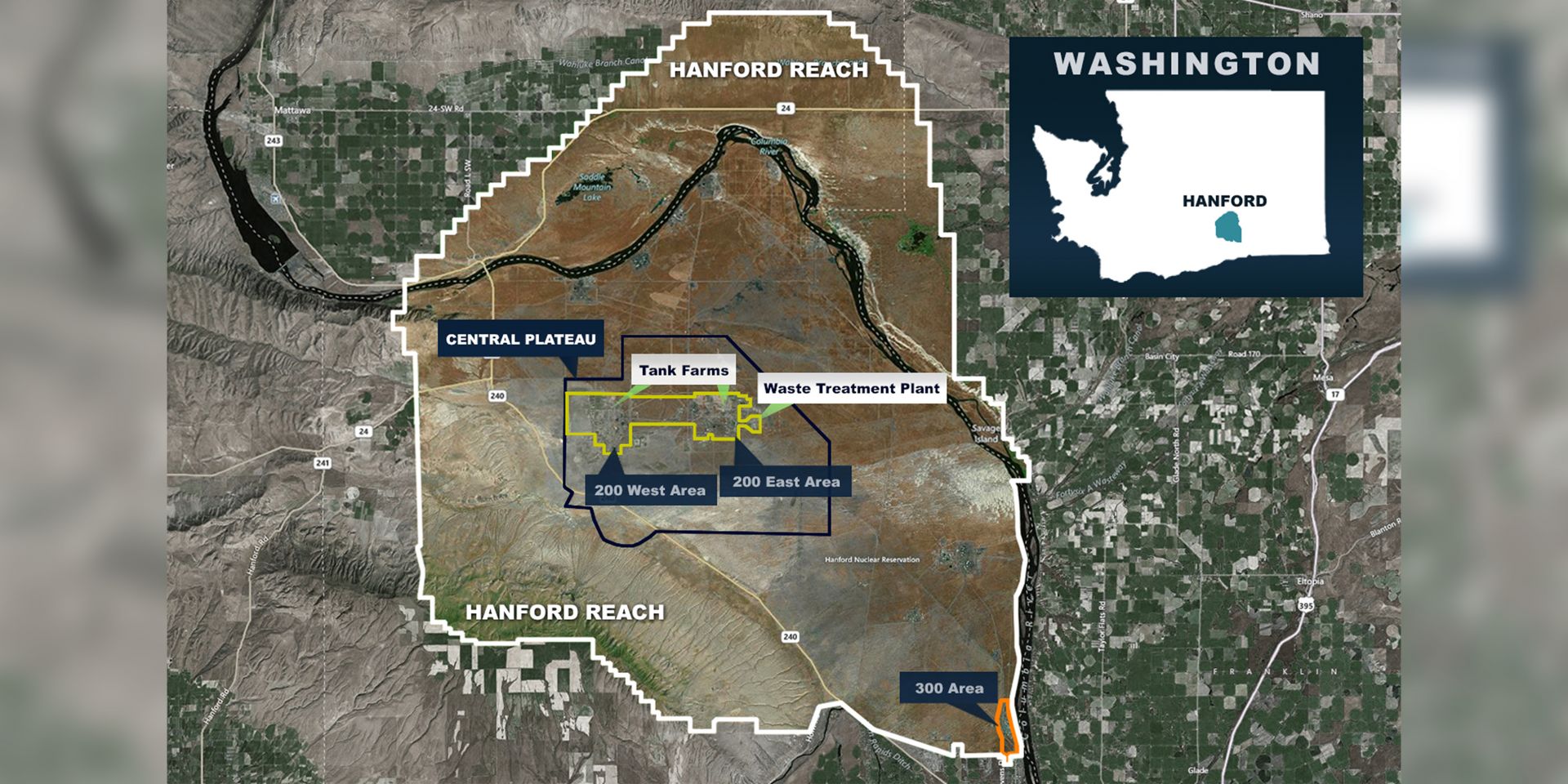
The DOE’s Hanford Site. (Image: Washington River Protection Solutions)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management issued for public comment the first request for qualifications (RFQ) related to the department’s Cleanup to Clean Energy initiative, which aims to increase energy production by making DOE land available for the potential development of carbon-free energy (CFE) electricity generation through leases.
A slide from the DOE-FES’s recent presentation to the Fusion Energy Sciences Advisory Committee. (Image: DOE)
The Office of Fusion Energy Sciences (FES) in the Department of Energy’s Office of Science introduced a new plan—"Building Bridges: A Vision for the Office of Fusion Energy Sciences”—during a Fusion Energy Sciences Advisory Committee (FESAC) hearing on December 13, and announced that news December 14. What’s included? A plan for the DOE to “establish the steps needed to help advance fusion energy, including addressing key science and technology gaps in the supply chain and industry.” The vision is less a guiding document than a preview of DOE-FES’s near-term intentions, which include drafting a fusion science and technology road map in 2024 to shape investments for the coming decade.
Homer at his work station. (Artwork from The Simpsons used with the permission of 20th Century Studios)
In the episode “Duffless” in season 4 of The Simpsons, Homer is deep in the bowels of the Springfield Nuclear Power Plant when he encounters a gigantic mutant spider. He turns to a map that says, “To overcome the spider’s curse, simply quote a Bible verse.” Homer starts with, “Uh, thou shalt not . . .” but then, unable to remember anything from the Bible, he instead brains the spider with a rock. This sort of nuttiness is often how we’ve depicted the power plant on the show, where I’ve been a writer and producer for 20 seasons.
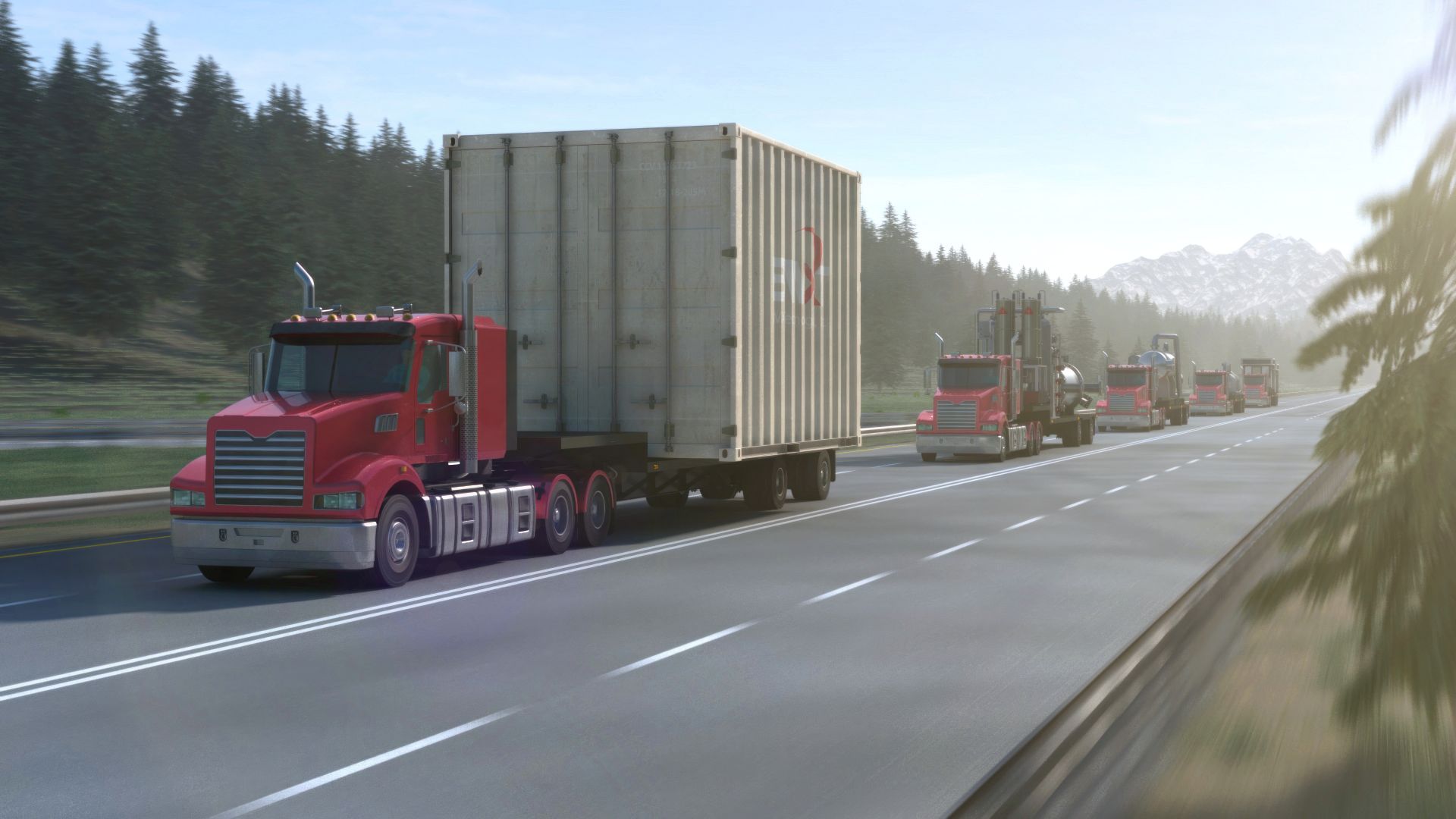
December 15, 2023, 4:56PMNuclear NewsDonna Kemp Spangler and Joel Hiller BWXT’s microreactor components would be designed to be transported directly from the factory to the deployment site. (Image: BWXT)
“The tools of the academic designer are a piece of paper and a pencil with an eraser. If a mistake is made, it can always be erased and changed. If the practical-reactor designer errs, he wears the mistake around his neck; it cannot be erased. Everyone sees it.”
Many in the nuclear community are familiar with this sentiment from Admiral Rickover. A generation of stagnation in the industry has underscored the truth of his words. But as economies around the world put a price on carbon emissions, there’s a renewed sense of urgency to deploy clean energy technologies. This shifts the global balance of economic competitiveness, and it’s clear that the best path forward for nuclear requires combining the agility of private innovators with the technology and capabilities of national laboratories.
STARFIRE is the name of an inertial fusion energy hub led by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory—one of three hubs announced in early December. (Image: LLNL)
The Department of Energy recently announced that it was establishing three inertial fusion energy (IFE) hubs and funding them with a total of $42 million over four years. The leaders of the three hubs selected by competitive peer review—Colorado State University, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, and the University of Rochester—all issued press releases touting the attributes and plans of their facilities and their research collaborators on the same day—December 7.
Operators in plastic suits prepare for drum venting operations. (Photo: DOE/SRNS)
Department of Energy contractor Savannah River Nuclear Solutions (SRNS) said its Savannah River Site employees recently used an innovative method to ensure the integrity of radioactive material storage containers currently in long-term dry storage at the South Carolina site.
Joint efforts of Argonne and private industry further nuclear reactor developments
Partnerships between the nuclear industry and national laboratories are making overall codes more robust and capable. (Photo: Argonne)
The development of modern nuclear reactor technologies relies heavily on complex software codes and computer simulations to support the design, construction, and testing of physical hardware systems. These tools allow for rigorous testing of theory and thorough verification of design under various use or transient power scenarios.
Savannah River Nuclear Solution’s supply chain management team discusses upcoming process changes during its first staff augmentation summit. (Photo: SRNS)
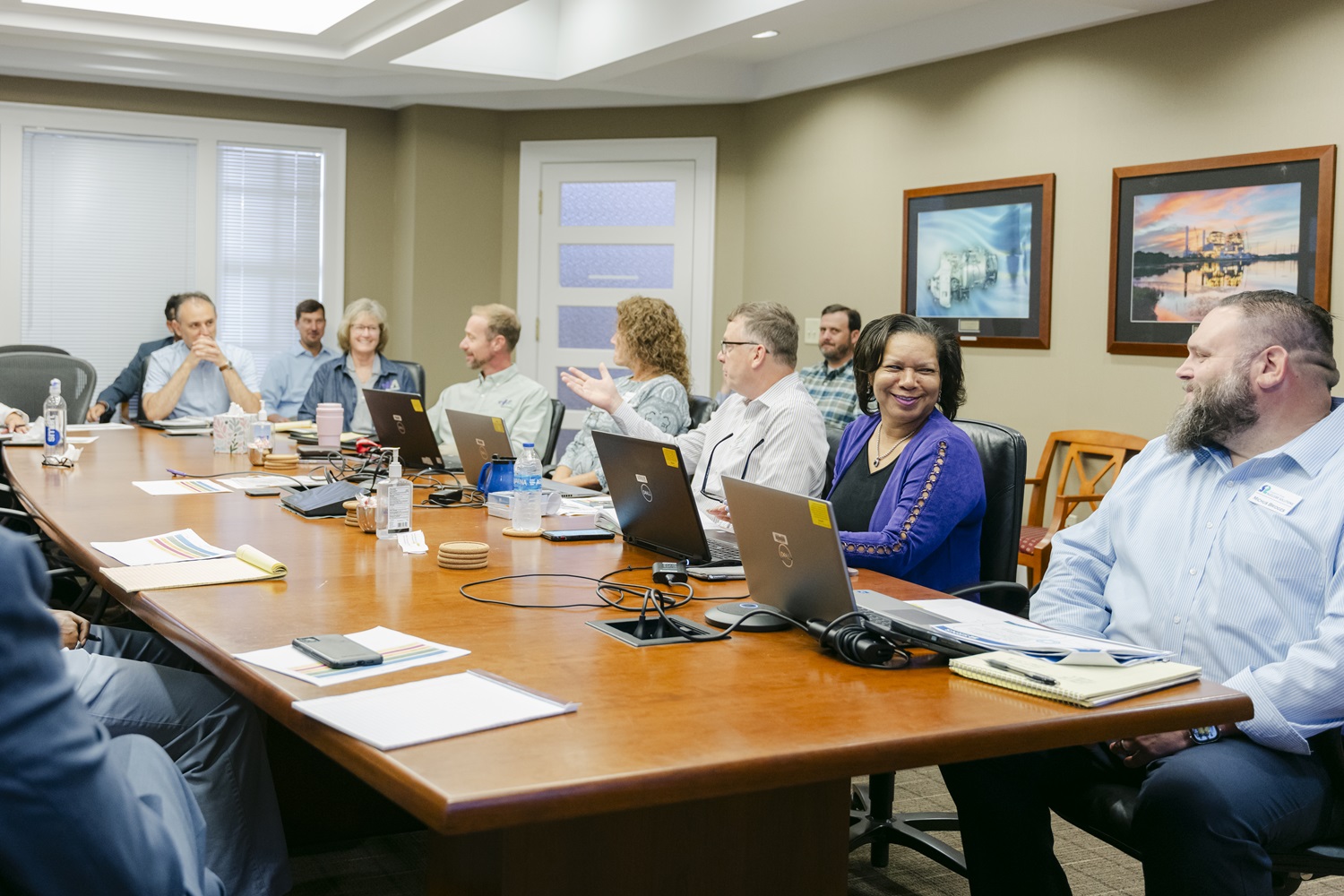
Savannah River Nuclear Solutions’ Supply Chain Management (SCM) team recently hosted its first staff augmentation summit to strengthen relationships with 25 staffing firms and provide upcoming process changes for fiscal year 2024.
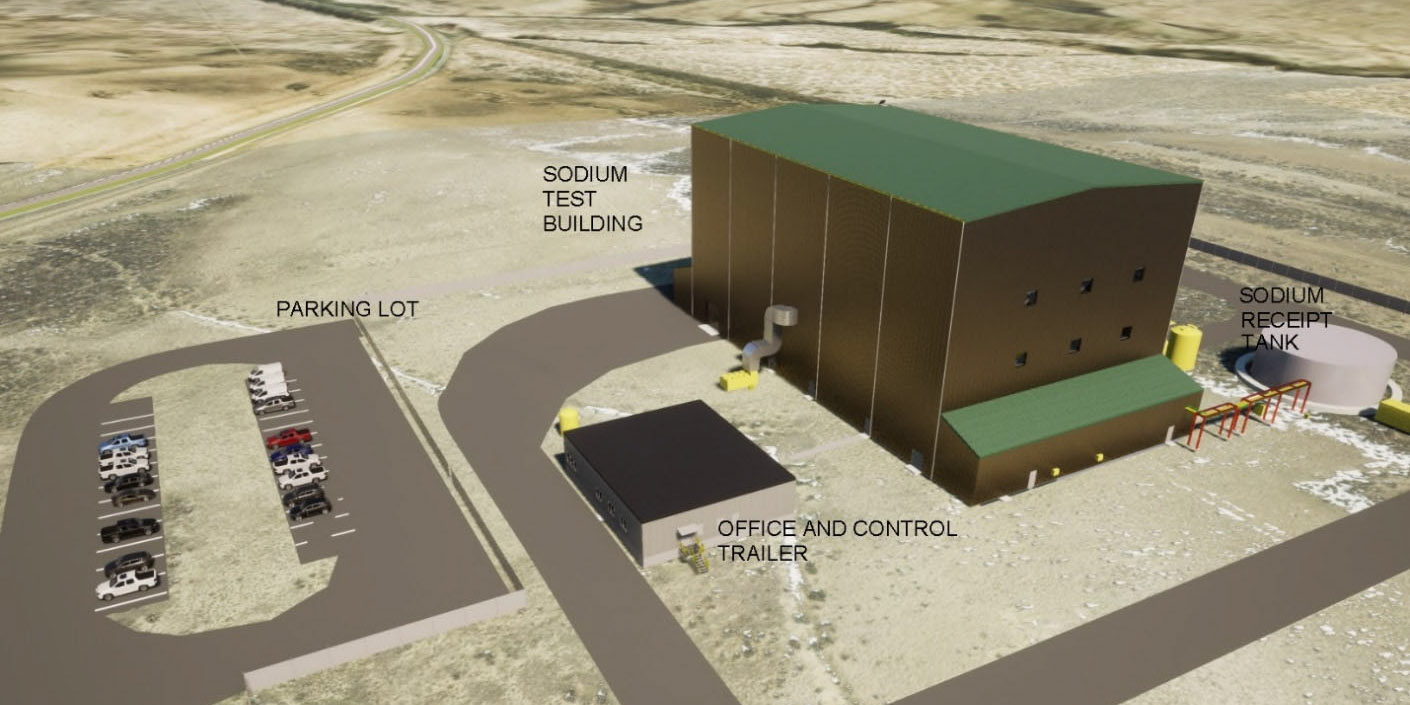
Image from the DOE’s draft EA showing a rendering of the TFF building. (Image: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Clean Energy Demonstrations issued a draft environmental assessment (EA) in early November for a test and fill facility (TFF) that TerraPower plans to build in Kemmerer, Wyo.—the town selected two years ago to host the company’s first Natrium sodium fast reactor. The draft EA, open for comment through December 1, describes TerraPower’s plans to construct a nonnuclear facility that would safely store about 400,000 gallons of sodium to test coolant system designs and ultimately fill the planned reactor.
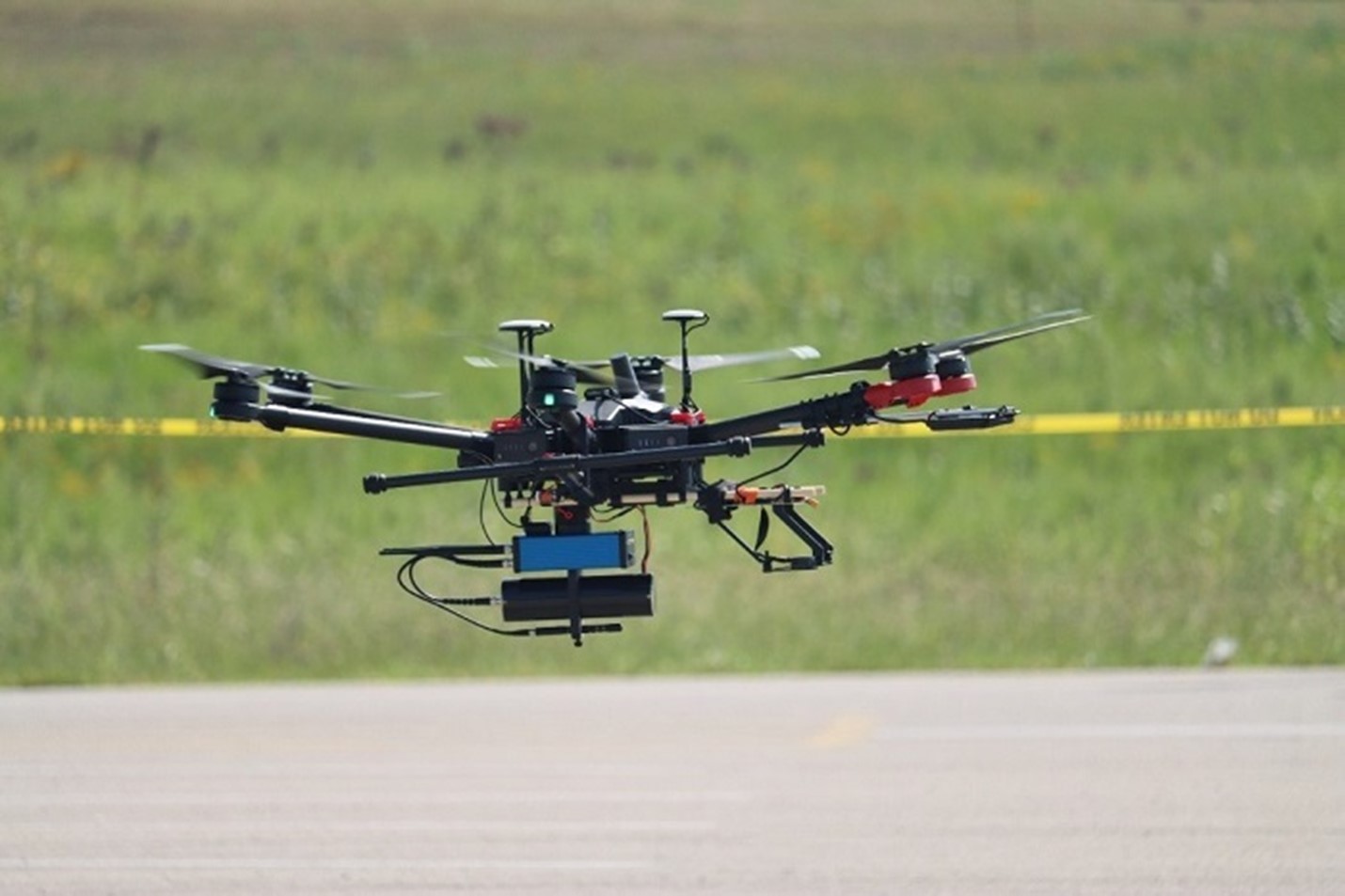
A radiation detection drone was tested at the Portsmouth site in southern Ohio. (Photo: DOE)
Through a collaborative effort between the Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management and the state of Ohio, a drone outfitted with radiation detectors underwent testing recently at the site of the Portsmouth Gaseous Diffusion Plant for potential future use.