Several-inch-diameter manganese nodules just sit on the ocean floor and can be collected with little to no actual mining, as opposed to severe mining on land. (Photo: Wikimedia Commons)
Regardless of how you power our grid or how you attempt to decarbonize our economy, we will need many various metals to achieve any future, or even to just continue with business as usual. Critical metals like cobalt, lithium, nickel, and neodymium are essential to a low-carbon-energy future if renewables and electric vehicles are to play a large role.1 Even if nuclear provides 100 percent of our power, just operating the grid and electrifying most sectors will take huge amounts of critical metals like copper, notwithstanding the fact that nuclear power requires the least amount of metals and other materials of any energy source.
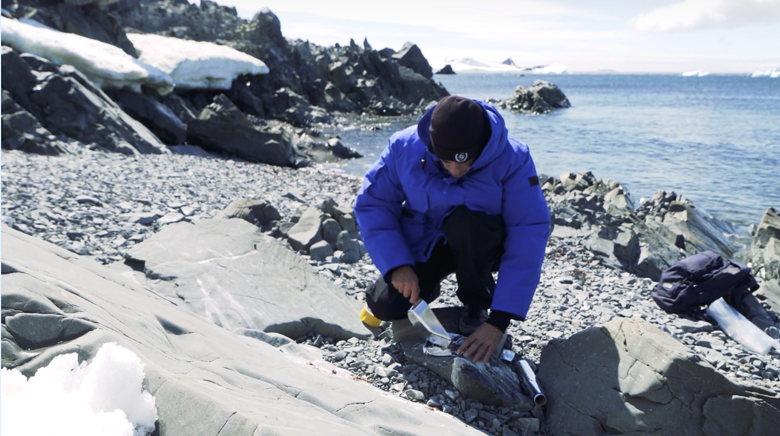
An IAEA researcher collects samples from the Antarctic shoreline. (Image: IAEA)
The International Atomic Energy Agency, in cooperation with Argentina, launched a scientific research expedition on January 6 to study microplastics in Antarctica—one of the planet’s most remote areas—as part of an effort to combat widespread microplastic pollution.
.jpg)