutonium reclamation facility, which was torn down in 2017.
The Snake River Plain Aquifer
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management will award the Idaho Cleanup Project contract for the Idaho National Laboratory site to Idaho Environmental Coalition (IEC), of Tullahoma, Tenn. The contract has an estimated ceiling of approximately $6.4 billion over 10 years, with cost reimbursement and fixed-price task orders to define the contract performance.
A salt dissolution campaign in Tank 37 at the Savannah River Site was completed ahead of schedule, creating tank space for evaporator operations and allowing for more feed to the Salt Waste Processing Facility. (Photo: DOE)
Department of Energy contractor Savannah River Remediation (SRR) announced on May 11 that it has completed a salt dissolution campaign in Tank 37, one of the underground tanks storing high-level radioactive liquid waste at the Savannah River Site (SRS) in South Carolina.
Ray Geimer with DOE contractor Central Plateau Cleanup Company, left, shows company president Scott Sax a mock-up of parts of a vertical pipe casing system at Hanford’s Maintenance and Storage Facility. Photo: DOE
Workers at the Department of Energy’s Hanford Site near Richland, Wash., recently completed testing a mock-up of a system that will be used to isolate and stabilize about 15,000 pounds of radioactive debris in the site’s K West Reactor spent fuel storage basin.
The B Complex area tank farm at the DOE’s Hanford Site in Washington. Photo: DOE
The Department of Energy announced that it has determined that an underground single-shell waste tank at its Hanford Site near Richland, Wash., is likely leaking into the soil beneath the tank. The DOE said that the leaking tank poses no increased health or safety risk to the Hanford workforce or the public.
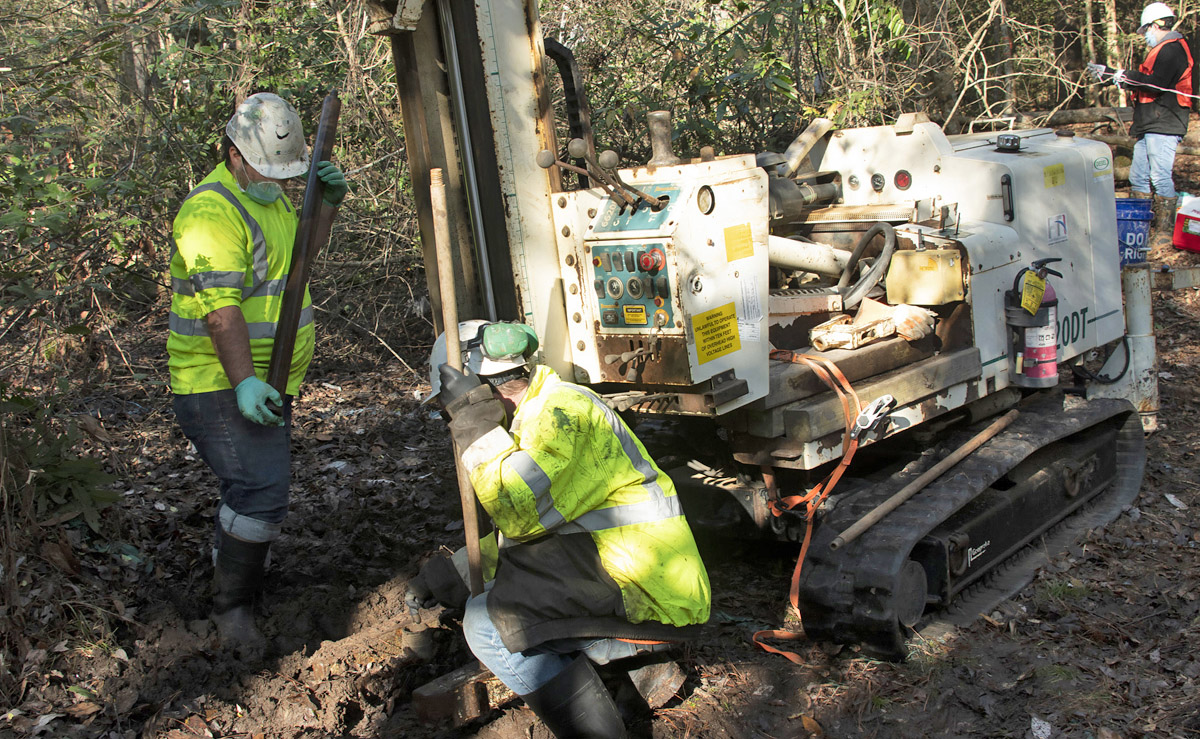
SRNS subcontractors Donald Miles and Richard Mooney drill for soil samples as part of a project to immobilize I-129 in the groundwater and soil at the Savannah River Site. Photo: DOE/SRNS
A silver chloride–based cleanup technology is expected to reduce radioactive iodine-129 contamination found in soil and groundwater near the center of the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site in South Carolina to levels well below regulatory limits. The I-129 was created during the production of plutonium and tritium at the site throughout the Cold War era.




 and Andrew Thompson.jpg)