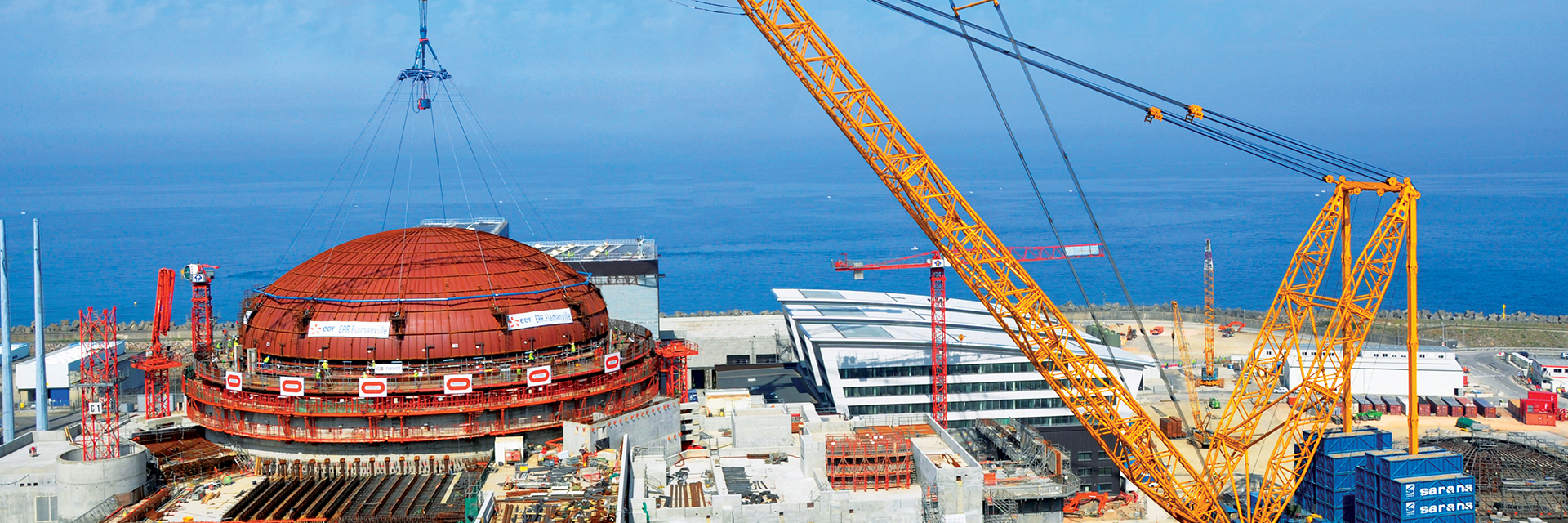
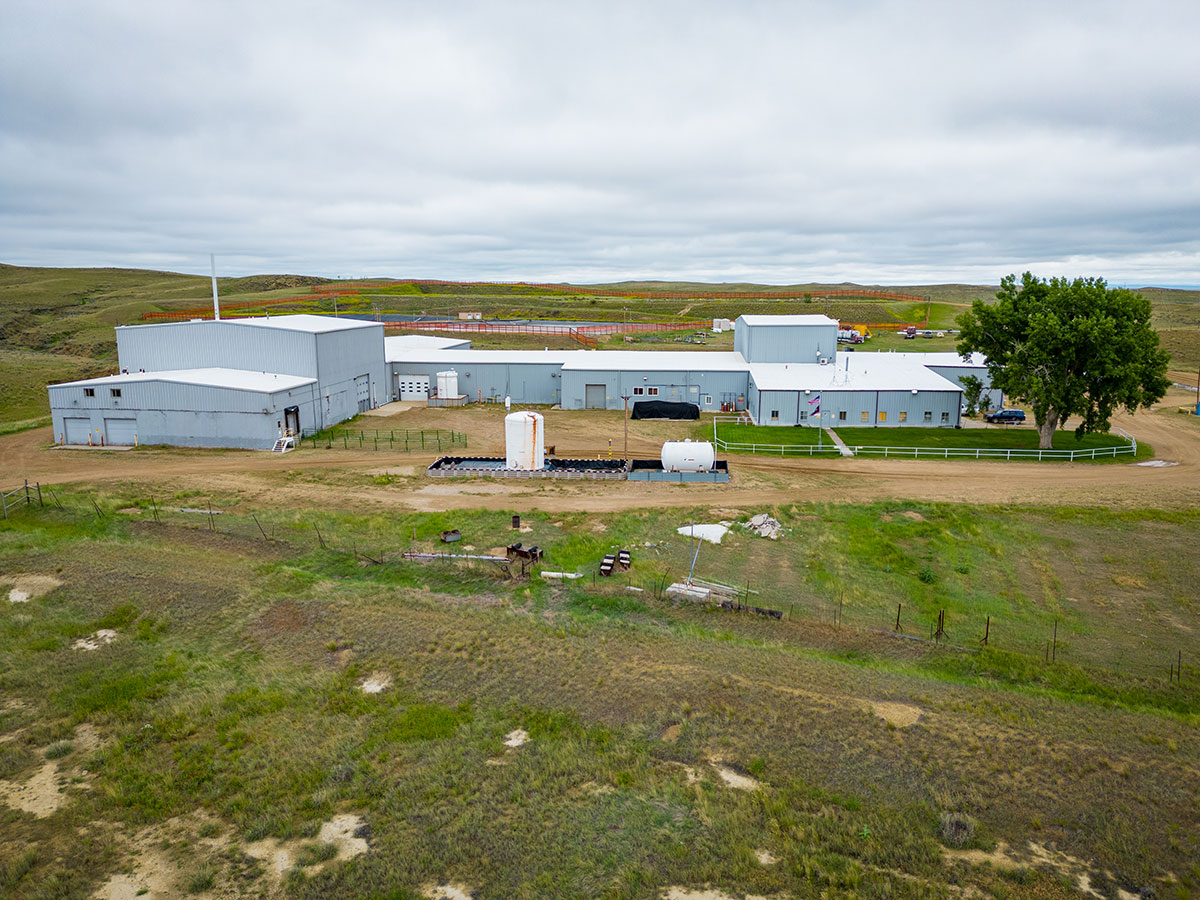
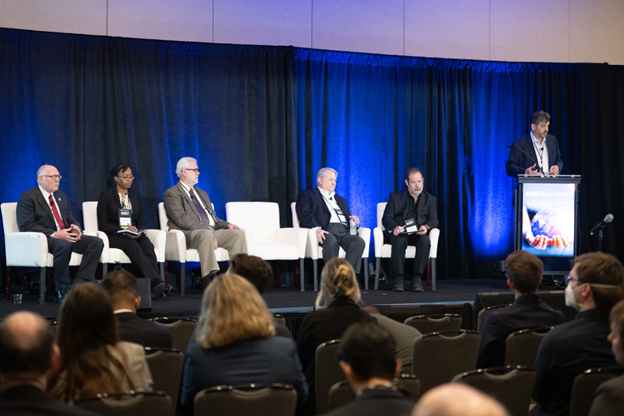
The Irigaray central processing plant, in Wyoming’s Powder River Basin. (Photo: Uranium Energy)
TerraPower and Uranium Energy announced today that they have signed a memorandum of understanding to “explore the potential supply of uranium” for TerraPower’s demonstration reactor in Kemmerer, Wyo.
Pictured, from left, are Steve Nesbit, Christina Leggett, John Kessler, Paul Dickman, John Mattingly, and Craig Hansen. Edwin Lyman, who joined the panel remotely, is not pictured.
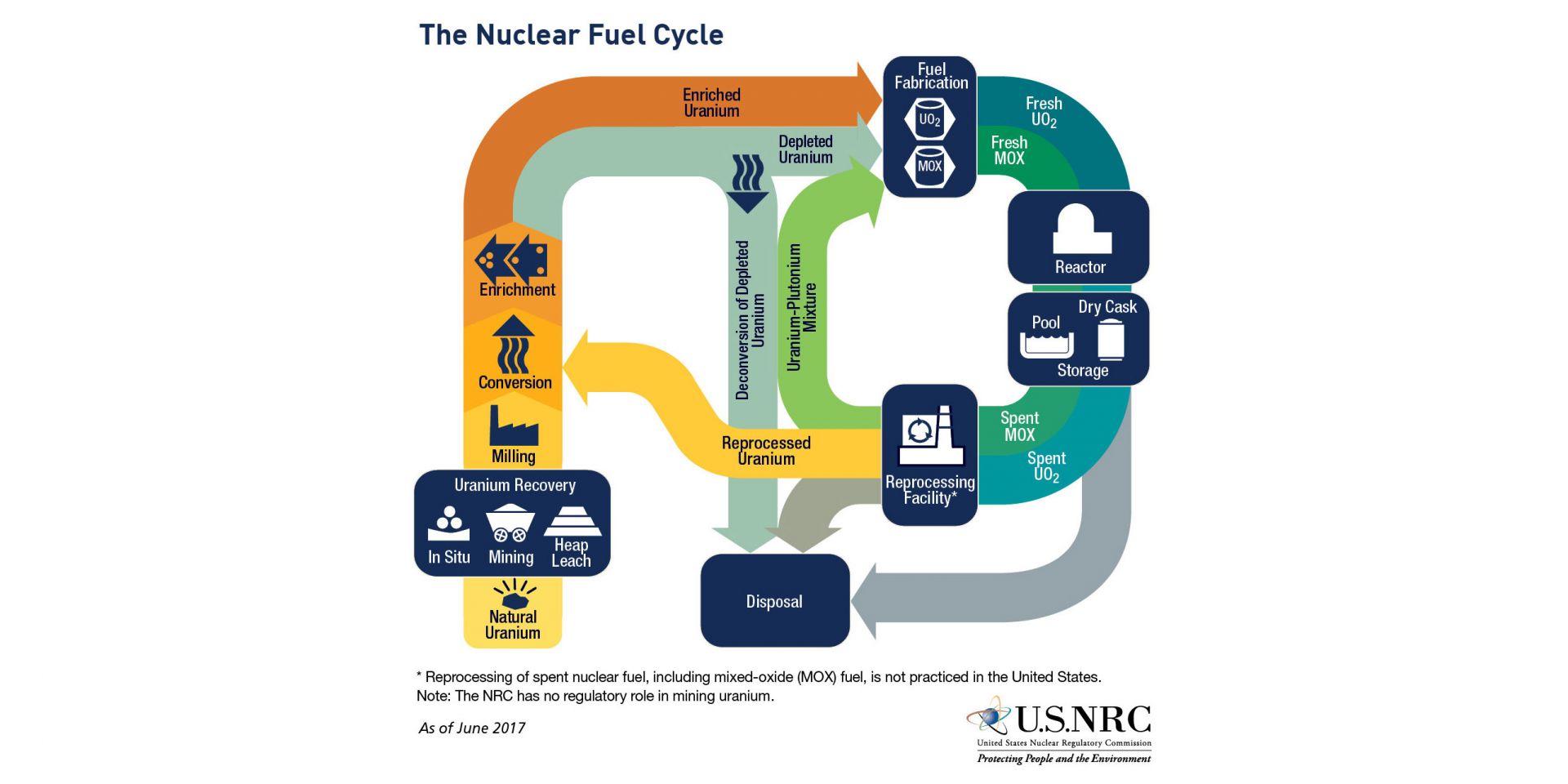
Advanced reactors may be key to a clean energy future, but to prove it they’re going to need fuel—and that fuel will be derived from limited uranium resources and managed throughout the nuclear fuel cycle, whether that cycle is open (like the current fuel cycle) or closed (with reprocessing). Six panelists convened on June 12 during the Annual Meeting of the American Nuclear Society for the executive session “Merits and Viability of Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles: A Discussion with the National Academies.” They discussed those fuel cycles and the findings of a National Academies of Science, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM) consensus committee released as a draft report in November 2022 and published earlier this year.
March 14, 2023, 9:39AMEdited March 14, 2023, 9:38AMNuclear News In this screenshot from a video recording of the hearing, Huff, Wagner, and Dominguez answer a series of questions from Sen. Manchin
“Right now, our country is deficient in nearly every aspect of the fuel cycle. This must change and it must change quickly,” said Sen. Joe Manchin (D., W.V.), chairman of the Senate Committee on Energy and Natural Resources (ENR), as he opened a Full Committee Hearing to Examine the Nuclear Fuel Cycle on March 9. “Whether it is uranium mining, milling, conversion, enrichment, nuclear fuel fabrication, power generation, or nuclear waste storage and disposal, there is much work to be done, starting with conversion and enrichment. Simply put, Russia dominates the global market, representing nearly half of the international capacity for both processes.”
Energy Fuels’ White Mesa Mill in southeastern Utah is the only operating conventional uranium mill in the United States. (Photo: Energy Fuels)
The bipartisan Nuclear Fuel Security Act (NFSA), introduced in the Senate last week, would authorize the Department of Energy to establish a Nuclear Fuel Security Program to “ensure a disruption in Russian uranium supply would not impact the development of advanced reactors or the operation of the United States’ light water reactor fleet.” The bill was introduced by Sen. Joe Manchin (D., W.V.), chairman of the Senate Energy and Natural Resources (ENR) Committee; Sen. John Barrasso (R., Wyo.), ranking member of the Senate ENR committee; and Sen. Jim Risch (R., Idaho).
Framatome’s GAIA fuel assembly with Protect EATF technologies. (Photo: Framatome)
Framatome has completed the second 18-month cycle of its GAIA Protect Enhanced Accident Tolerant Fuel (EATF) technology at Vogtle’s Unit 2 in Waynesboro, Ga. Inspections afterward revealed that the full-length chromium-coated fuel rods maintained their original characteristics, while the chromia-enhanced pellets operated as designed during 36 months of reactor operation.
The cover of the May 1977 issue of Nuclear News (left), an image of the story discussing Carter's decision to cancel the breeder reactor program (center) and the cover of the June 1977 Nuclear News (right).
The ANS Fuel Cycle and Waste Management Division will present a webinar today at noon EST (the recording will be available via the webinar archive to all ANS members) featuring an international panel of experts on nuclear waste reprocessing. The panel will explore the idea of separating certain radionuclides from waste using recycling technology that enables pure materials to be used for other purposes.
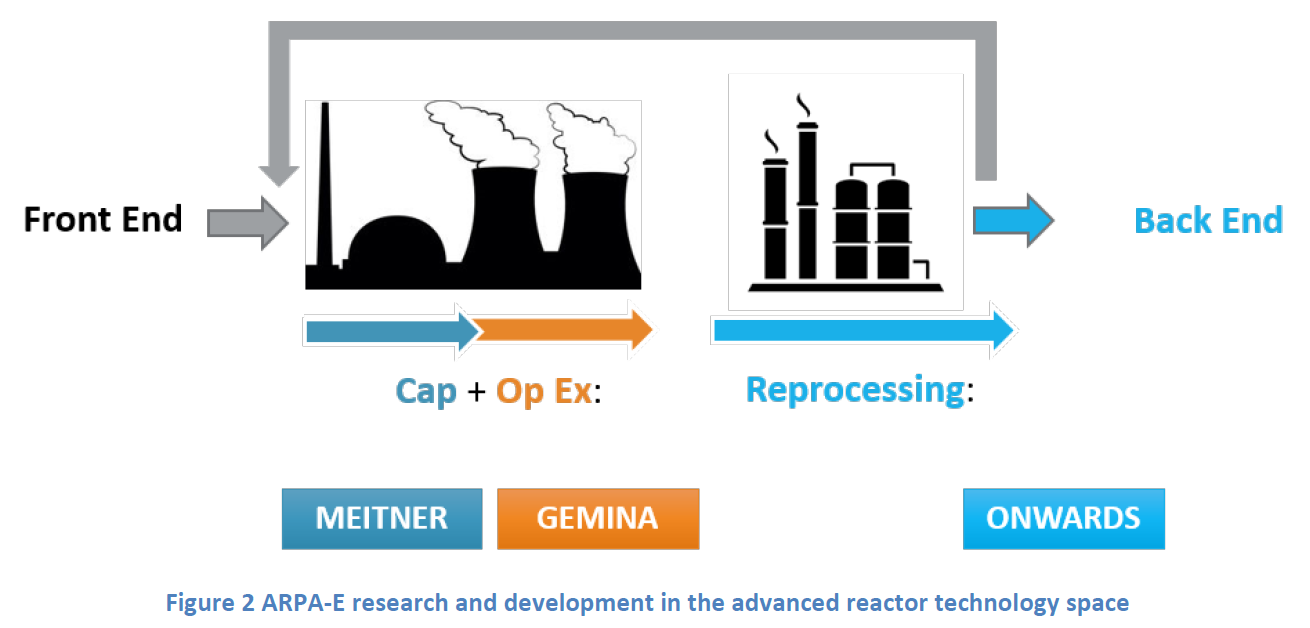
This figure, included in the ONWARDS funding opportunity announcement, shows how ARPA-E R&D programs address different stages of advanced reactor development. (Figure: ARPA-E)
The Department of Energy has announced up to $40 million in funding for a new Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy (ARPA-E) program to conduct research and development into technologies for reprocessing and ultimately disposing of used nuclear fuel. The program, “Optimizing Nuclear Waste and Advanced Reactor Disposal Systems” (ONWARDS), announced on May 19, targets both open (once-through) and closed (reprocessing) fuel cycles to reduce the amount of waste produced from advanced reactors tenfold when compared to light water reactors.