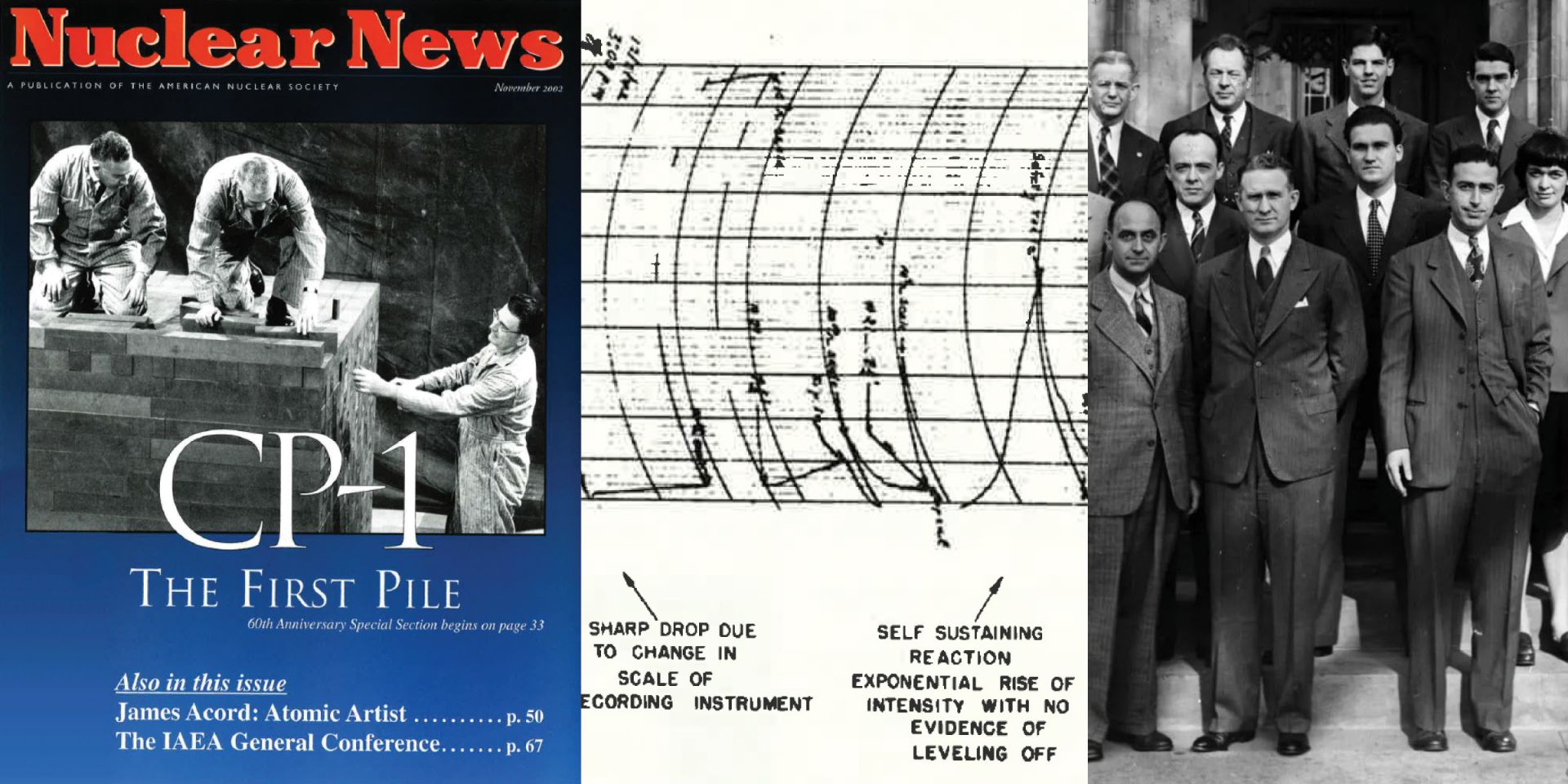
A replica of the chianti bottle signed by many of those present on December 2, 1942, alongside the image of a document signed 20 years later by most of those present (Photo: ANL); a portion of a photo of CP-1 scientists taken on December 2, 1946 (Photo: ANL); January 1993 Nuclear News coverage of CP-1 50th anniversary commemorations during the 1992 ANS Winter Meeting.
Nuclear Newswire is back with the final #ThrowbackThursday post honoring the 80th anniversary of Chicago Pile-1 with offerings from past issues of Nuclear News. On November 17, we took a look at the lead-up to the first controlled nuclear chain reaction and on December 1, the events of December 2, 1942, the day a self-sustaining nuclear fission reaction was created and controlled inside a pile of graphite and uranium assembled on a squash court at the University of Chicago’s Stagg Field.
From left, the cover of the December 1962 issue of NN, featuring a model and a medal, both displayed at the 1962 ANS Winter Meeting; a photo of CP-1 during construction, as published in the November 1992 issue of NN; the opening page of a chronological account of CP-1, published in November 1992 to mark the 50th anniversary.
As we approach the 80th anniversary of controlled nuclear fission, Nuclear Newswire is prepared to deliver not one but three #ThrowbackThursday posts of CP-1 highlights unearthed from past issues of Nuclear News.
ANS was founded in 1954, nearly 12 years after the first controlled nuclear chain reaction was achieved on December 2, 1942, inside a pile of graphite and uranium assembled on a squash court at the University of Chicago’s Stagg Field. By 1962, ANS was prepared to “salute the 20th anniversary of the first chain reaction” at their Winter Meeting, displaying a model of Chicago Pile-1 and presenting a specially cast medal to Walter Zinn, a representative of Enrico Fermi’s scientific team. Over the years, ANS has continued to mark significant anniversaries of CP-1 at national meetings and in NN.





 Jack Steinberger, a Nobel Prize–winning scientist with a distinguished career in experimental physics,
Jack Steinberger, a Nobel Prize–winning scientist with a distinguished career in experimental physics,