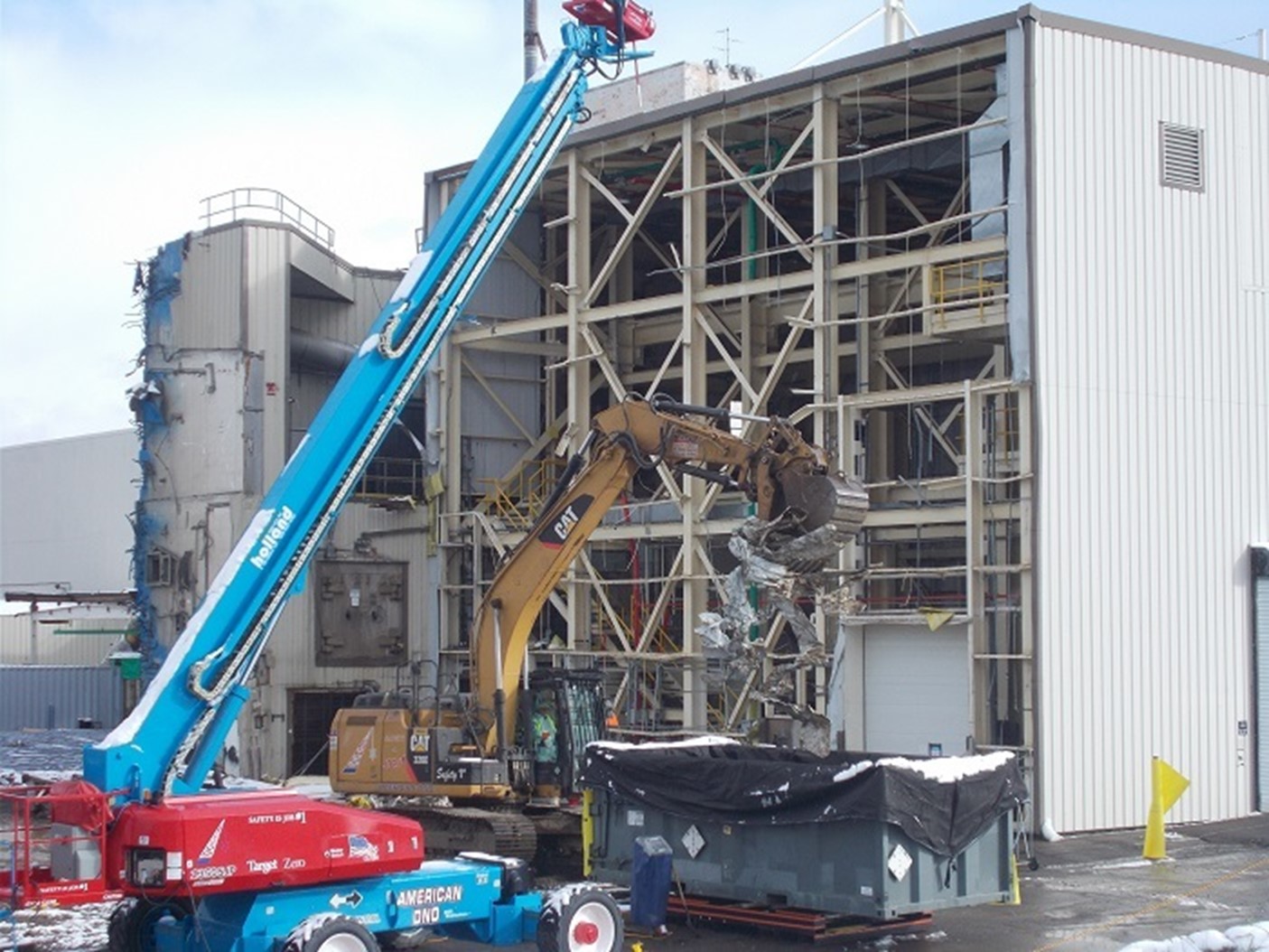
Crews take down the Load-In Facility at the West Valley Demonstration Project. The demolition is scheduled for completion early next year. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) is set to complete the 69th building demolition at the West Valley Demonstration Project early next year, when crews finish knocking down the last structure standing that supported operations at the former Main Plant Process Building.
Electrician Ralph Bisla conducts tests of the finishing line inside Hanford’s WTP Low-Activity Waste Facility. (Photo: DOE)
Having completed all startup testing of components and systems, the Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant (WTP) at the Hanford Site near Richland, Wash., has moved to the commissioning phase, the Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) announced last week. During the commissioning phase, the final steps will be taken to prepare for the vitrification of radioactive and chemical waste as part of Hanford’s Direct-Feed Low-Activity Waste (DFLAW) program.
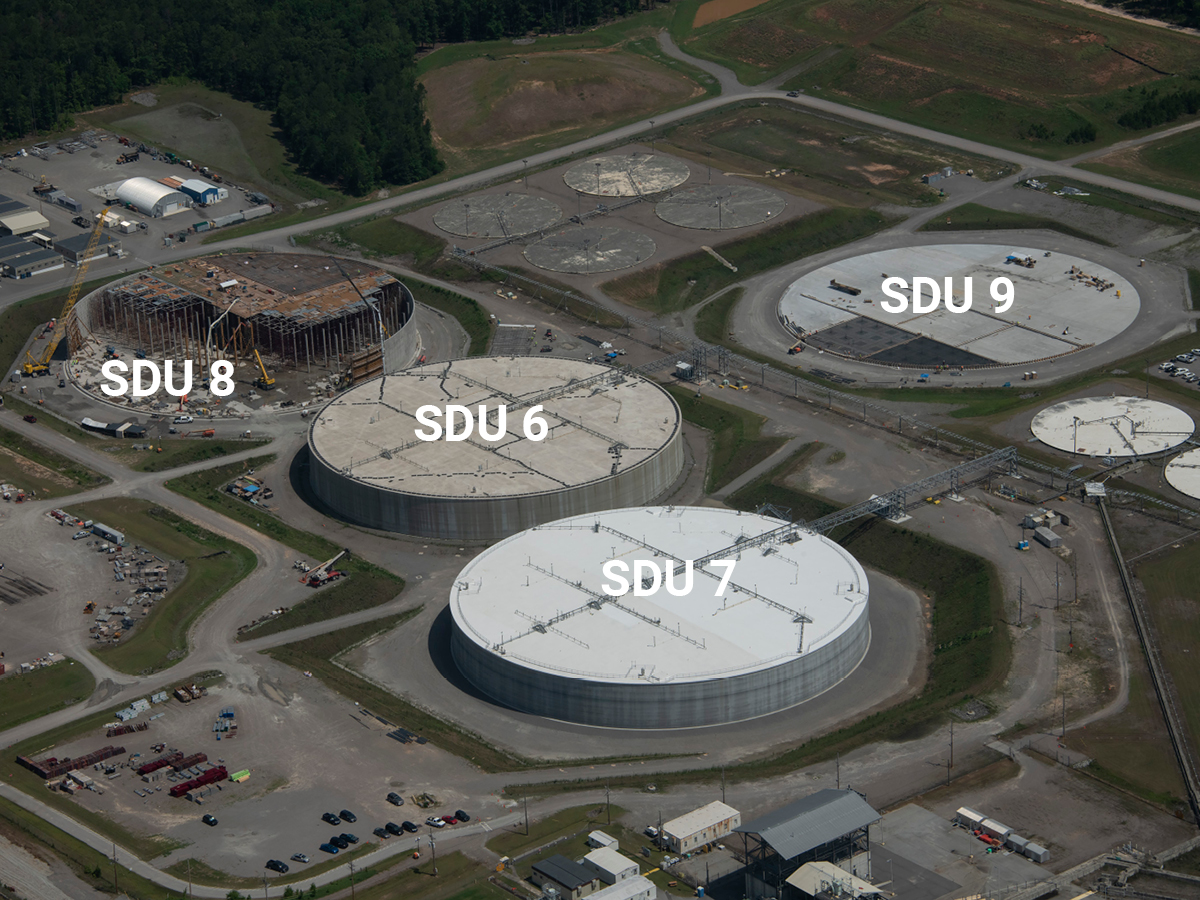
DOE liquid waste contractor Savannah River Remediation is moving forward with Saltstone Disposal Unit projects to support the Salt Waste Processing Facility at the Savannah River Site.
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) has authorized the use of a second mega-volume saltstone disposal unit (SDU) at the Savannah River Site in South Carolina. Savannah River Remediation (SRR), EM’s liquid waste contractor at SRS, received Critical Decision-4 for Saltstone Disposal Unit 7, marking the final step in the approval process before beginning operations.
The Defense Waste Processing Facility at the Savannah River Site in South Carolina. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) has awarded Savannah River Mission Completion (SRMC), of Lynchburg, Va., the Integrated Mission Completion Contract at the Savannah River Site near Aiken, S.C. The single-award, master indefinite delivery/indefinite quantity contract has an estimated contract ceiling of approximately $21 billion over a 10-year ordering period, with cost-reimbursement and fixed-price task orders to define the contract performance.
EM crews demolish Building 9207 in the former Y-12 Biology Complex at Oak Ridge earlier this year. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) has awarded a 10-year, $8.3 billion contract to United Cleanup Oak Ridge (UCOR), of Germantown, Md., for the cleanup of the Oak Ridge Reservation in Tennessee, including the Y-12 National Security Complex, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, and the East Tennessee Technology Park (ETTP).
Sealed steel containers of uranium mill tailings are loaded onto railcars at the DOE’s Moab Site in preparation for transport to the Crescent Junction disposal cell. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) announced that it has accomplished another of its 2021 priorities by permanently disposing of a cumulative 12 million tons of uranium mill tailings from the Moab Site in Utah. The announcement, made on October 26, follows last week’s report by EM that it has shipped more than 1 million tons of tailings for disposal in fiscal year 2021, which ended on September 30, the largest annual amount since FY 2012.
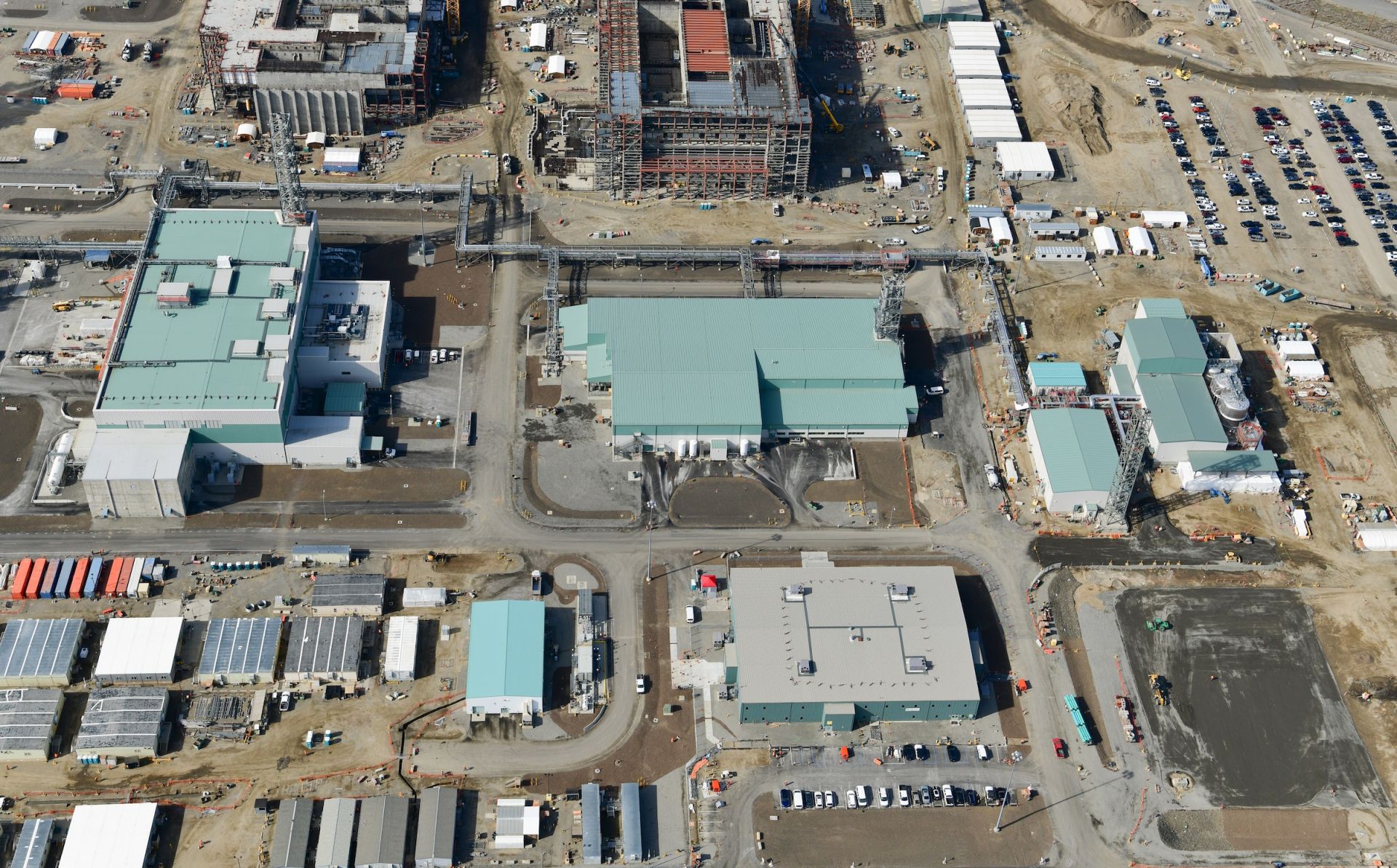
Hanford’s Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant, also known as the Vit Plant. (Photo: Bechtel National)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) has issued a final request for proposal (RFP) for the Hanford Integrated Tank Disposition Contract, a 10-year, $45 billion deal to oversee waste tank operations at the DOE’s Hanford Site near Richland, Wash. Proposals are due by December 20.
The 100-BC Area (in green) within the Hanford Site. (Image: DOE)
Soil and groundwater contamination at the Hanford Site’s 100-BC Area will be treated under a record of decision (ROD) signed by the Department of Energy and the Environmental Protection Agency, with the concurrence of the Washington State Department of Ecology.
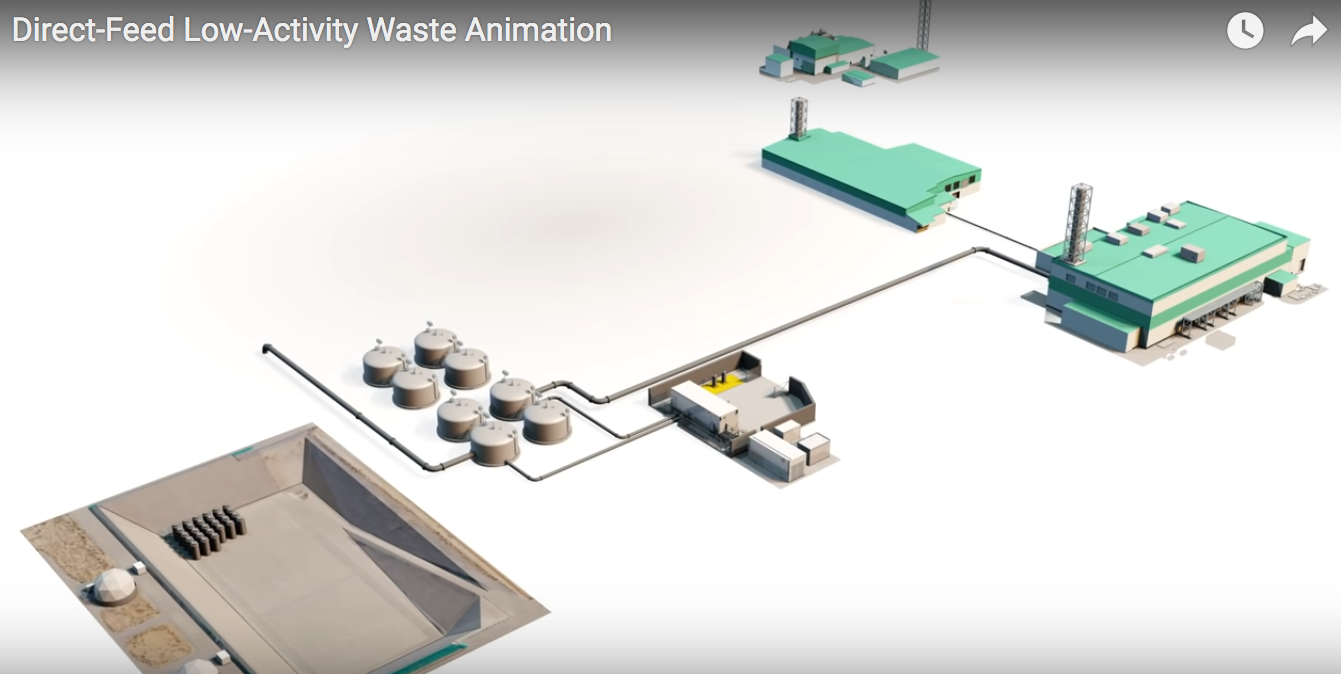
A screen shot from Hanford’s DFLAW animation. (Image: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) has released an animated video of the Direct-Feed Low-Activity Waste (DFLAW) Program at the Hanford Site near Richland, Wash. The video shows the integrated procedure for treating Hanford’s radioactive tank waste, a process EM says is a key component of its strategic cleanup vision.
View the animation here.
A view of the final remaining hot cell at the former Radioisotope Development Laboratory at Oak Ridge National Laboratory as it is prepared for demolition. (Photo: DOE)
Using a specialized radiation detector, Department of Energy cleanup contractor UCOR is characterizing a hot cell at Oak Ridge National Laboratory in preparation for its demolition. The detector overlays a radiation-intensity color-map on a picture of the environment and identifies gamma-emitting nuclides and their locations.
An electric continuous miner machine chews through the last wall of salt in Panel 8’s Room 7 of the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant to complete the rough cut of the panel. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management this week announced that after seven years, mining of the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant’s Panel 8 is finished. Created from an ancient salt formation 2,150 feet below the surface, Panel 8’s seven emplacement rooms are the next destination for transuranic waste brought to WIPP from DOE sites throughout the country.
Nitya Chandran, a facility engineer with the Washington State Department of Ecology, inspects Hanford’s tank-side cesium removal system. (Photo: DOE)
Washington state and Oregon will receive approximately $33.5 million through four financial assistance grants from the Department of Energy to fund programs related to the cleanup of the department’s Hanford Site near Richland, Wash. The grants will support environmental response regulatory activities, emergency preparedness, and public information programs in the two states.
All four grants, which were noncompetitively awarded, are for fiscal years 2022 through 2026.
Savannah River Remediation workers double-stack HLW canisters in an underground vault in Savannah River’s Glass Waste Storage Building 2 using a one-of-a-kind shielded canister transporter. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) has demonstrated the capability to expand the double-stacking of high-level waste canisters at the Savannah River Site in South Carolina. That approach will save the site’s cleanup program millions of dollars, according to the DOE.
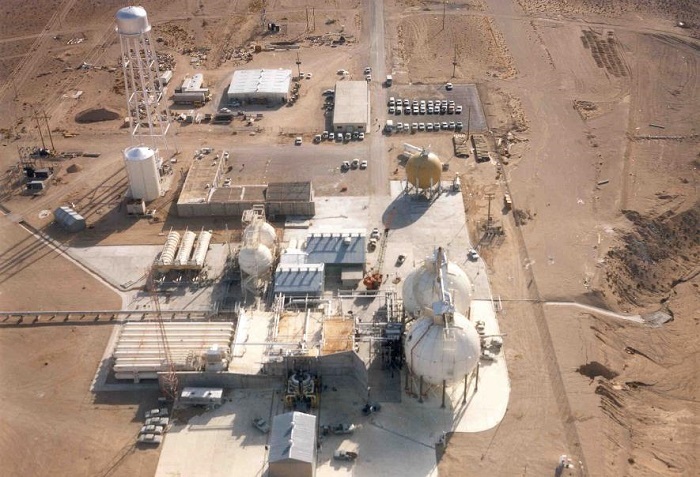
The Sodium Pump Test Facility was the last DOE building to be demolished at the Energy Technology Engineering Center site in California. (Photo: DOE)
The demolition of the final of 18 DOE-owned buildings at the Energy Technology Engineering Center (ETEC) has been completed, according to the DOE. The ETEC is the former liquid metals research facility located at the Santa Susana Field Laboratory (SSFL), northwest of Los Angeles.
U.S. Forest Service employees Secunda Hughes (left) and Andrew Thompson inspect irrigation piping and sprinkler heads, part of a 62-acre pine plantation used to safely disperse tritium at the Savannah River Site.
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) is managing the release of tritiated water using a 62-acre plantation of pine trees and other natural resources to limit radioactively contaminated groundwater from reaching waterways on the Savannah River Site in South Carolina.
An archive photo of the Nevada National Security Site’s Test Cell C complex, which is being prepared for demolition and closure. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy is preparing to demolish two large, complex facilities at the Nevada Nuclear Security Site with ties to historical nuclear propulsion rocket development and testing programs. The DOE’s Environmental Management (EM) Nevada Program and its environmental program services contractor, Navarro Research and Engineering, have begun characterization and hazard reduction work on the site’s Engine Maintenance, Assembly, and Disassembly (EMAD) and Test Cell C (TCC) complexes.
F Area operator Thomas Harman (left) and SRNS scientist Kevin Boerstler check the pumps, sensors, and piping that blend a base concentrate to inject into acidic groundwater at the Savannah River Site. (Photo: DOE)
The Savannah River Site is reducing the flow of hazardous and radioactive metal contaminants to South Carolina’s rivers and streams by injecting a mix of clean water and baking soda into the site’s groundwater. The base mix neutralizes groundwater that has become acidic as a result of SRS’s chemical separations work, helping restrict the flow of contaminants.
 The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) has established its key priorities for calendar year 2022, covering planned cleanup, project construction, acquisition, and other important accomplishments to advance the office’s environmental and risk-reduction mission. EM is responsible for handling the nation’s Cold War environmental legacy resulting from five decades of nuclear weapons production and government-sponsored nuclear energy research.
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) has established its key priorities for calendar year 2022, covering planned cleanup, project construction, acquisition, and other important accomplishments to advance the office’s environmental and risk-reduction mission. EM is responsible for handling the nation’s Cold War environmental legacy resulting from five decades of nuclear weapons production and government-sponsored nuclear energy research.









 within the Hanford Site.png)





 and Andrew Thompson.jpg)

