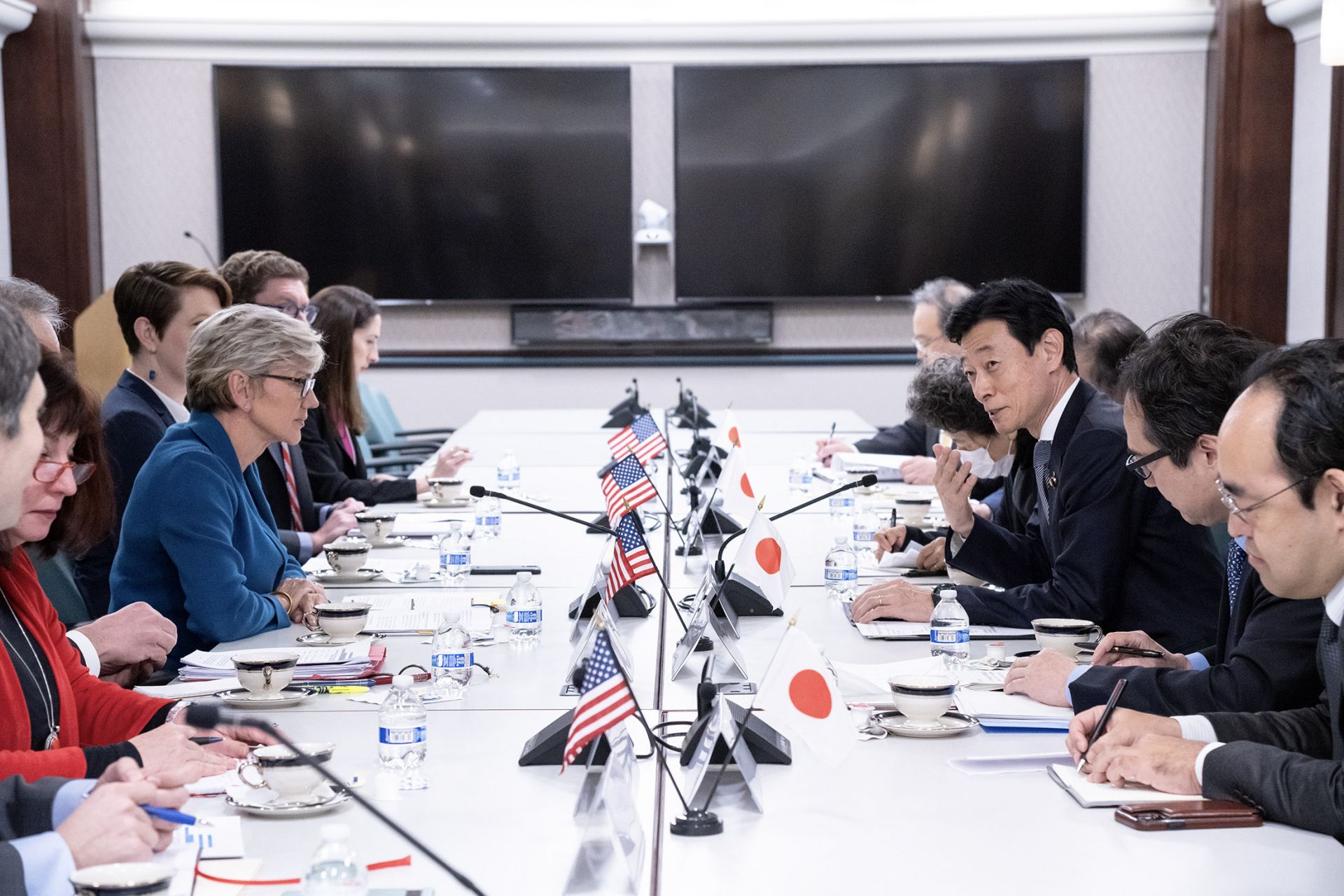
U.S. secretary of energy Jennifer Granholm and Japan’s minister of economy, trade, and industry Yasutoshi Nishimura lead energy discussions on January 9 in Washington, D.C. (Photo: DOE)
Researchers at Idaho National Laboratory have completed initial testing on a newly developed fuel test capsule that is expected to provide crucial performance data for sodium-cooled fast reactors. The Department of Energy announced on January 12 that the series of fuel testing experiments being carried out now at INL’s Transient Reactor Test Facility (TREAT) was developed through a joint project between the United States and Japan.
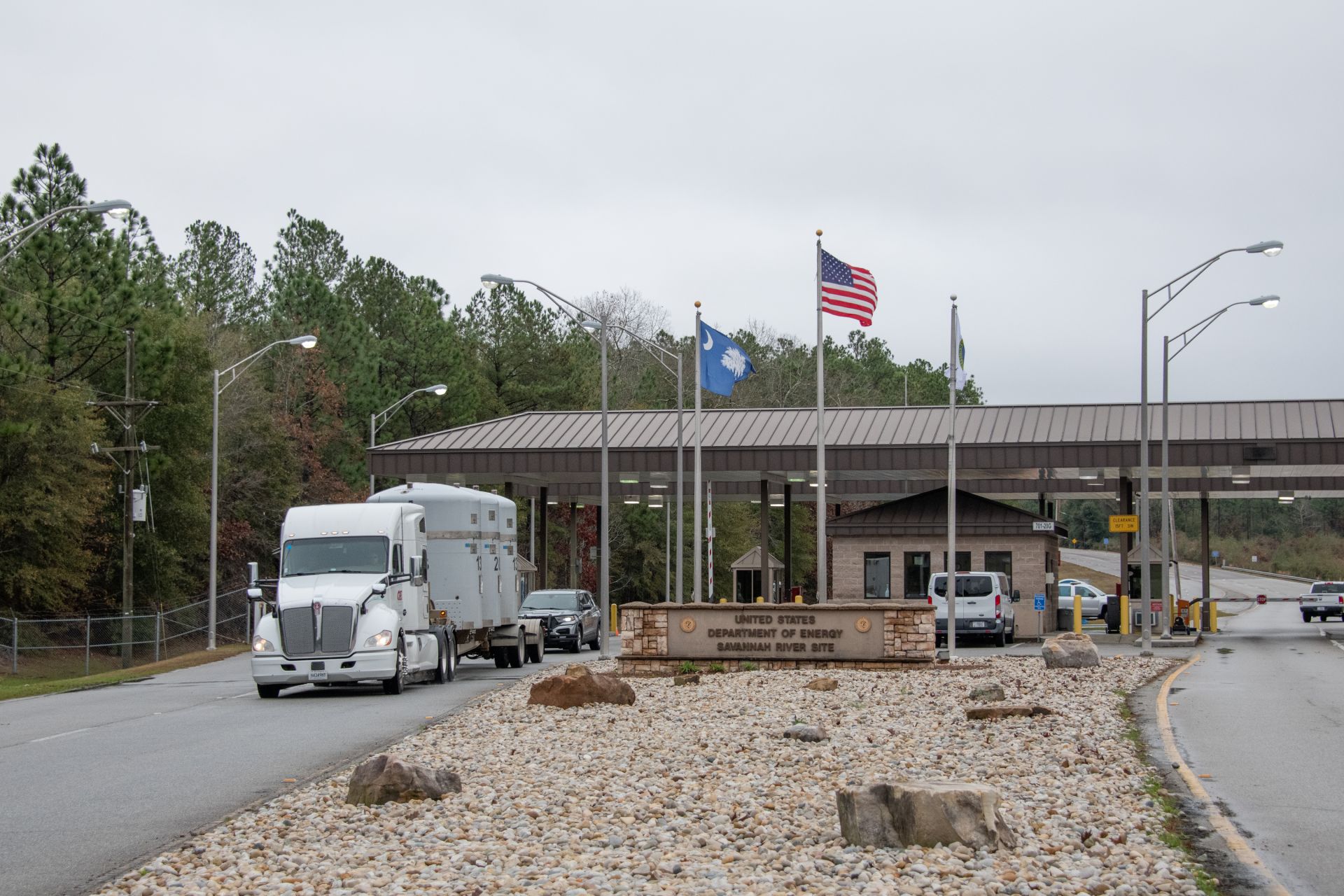
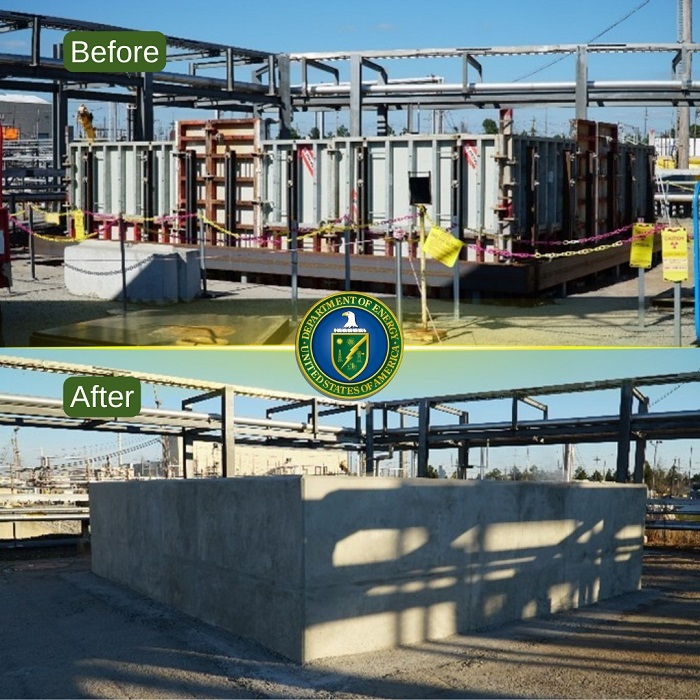
The first shipment of downblended surplus plutonium from SRS’s K Area leaves SRS. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration and Office of Environmental Management have completed the first shipment of downblended surplus plutonium transuranic (TRU) material from the K Area at the Savannah River Site in South Carolina to the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant in New Mexico.
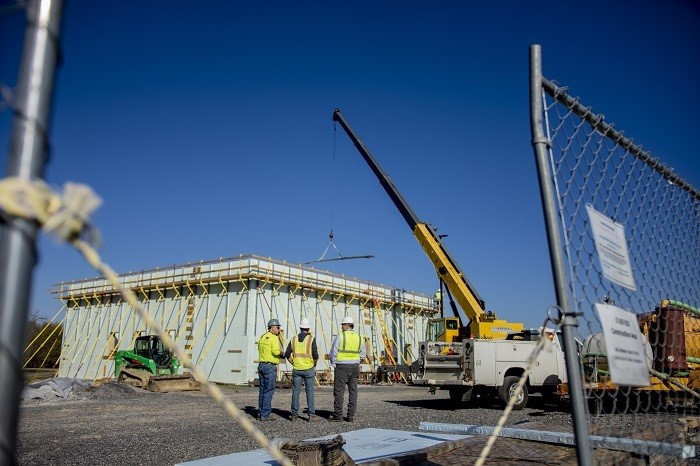
Construction is underway on the Paducah Site's new Emergency Operations Center. (Photo: DOE)
Construction crews at the Department of Energy's Paducah Site in Kentucky have broken ground on a new Emergency Operations Center (EOC) to improve coordination and response to emergencies across the site.
The 3,500-square-foot facility will replace the existing EOC, which was established in the site’s C-300 Control Building around 1990. The C-300 Control Building was built during the 1950s. The new modern facility will be used to monitor environmental conditions and house emergency management personnel.
The new EOC is scheduled for completion in this year.
A video is available on the construction of the new EOC.
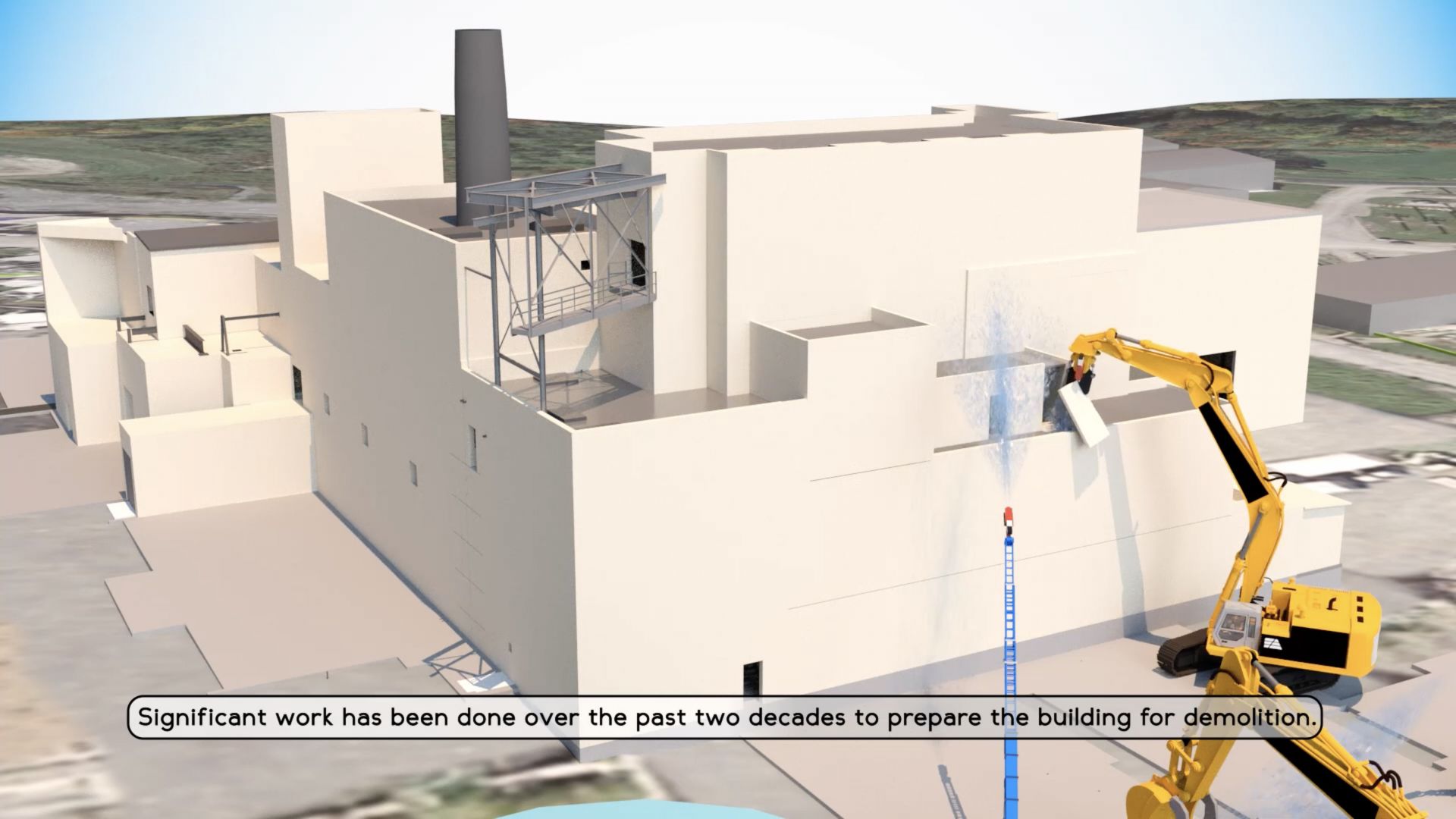
A screen capture from the DOE's West Valley video. (Image: DOE)
A new animated video from the Department of Energy's Office of Environmental Management (EM) shows how cleanup contractor CH2M HILL BWXT West Valley (CHBWV) will take down the main plant process building at the West Valley Demonstration Project (WVDP).
The EM team at West Valley wanted to convey the project to the public, and they believe the animation accomplishes that goal, according to Stephen Bousquet, EM WVDP federal project director for the Main Plant Deconstruction Project.
Click here to watch the video.
Researchers are looking for the ideal characteristics of molten salt, which can serve as both coolant and fuel in advanced nuclear reactors. (Photo: Argonne National Laboratory)
Scientists are searching for new materials to advance the next generation of nuclear power plants. In a recent study, researchers at the Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory showed how artificial intelligence could help pinpoint the right types of molten salts, a key component for advanced nuclear reactors.
The Human Systems Simulation Laboratory at INL allows researchers to simulate industrial control rooms to improve performance. (Photo: INL)
In the 1960s, nuclear energy established itself as a mainstay of the electrical grid for its ability to produce carbon-free, safe, and reliable power. Indeed, nuclear energy currently provides about 50 percent of carbon-free electricity in the United States, but a major challenge is its cost.
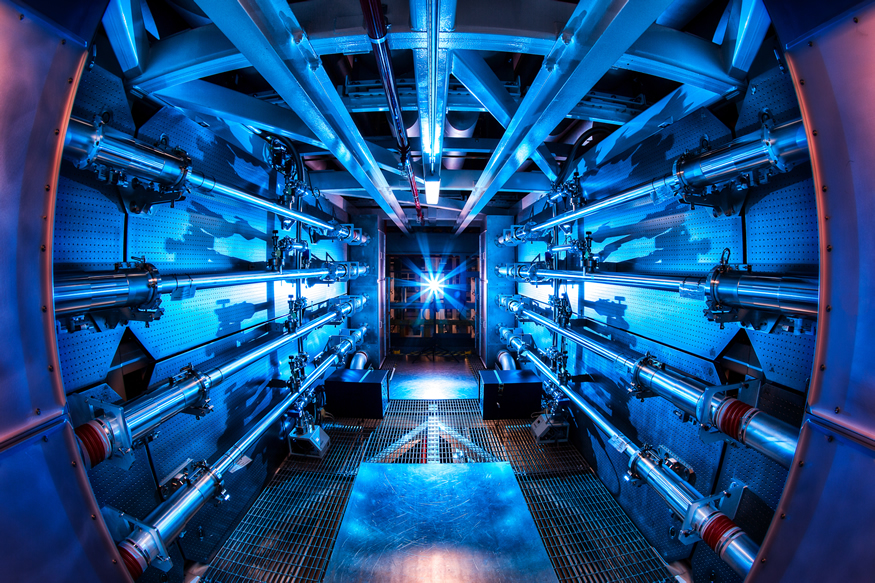
A color-enhanced image of the inside of a NIF preamplifier support structure. (Image: LLNL/Damien Jemison)
On December 5, researchers at the National Ignition Facility (NIF) at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory achieved fusion energy breakeven. It was a gain for stockpile stewardship that also—as headlines gushed prior to the Department of Energy’s December 13 announcement—boosted the prospects of inertial fusion energy (IFE). The timing of the landmark achievement may have been especially welcome to private fusion companies with inertial or hybrid magneto-inertial confinement concepts, because it occurred as the DOE was getting ready to consider applications for $50 million in funding for fusion pilot plant design work.
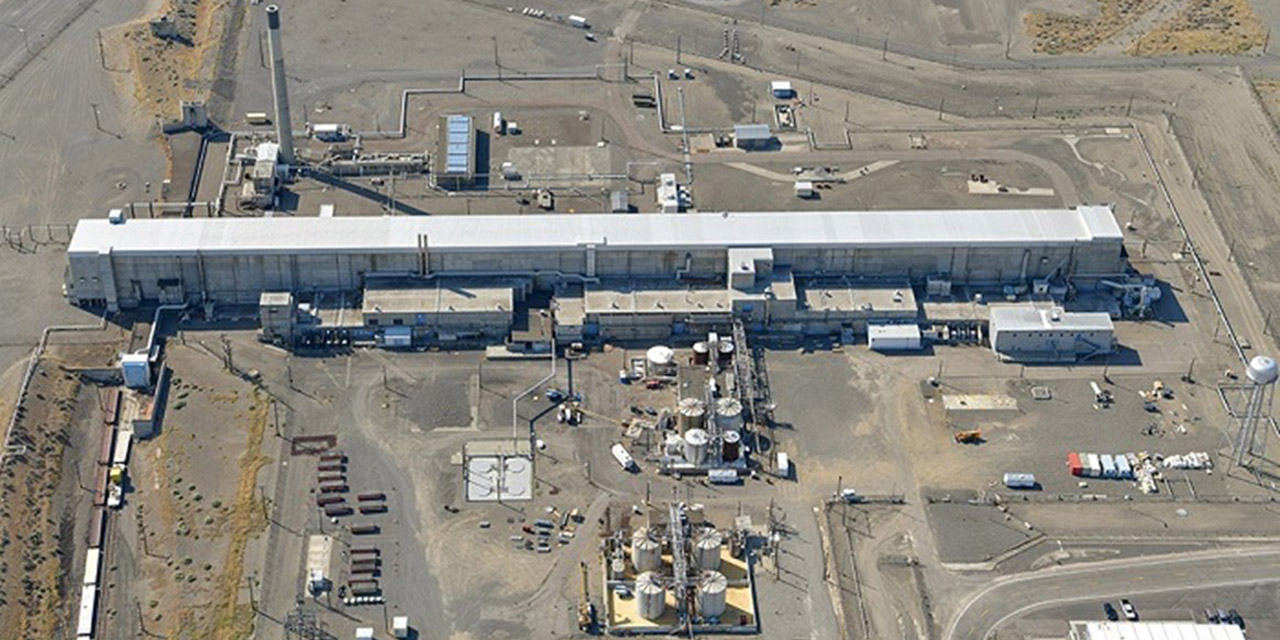
An aerial view of Hanford’s Plutonium Uranium Extraction plant, showing the main facility (at center), the 211-A chemical storage area, and (in foreground) the 203-A acid storage area. (Photo: DOE)
Work crews at the Department of Energy’s Hanford Site in Washington state are performing risk-reduction activities at the Plutonium Uranium Extraction (PUREX) plant to prepare it for eventual disposition.
“It will be a yearslong effort to get this large facility ready for disposition, and I’m encouraged by the progress to safely and efficiently advance this work,” said Andy Wiborg, the DOE’s Projects and Facilities Division team lead for Hanford’s Central Plateau cleanup project.