Rep. Jeff Duncan (Image: House.gov)
At a legislative markup session last week, a House Energy and Commerce subcommittee approved 17 energy bills for consideration by the full E&C committee, including 12 measures to boost and streamline the deployment of nuclear power. The nuclear-related bills cleared the subcommittee by voice vote with bipartisan support.
“Our shared goal in this committee is to advance bipartisan, durable policy that will expand nuclear energy and its benefits for the nation,” said Rep. Jeff Duncan (R., S.C.), chair of the E&C’s Energy, Climate, and Grid Security Subcommittee, in his opening remarks on October 24. “Chair Rodgers, ranking members Pallone and DeGette, and I sent a bipartisan request for information to a variety of stakeholders this past April. Based on feedback from this request and the hearings we’ve had since, it’s clear that more can be done to modernize the Nuclear Regulatory Commission and Department of Energy to advance nuclear energy in this country.”
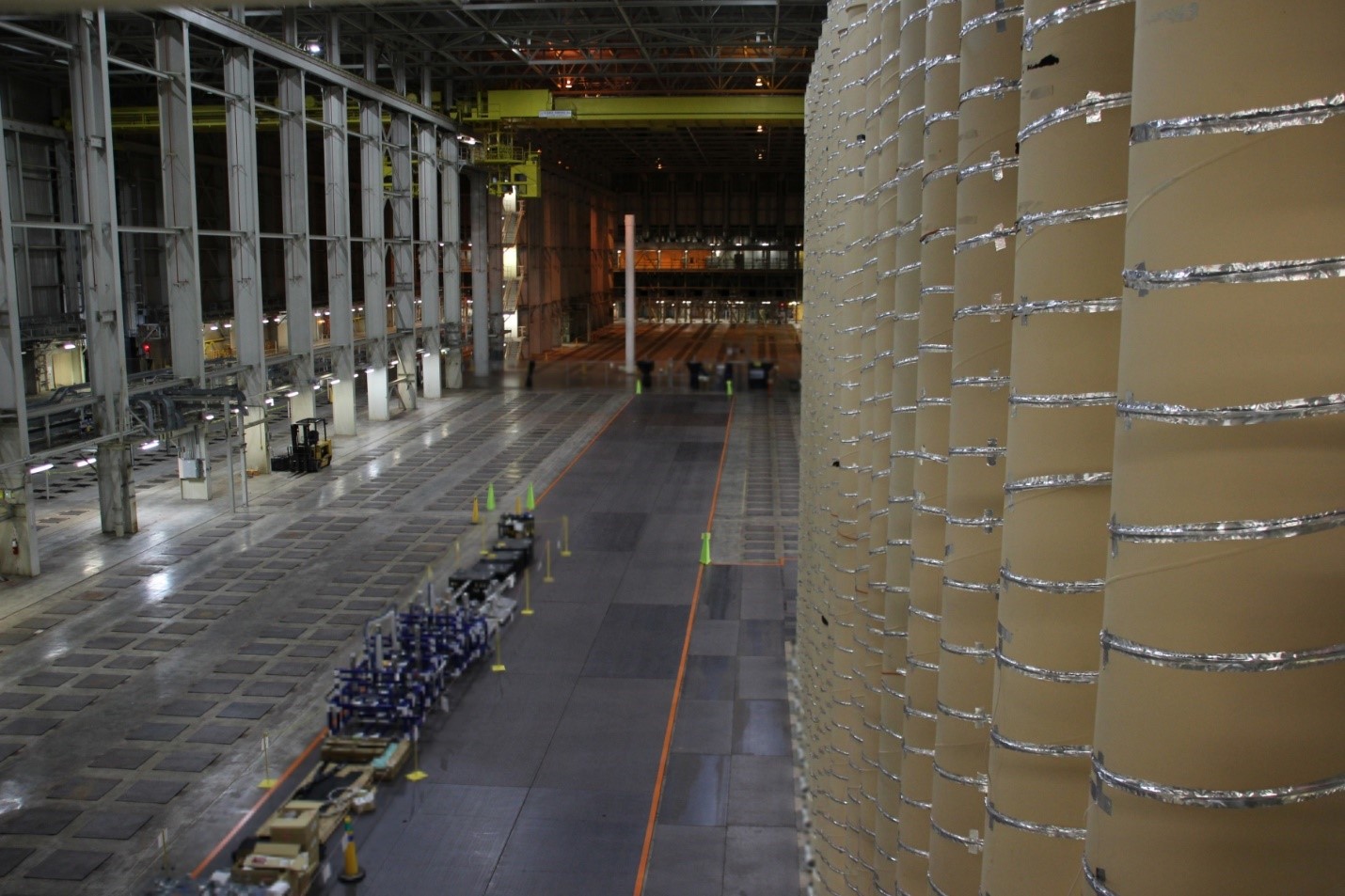
The 16-centrifuge HALEU demonstration cascade sits within a vast DOE-owned facility with room for more than 11,000 centrifuges. (Photo: Centrus)
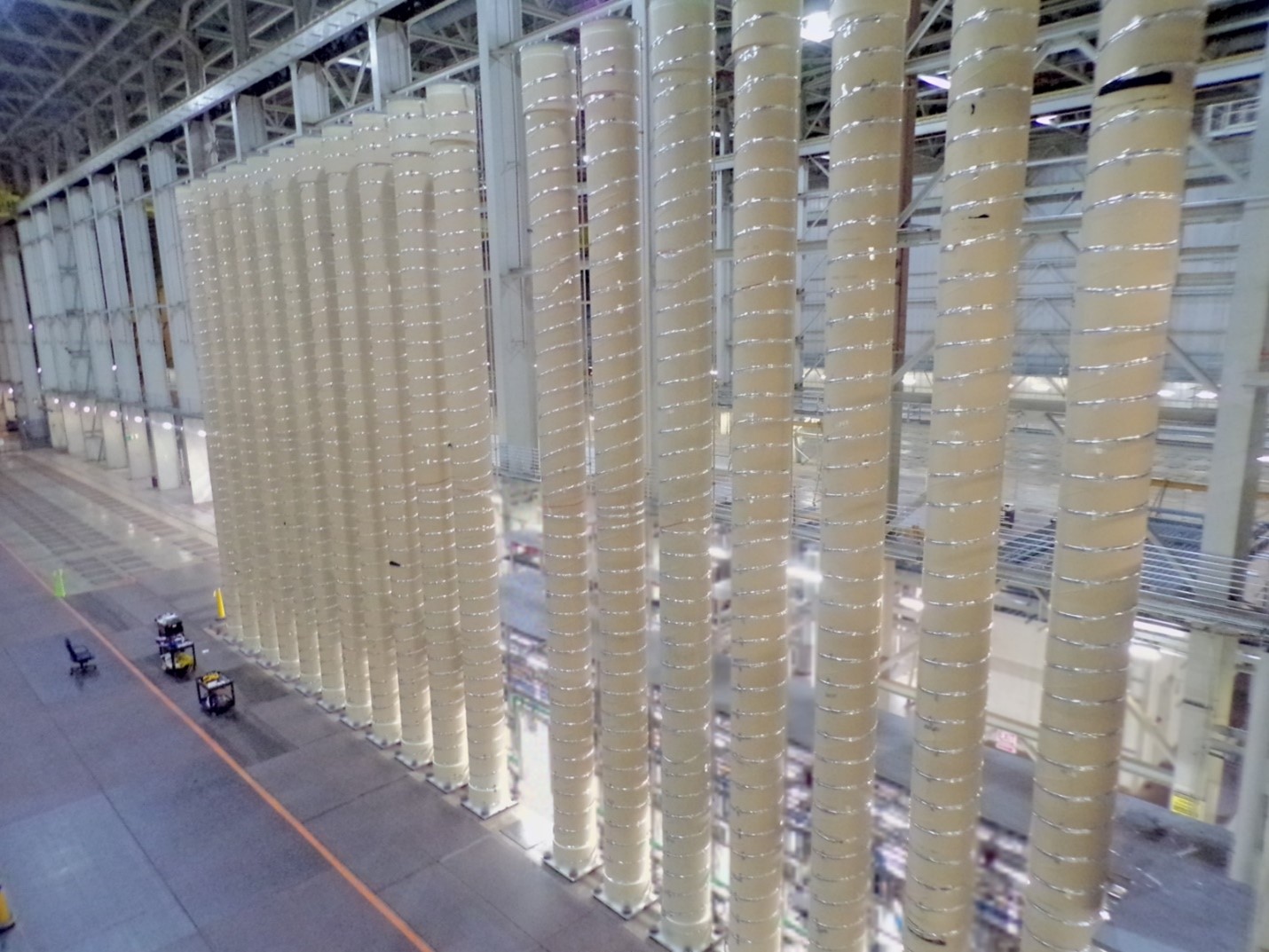
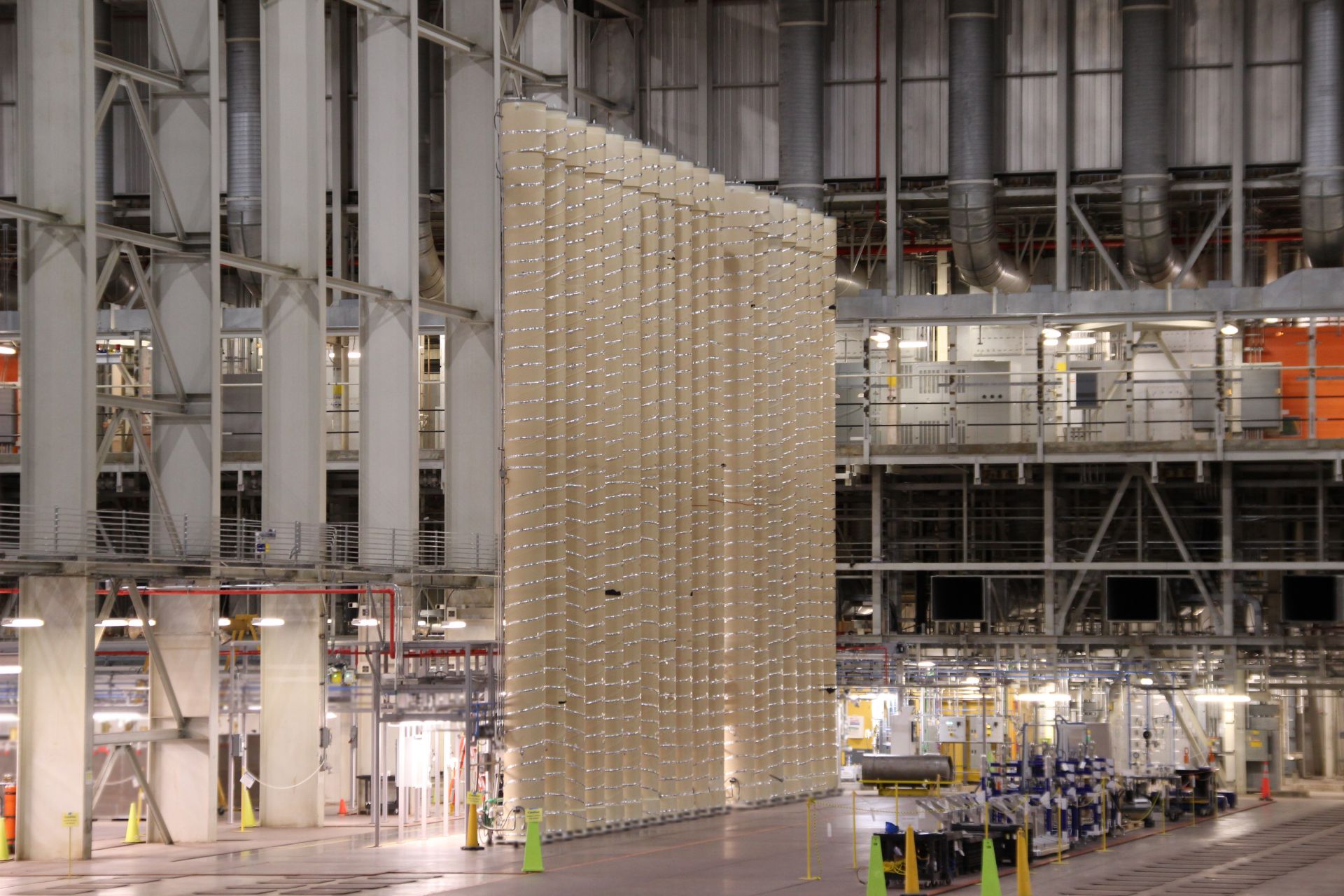
American Centrifuge Operating (ACO), a subsidiary of Centrus Energy, has started enriching uranium hexafluoride gas to high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU) levels at the Department of Energy’s enrichment facility in Piketon, Ohio, the DOE announced October 11. The HALEU will be used to help fuel the initial cores of two demonstration reactors awarded under DOE’s Advanced Reactor Demonstration Program and will also support fuel qualification and the testing of other new advanced reactor designs.
Upper-level view of Centrus’s HALEU cascade. (Photo: Centrus Energy)
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission is requesting comments on the regulatory basis for a proposed rule for light water reactor fuel designs featuring high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU), including accident tolerant fuel (ATF) designs, and on draft guidance for the environmental evaluation of ATFs containing uranium enriched up to 8 percent U-235. Some of the HALEU feedstock for those LWR fuels and for advanced reactor fuels could be produced within the first Category II fuel facility licensed by the NRC—Centrus Energy’s American Centrifuge Plant in Piketon, Ohio. On September 21, the NRC approved the start of enrichment operations in the plant’s modest 16-machine HALEU demonstration cascade.
The site in Piketon, Ohio, where Oklo plans to deploy two microreactors under an agreement with Southern Ohio Diversification Initiative. (Photo: Oklo)
Oklo Inc. and Centrus Energy announced a new memorandum of understanding on August 28 to support the deployment of Oklo’s microreactor design, dubbed Aurora, near the Piketon, Ohio, site where Centrus plans to operate a high-assay, low-enriched uranium (HALEU) enrichment demonstration under contract to the Department of Energy by the end of the year.
An artist’s rendering of Natrium. (Image: TerraPower)
Advanced nuclear technology firm TerraPower announced today the selection of four suppliers to support its Natrium reactor demonstration project, in development near a retiring coal plant in Kemmerer, Wyo.
View of the machine controls electronics of Centrus’s HALEU demonstration cascade. (Photo: Centrus)
TerraPower and Centrus Energy Corp. announced on July 17 that they have signed a memorandum of understanding to “significantly expand their collaboration aimed at establishing commercial-scale, domestic production capabilities for high-assay, low-enriched uranium (HALEU)” to supply fuel for TerraPower’s first Natrium reactor. Nearly three years ago, TerraPower first announced plans to work with Centrus to establish commercial-scale HALEU production facilities. The two companies signed a contract in 2021 for services to help expedite the commercialization of enrichment technology at Centrus’s Piketon, Ohio, facility.
Pictured, from left, are Steve Nesbit, Christina Leggett, John Kessler, Paul Dickman, John Mattingly, and Craig Hansen. Edwin Lyman, who joined the panel remotely, is not pictured.
Advanced reactors may be key to a clean energy future, but to prove it they’re going to need fuel—and that fuel will be derived from limited uranium resources and managed throughout the nuclear fuel cycle, whether that cycle is open (like the current fuel cycle) or closed (with reprocessing). Six panelists convened on June 12 during the Annual Meeting of the American Nuclear Society for the executive session “Merits and Viability of Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles: A Discussion with the National Academies.” They discussed those fuel cycles and the findings of a National Academies of Science, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM) consensus committee released as a draft report in November 2022 and published earlier this year.