A rendering of the planned demo plant. (Image: General Fusion)
SHINE’s isotope production building, called the Chrysalis, under construction in October 2022.
In a former farm field just outside the historic town of Janesville in south-central Wisconsin, a large concrete-and-steel building is taking shape. Dubbed the Chrysalis, the building will eventually house eight accelerator-based neutron generators, which start-up company SHINE Technologies will use to produce molybdenum-99. As the precursor to the medical radioisotope technetium-99m, Mo-99 is used in tens of millions of diagnostic procedures every year, primarily as a radioactive tracer.
At the heart of the Chrysalis will be the high-flux neutron generators, being supplied by SHINE’s sister company, Phoenix. The compact accelerators use a deuterium-tritium fusion process to produce neutrons, which in turn induce a subcritical fission reaction in an aqueous low-enriched uranium target (19.75 percent uranium-235) to produce Mo-99.
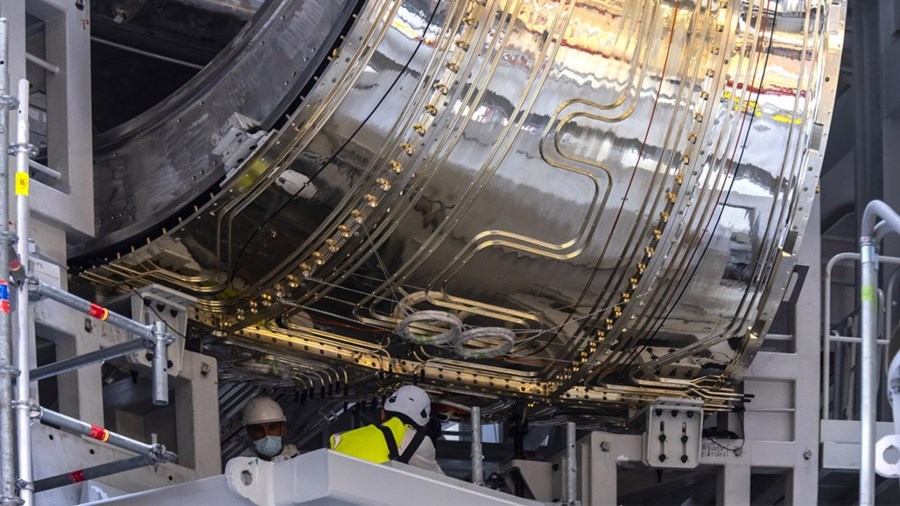
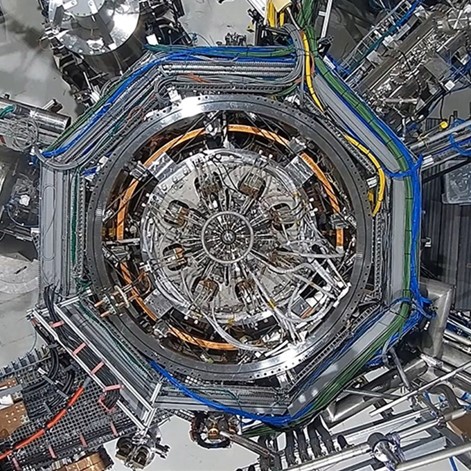
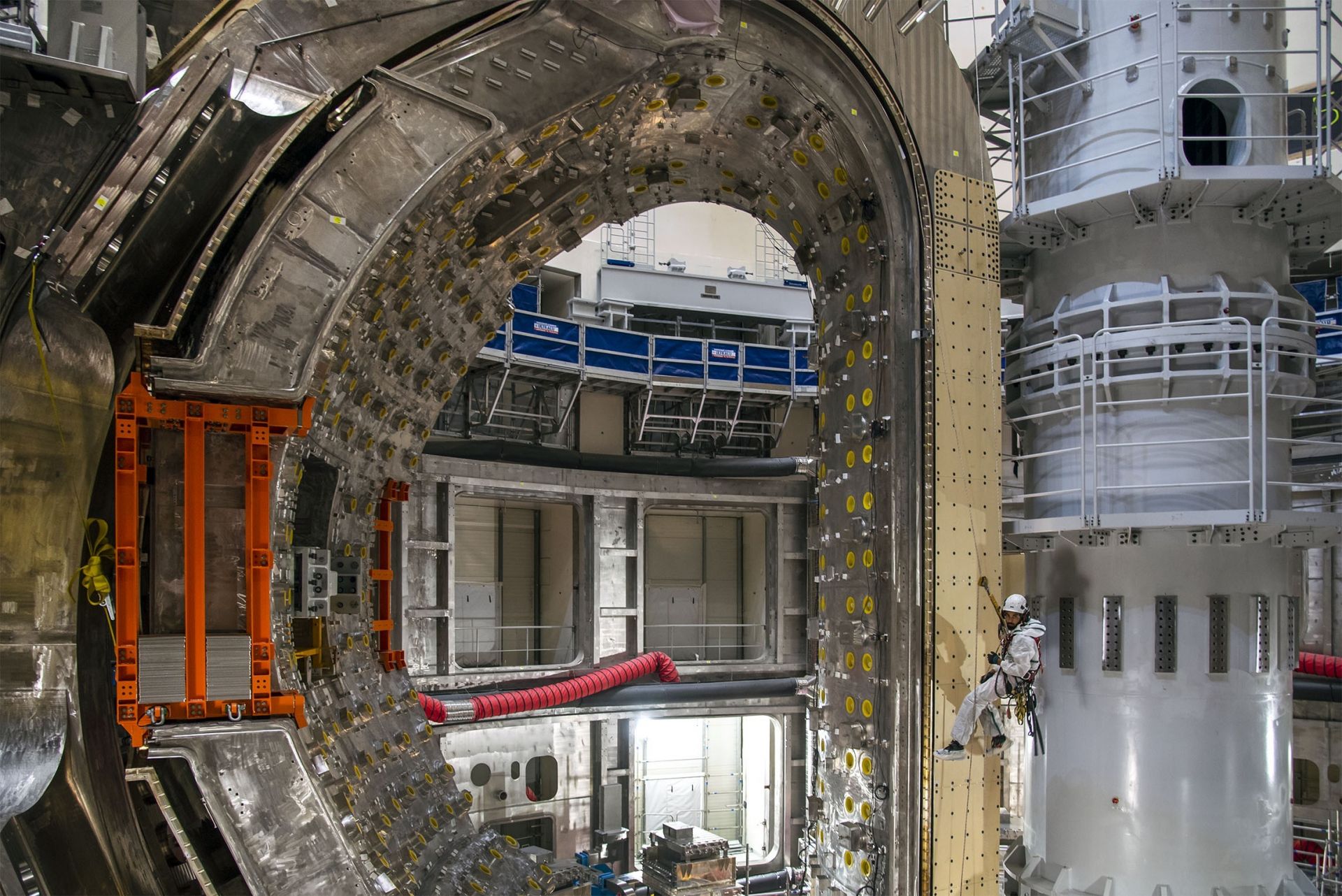
The cooling pipes that snake along the surface of the vacuum vessel thermal shield will be removed and replaced. Here, on a right-hand outboard panel, workers determine the impact of pipe removal on the surface of the component. (Photo: ITER Organization)
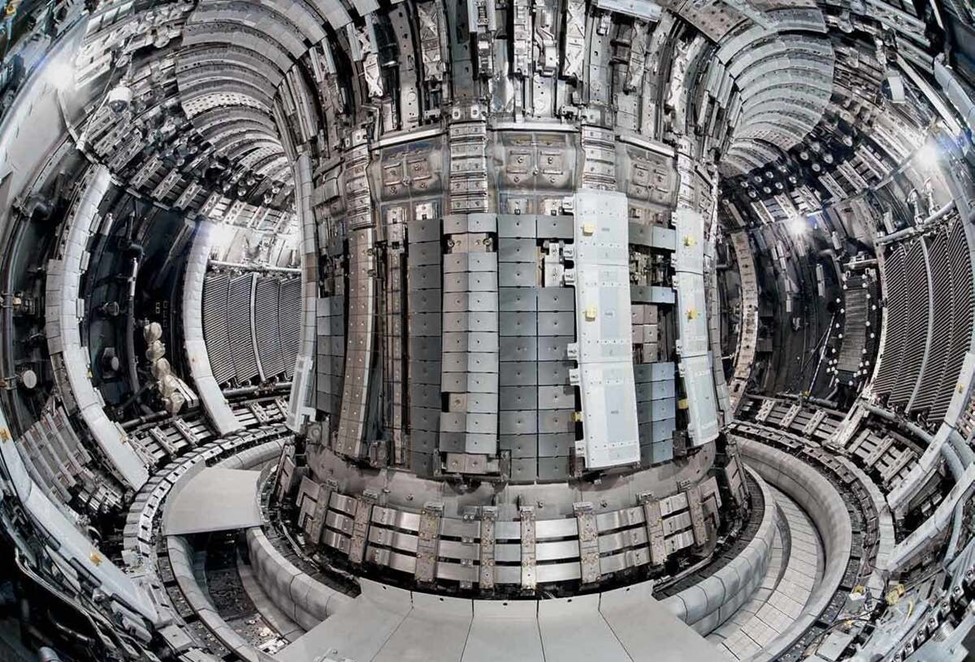
ITER’s machine assembly phase began about two and a half years ago. Now, staff are reversing some of that assembly work to make needed repairs. According to a news article published by the ITER Organization on January 9, ITER is “facing challenges common to every industrial venture involving first-of-a-kind components.” Over one year after problems were first detected and less than two months after they were made public in late November, tests and analysis are producing a clearer picture of necessary repairs to the tokamak’s thermal shield panels and vacuum vessel sectors.
“There is no scandal here,” said ITER director general Pietro Barabaschi. “Such things happen. I've seen many issues of the kind, and much worse.”
A color-enhanced image of the inside of a NIF preamplifier support structure. (Image: LLNL/Damien Jemison)
On December 5, researchers at the National Ignition Facility (NIF) at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory achieved fusion energy breakeven. It was a gain for stockpile stewardship that also—as headlines gushed prior to the Department of Energy’s December 13 announcement—boosted the prospects of inertial fusion energy (IFE). The timing of the landmark achievement may have been especially welcome to private fusion companies with inertial or hybrid magneto-inertial confinement concepts, because it occurred as the DOE was getting ready to consider applications for $50 million in funding for fusion pilot plant design work.
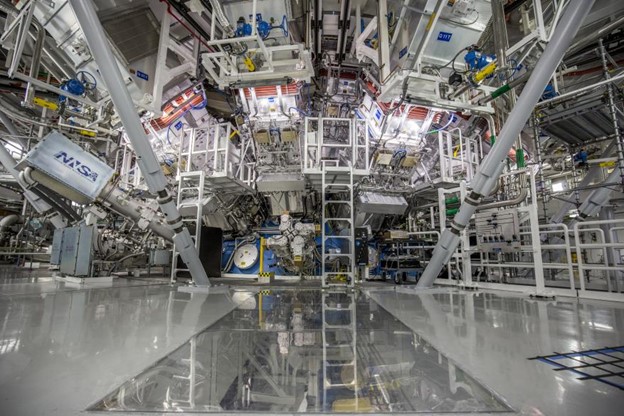
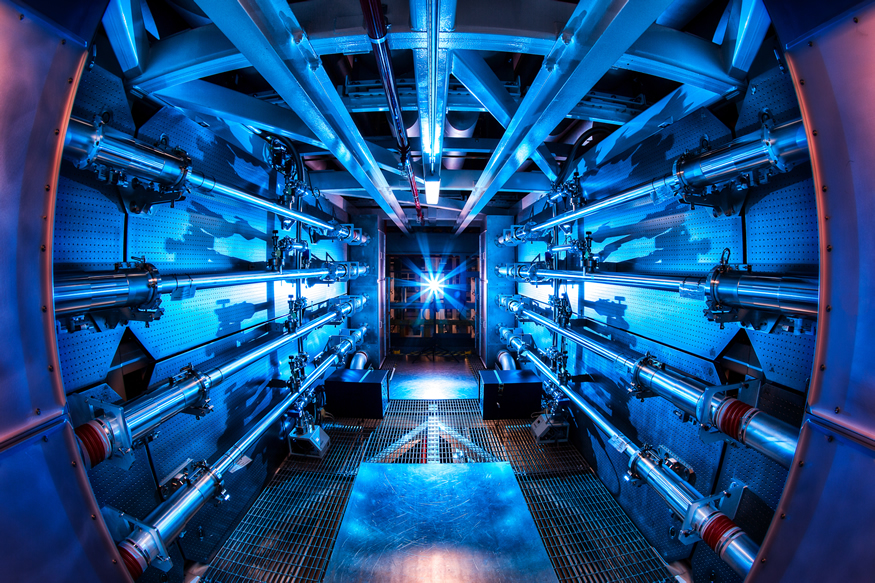
The target chamber of LLNL’s NIF, where 192 laser beams delivered more than 2 million joules of ultraviolet energy to a tiny fuel pellet to create fusion ignition on December 5, 2022.
It’s official: Early in the morning on December 5 at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s National Ignition Facility (NIF), the laser-triggered implosion of a meticulously engineered capsule of deuterium and tritium about the size of a peppercorn yielded, for the first time on Earth, more energy from a fusion reaction than was delivered to the capsule. The input of 2.05 megajoules (MJ) to the target heated the diamond-shelled, spherical capsule to over 3 million degrees Celsius and yielded 3.15 MJ of fusion energy output. The achievement was announced earlier today by officials and scientists representing the Department of Energy and its National Nuclear Security Administration, the White House, and LLNL during a livestreamed event.
A total of about 23 kilometers (about 14 miles) of piping are welded to the surface of the thermal shield panels. The piping on a vacuum vessel thermal shield panel is clearly visible in this photo. (Photo: ITER Organization)
The ITER Organization is working on a new baseline schedule for the magnetic confinement fusion experiment launched in 1985 and now under construction in southern France. First plasma was scheduled for December 2025 and deuterium-tritium operations for 2035 under a schedule approved in November 2016 that will soon be shelved. In addition to impacts from COVID-19 delays and uncertainty resulting from Russia’s war in Ukraine, ITER leaders must now factor in repair time for “component challenges.”
The JET tokamak. (Photo: European Consortium for the Development)
Nuclear fusion “might actually be on the cusp of commercial viability” today, says a recent article in Fortune magazine. The article offers a brief review of recent technical and entrepreneurial developments in fusion energy. It also places these developments in perspective regarding the hurdles that remain before commercialization can be realized.
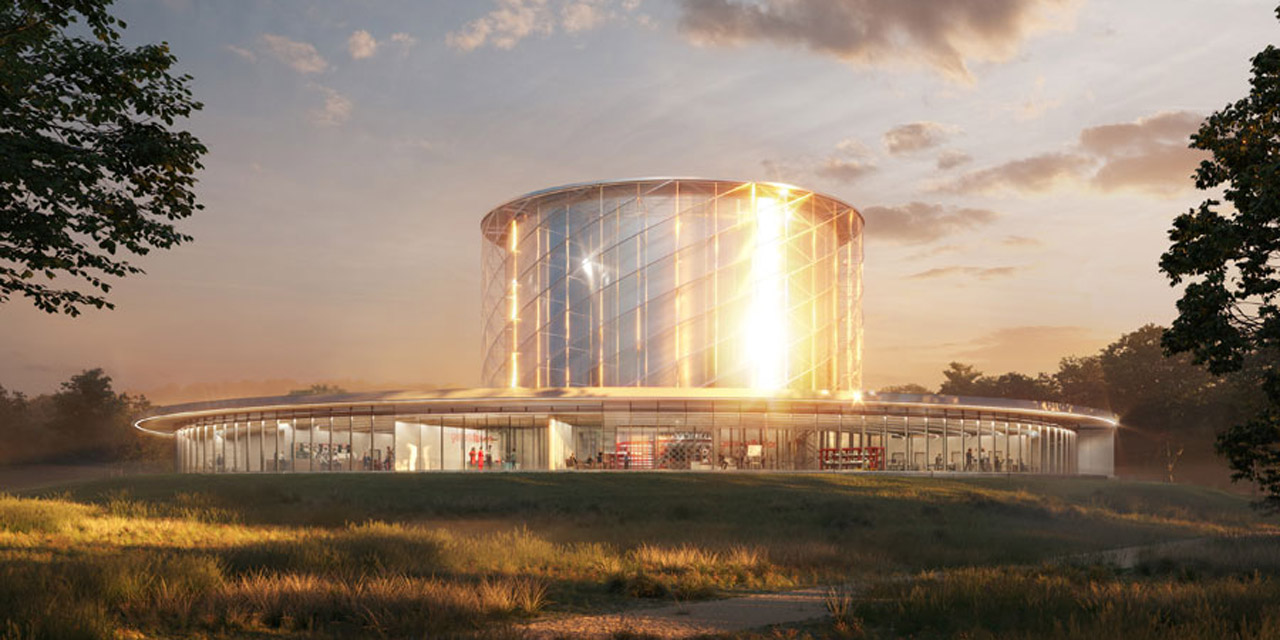
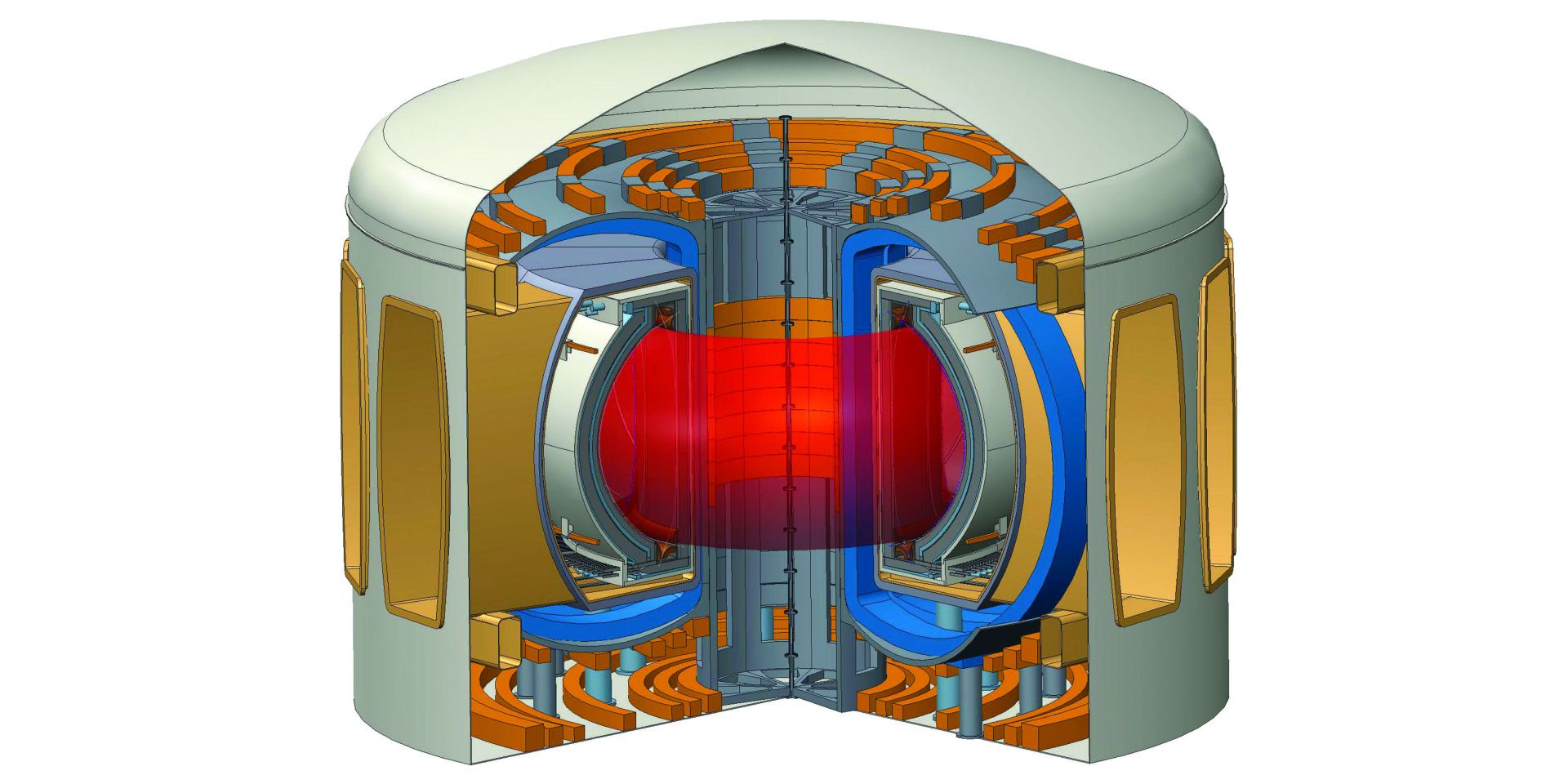
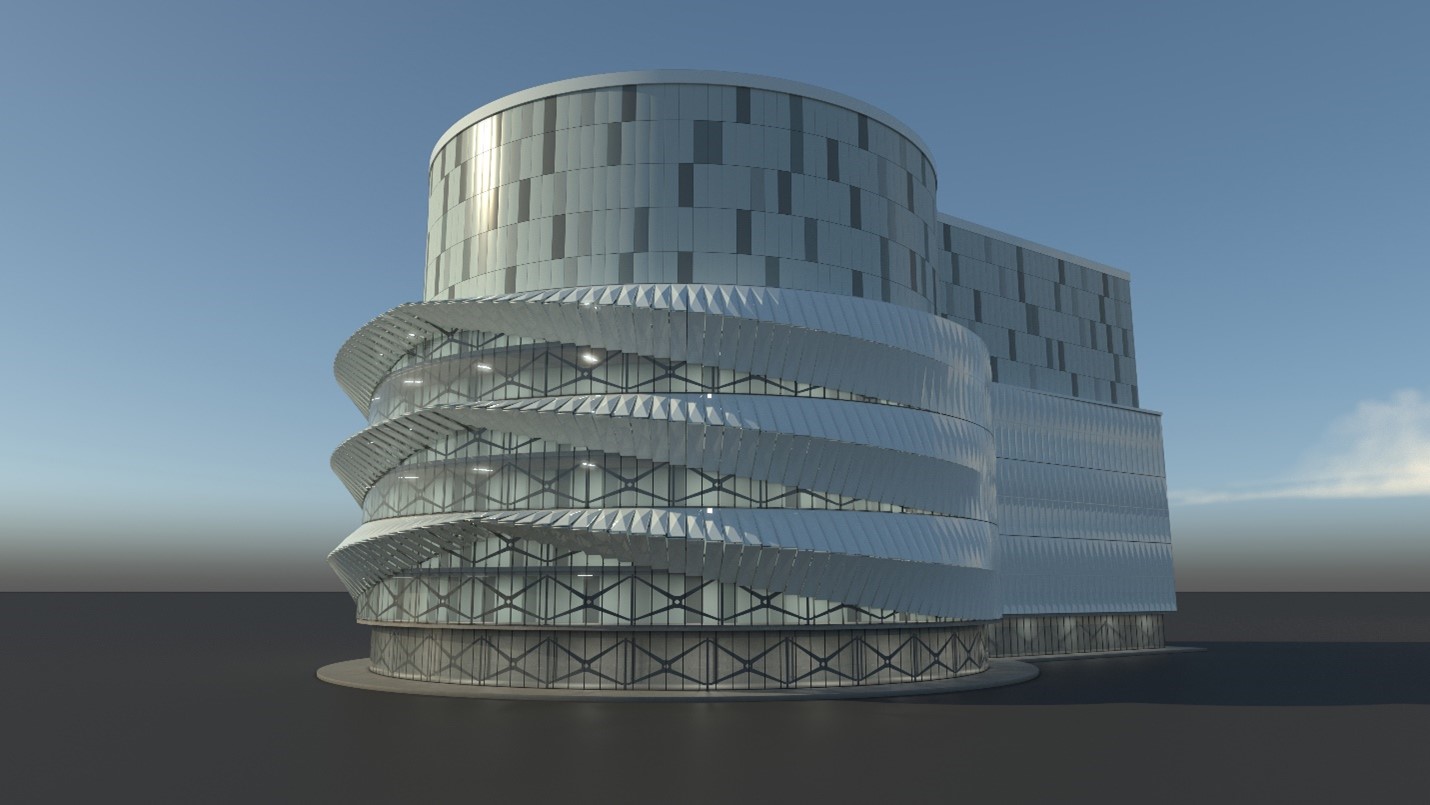
This still image, taken from a General Fusion video, depicts the demo plant that will be built near Oxford, U.K. (Image: General Fusion)
Canadian Nuclear Laboratories (CNL) and General Fusion have announced a memorandum of understanding (MOU) to “develop fusion energy research capabilities within CNL, to support the goal of constructing a potential General Fusion commercial power plant in Canada before 2030.” The plant would follow on a demonstration-scale plant that General Fusion wants to have operating in the United Kingdom by 2027 to validate the performance and economics of the technology.
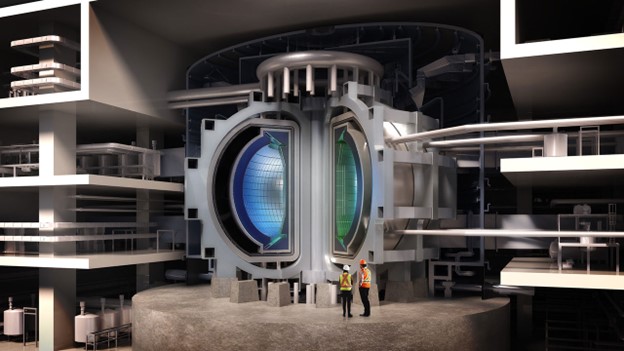
The U.S. ITER Project Office in Oak Ridge, Tenn. U.S. ITER has received $256 million in Inflation Reduction Act funding. (Photo: U.S. ITER)
Just days before COP27 and the U.S. midterm elections, the White House announced $1.55 billion in Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) funding for national laboratories and the launch of a Net-Zero Game Changers Initiative based on a new report, U.S. Innovation to Meet 2050 Climate Goals. Out of 37 research and development opportunities identified, fusion energy was selected as one of just five near-term priorities for the new cross-agency initiative. Together, the announcements signal policy and infrastructure support for fusion energy—the biggest chunk of Department of Energy Office of Science (DOE-SC) IRA funding went to ITER, via Oak Ridge National Laboratory—and for advanced nuclear technologies to power the grid and provide process heat to hard-to-decarbonize industrial sectors.
A rendering of the GA fusion pilot plant. (Image: GA)
General Atomics (GA) announced on October 20 that it has developed a steady-state, compact advanced tokamak fusion pilot plant concept “where the fusion plasma is maintained for long periods of time to maximize efficiency, reduce maintenance costs, and increase the lifetime of the facility.”
The Spherical Tokamak for Energy Production, shown here in an artist's rendition, is a government-backed prototype fusion energy plant planned for operation in the U.K. in the early 2040s. (Image: UKAEA)
The U.K. Atomic Energy Authority (UKAEA) and Tokamak Energy announced on October 10 that they signed a framework agreement to collaborate on developing spherical tokamaks for power production. This news is a complement to last week’s announcement from the U.K. government that the West Burton A coal-fired power plant site in Nottinghamshire has been selected as the future home of STEP (Spherical Tokamak for Energy Production), the U.K.’s planned prototype fusion energy plant. The government is providing £220 million (about $250 million) of funding for the first phase of STEP, which will see the UKAEA produce a concept design by 2024.
(Image: Ana Kova /USFusionEnergy.org)
The Department of Energy announced up to $50 million for a new milestone-based fusion energy development program on September 22. The funding opportunity announcement is open to for-profit companies—possibly teamed with national laboratories, universities, and others—that are prepared to meet major technical and commercialization milestones leading to a pilot fusion power plant design.
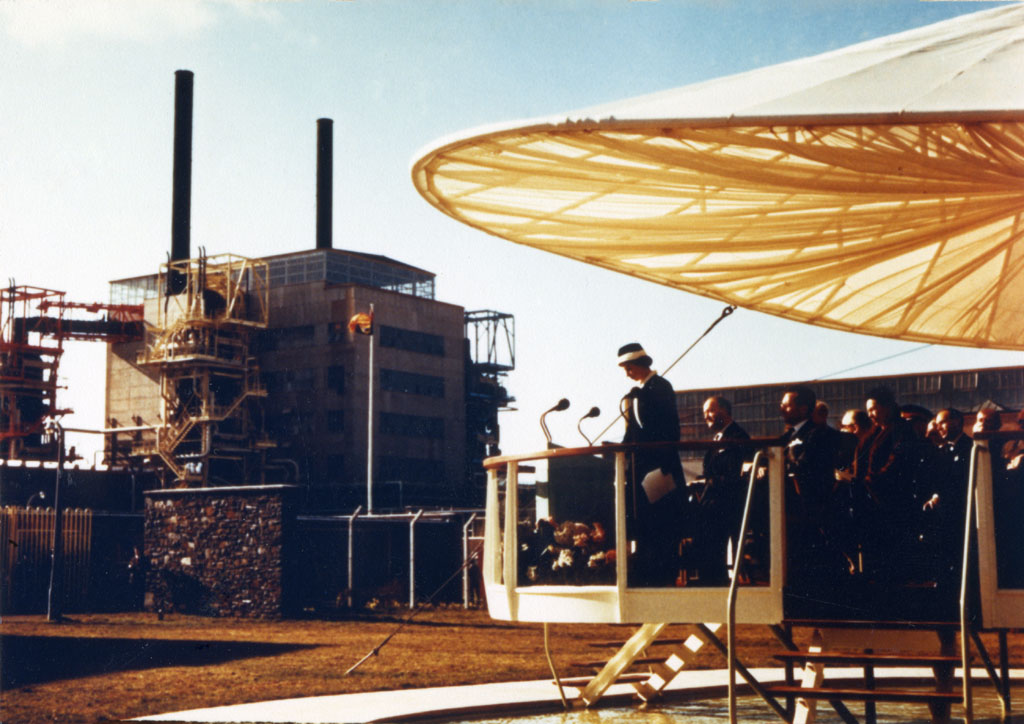
Queen Elizabeth II visits Calder Hall for its ceremonial opening in 1956. (Photo: U.K. Nuclear Decommissioning Authority)
As citizens of the United Kingdom and others around the world mourn the death of Queen Elizabeth II, many have reflected on how the world has changed during the seven decades of the queen’s reign—the same decades that saw the rise of civilian nuclear power.
Calder Hall was already under construction at the Sellafield site in West Cumbria when Princess Elizabeth became queen in 1953. Queen Elizabeth traveled to the site in October 1956 and declared, in a televised ceremony, that “It is with pride that I now open Calder Hall, Britain’s first atomic power station.” Watch the fanfare in a historical clip uploaded to YouTube by Sellafield Ltd below.
The first sector of the ITER vacuum vessel was placed in the assembly pit in May. Here, a technician positions targets on the surface of the component to be used in laser metrology. (Photo: ITER Organization)
Delivery of electricity from fusion is considered by the National Academies of Engineering to be one of the grand challenges of the 21st century. The tremendous progress in fusion science and technology is underpinning efforts by nuclear experts and advocates to tackle many of the key challenges that must be addressed to construct a fusion pilot plant and make practical fusion possible.
A stylized image of a cryogenic target used in NIF experiments. (Image: James Wickboldt/LLNL)