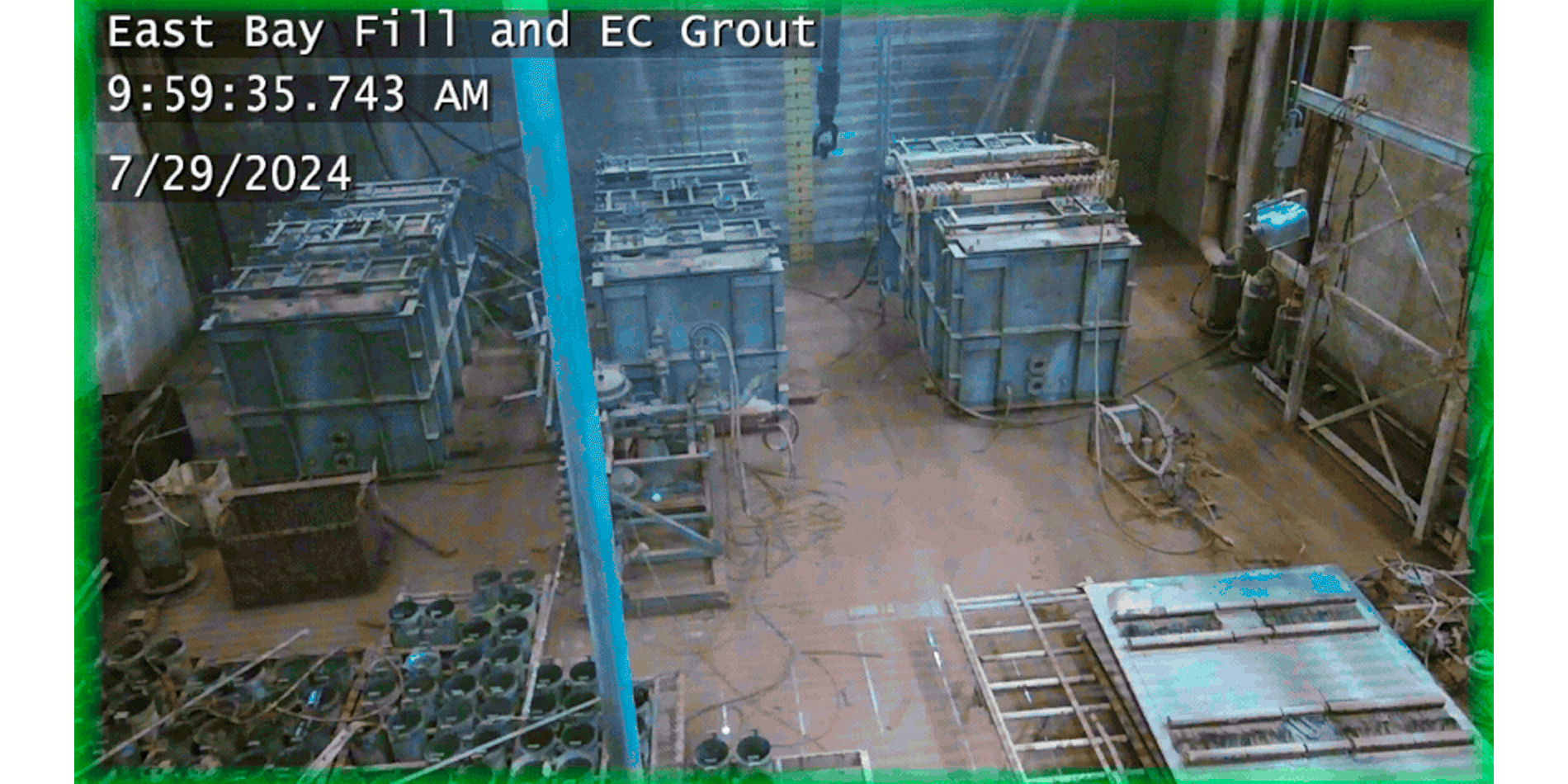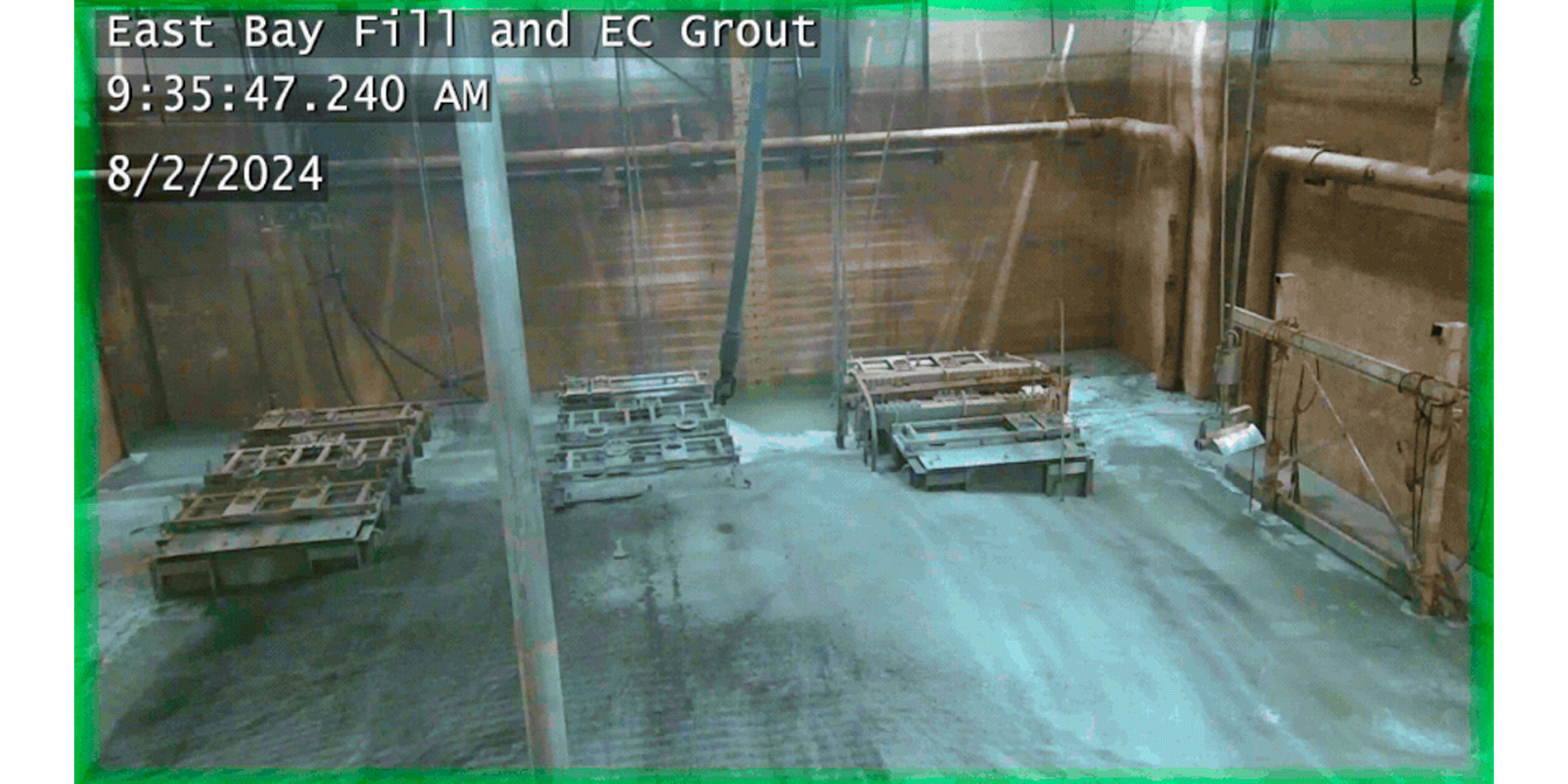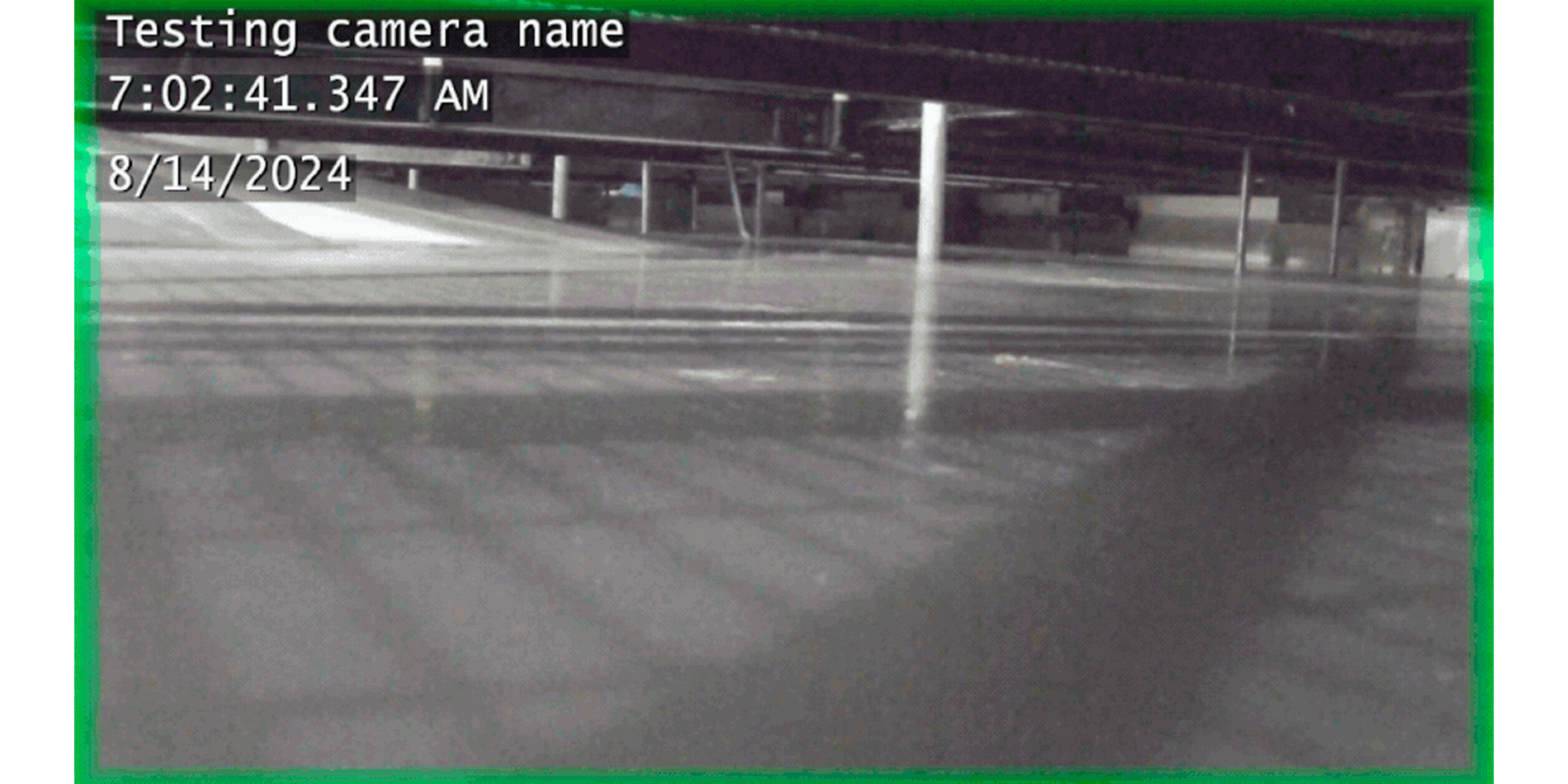
Demolition work being conducted on Hanford’s REDOX facility in July 2024. (Photo: DOE)
Work to prepare Hanford’s Reduction Oxide Plant (REDOX) for decontamination and demolition has been put on hold as the Department of Energy shifts focus to higher-priority work at the nuclear site in Washington state.
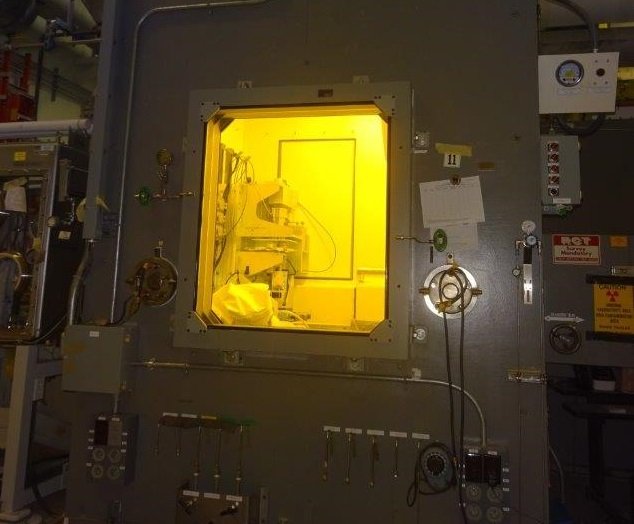
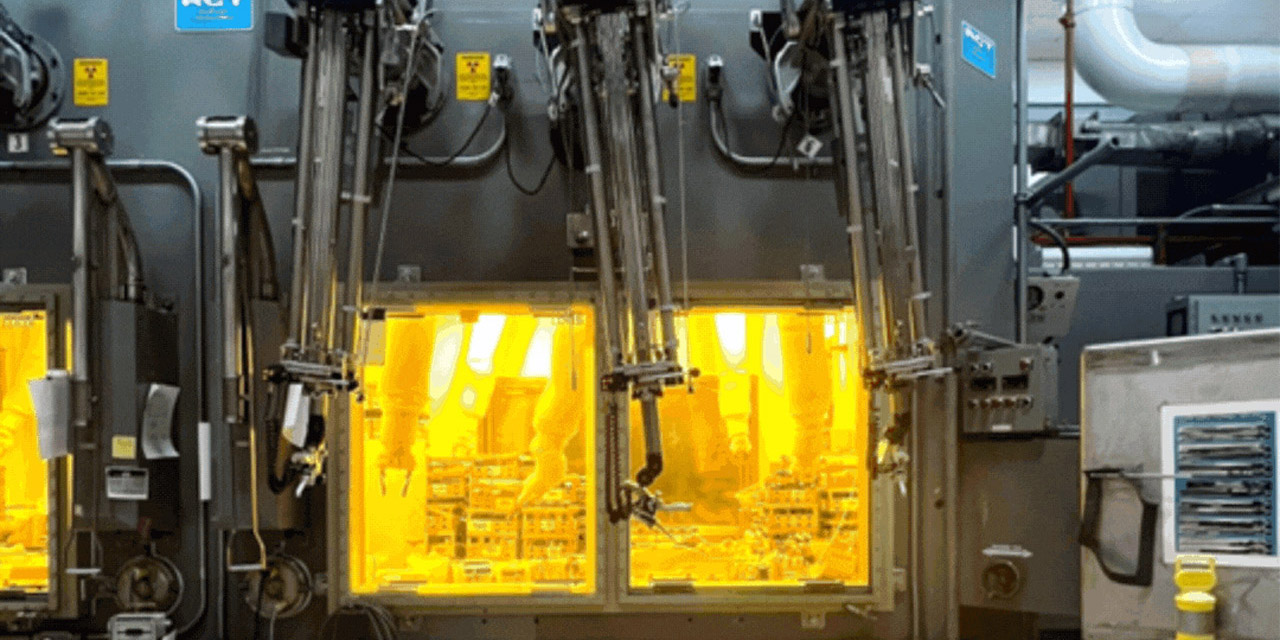
Workers recently completed an 18-month project replacing 11 hot cell windows at the 222-S Laboratory at the Department of Energy’s Hanford Site in Washington state. Hanford contractor Navarro-ATL manages the lab.
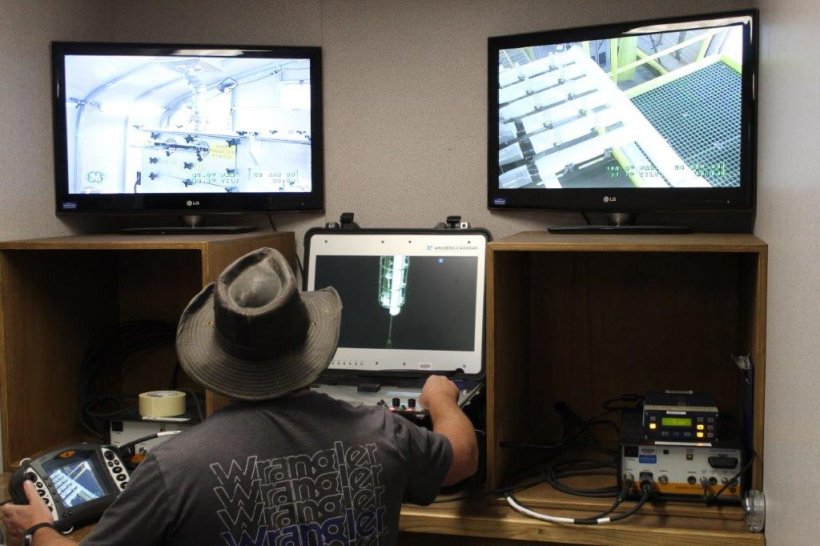
Using cameras placed inside a temporary shelter, nuclear chemical operator Joe McCoy monitors the pretreatment activities of the Hanford Site’s TBI demonstration. (Photo: DOE-EM)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management said that contractors have completed the treatment of 2,000 gallons of radioactive and chemical waste as part of the Hanford Site’s Test Bed Initiative project, which aims to demonstrate the feasibility of alternative options for retrieving and treating low-activity tank waste at the site in Washington state.
Hanford’s Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant, also known as the Vit Plant. (Photo: Bechtel National)
BWX Technologies announced that the Department of Energy has approved Hanford Tank Waste Operations & Closure (H2C) to begin work under a contract valued at up to $45 billion to clean up tank waste at the Hanford Site near Richland, Wash. H2C is a limited liability company made up of BWXT Technical Services Group, Amentum Environment and Energy, and Fluor Federal Services.
The Hanford Field Office leadership team gathers around a new sign at the Stevens Center Complex in Richland, Wash., on October 1. (Photo: DOE)
Beginning last week, the two Department of Energy offices responsible for the environmental cleanup of the department’s Hanford Site have been combined under a new name: the Hanford Field Office. Previously, management of the 586-square-mile site near Richland, Wash., was split between the Richland Operations Office and the DOE Office of River Protection (ORP).
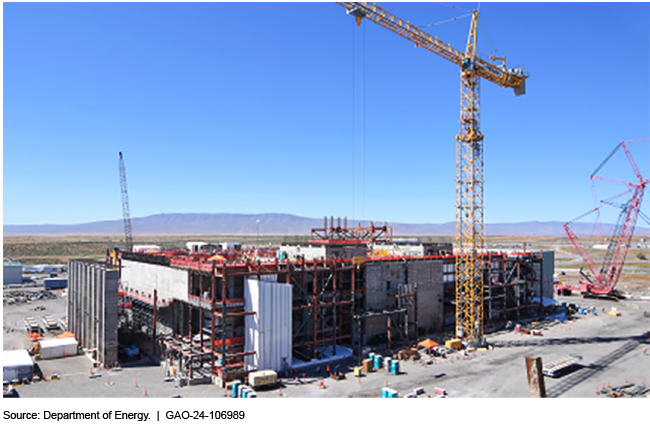
Hanford’s HLW Facility under construction in early 2024. (Photo: Bechtel National)
The Government Accountability Office has recommended that the Department of Energy put a hold on construction of its High-Level Waste Facility at the Hanford Site near Richland, Wash. The GAO said design and construction of the facility, part of Hanford’s Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant, also known as the Vit Plant, should be paused until several actions are taken, including considering other alternatives for managing the site’s high-level radioactive liquid waste.
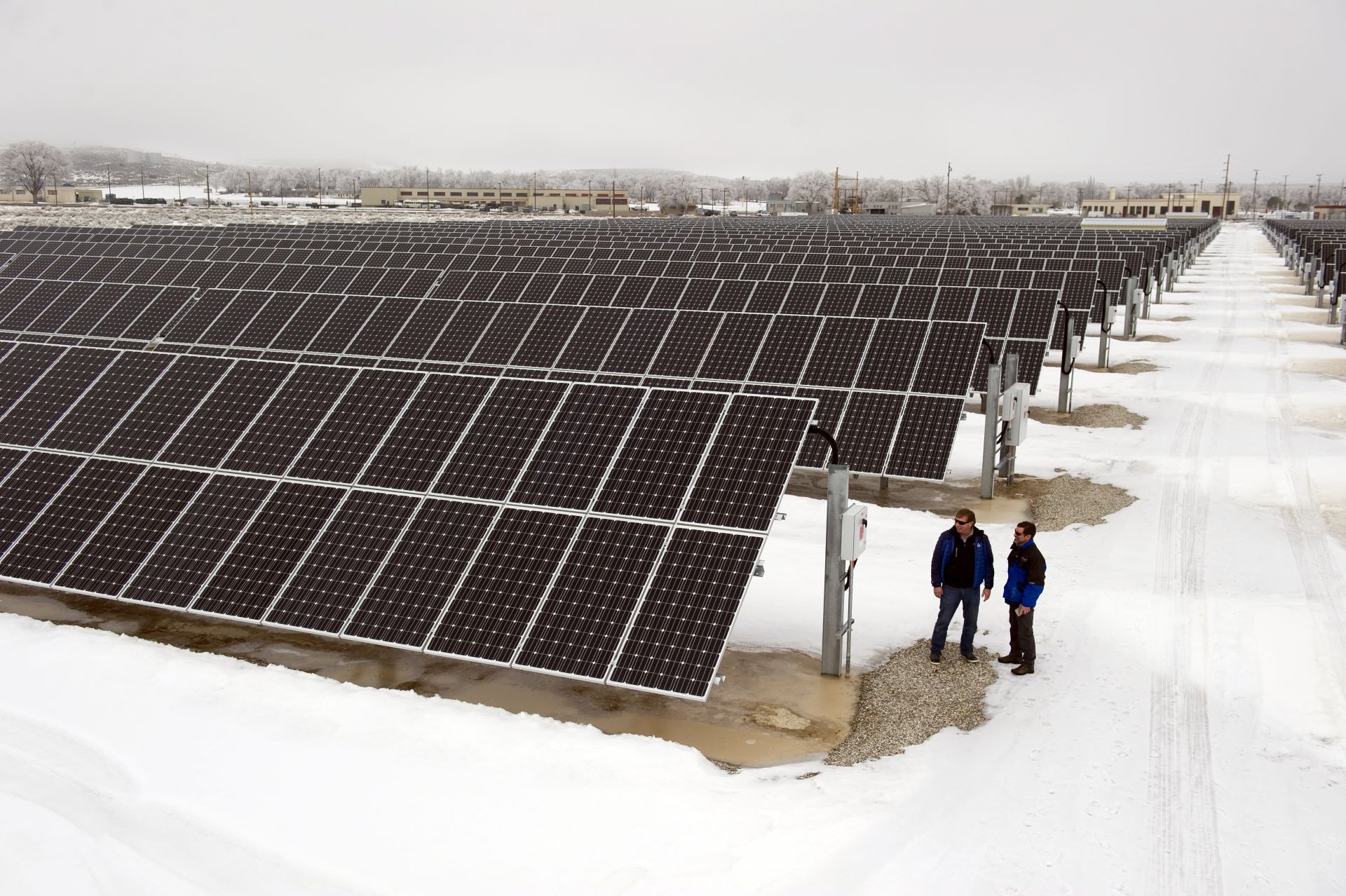
Idaho National Laboratory employees consult on a microgrid at Utah’s Dugway Proving Ground. Two solar projects were selected for development on INL land. (Photo: INL)
On July 28, 2023, the Department of Energy launched its Cleanup to Clean Energy initiative, an effort to repurpose underutilized DOE-owned property—portions of which were previously used in the nation’s nuclear weapons program—into the sites of clean-energy generation.
Hanford workers recently transferred three containers of nonradioactive test glass from the site’s WTP to the nearby Integrated Disposal Facility. (Photos: DOE)
According to the Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management, two contractors at its Hanford Site in Washington state have finished a first-time relay of test glass as the site prepares to vitrify—or immobilize in glass—millions of gallons of radioactive and chemical waste from its large underground tanks.
Video: Watch an “instant replay” of the test glass relay here.
Work begins on the TBI demonstration at the Hanford Site, during which 2,000 gallons of low-activity waste will be treated and shipped off-site for disposal. (Photo: DOE)
The Energy Communities Alliance (ECA), which advocates for communities adjacent to or impacted by Department of Energy sites, is asking the department to conduct an independent analysis evaluating the impacts of delaying the implementation of its statutory interpretation of high-level radioactive waste, which holds that some waste from the reprocessing of spent nuclear fuel may be classified as non-HLW.
This series of photos shows the grouting of the K West Reactor spent fuel storage basin. Workers removed nearly 1 million gallons of contaminated water before filling the 16-foot-deep basin with about 6,500 cubic yards of grout—enough to fill two Olympic-size swimming pools. (Images: DOE)
Workers at the Department of Energy’s Hanford Site in Washington state recently finished filling the last large concrete basin at the K Reactor Area with cement-like grout. The basin stored reactor fuel rods from historic plutonium production in the 1950s.
A June 2024 photo shows solid waste inside the single-shell Tank A-101 at the Hanford Site’s A Tank Farm. (Photo: DOE)
Work crews have started retrieval of radioactive and chemical waste from a third set of underground storage tanks at the Hanford Site, according to the Department of Energy's Office of Environmental Management. Contractor Washington River Protection Solutions (WRPS) is retrieving and transferring more than 325,000 gallons of waste from the single-shell Tank A-101 at the site's A Tank Farm. The waste is being sent to a newer double-shell tank for continued safe storage.
Retrieval activities began one month after workers emptied the site’s 21st single-shell tank. Waste removed from the 21 tanks totals about 3 million gallons.
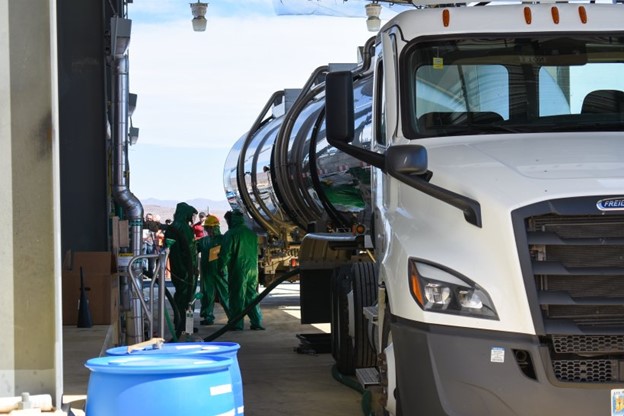
Workers at the Hanford Site’s WTP unload a tanker truck carrying sodium hydroxide. (Photo: DOE)
Workers at the Department of Energy’s Hanford Site in Washington state recently unloaded a shipment of more than 10,000 gallons of sodium hydroxide delivered to the site’s Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant (WTP). The liquid sodium hydroxide will be the first chemical fed into the plant’s melters to simulate Hanford’s radioactive and chemical tank waste.
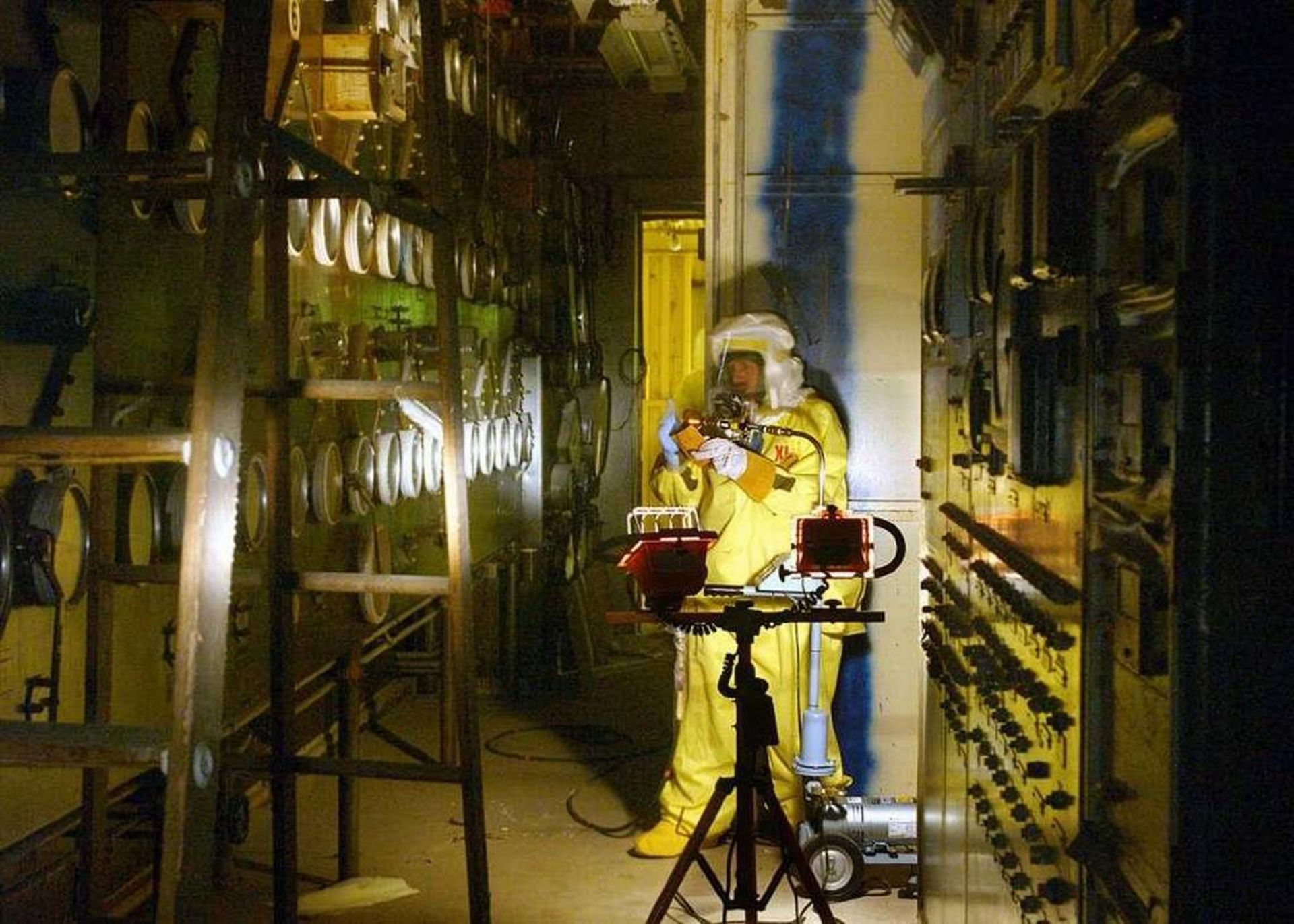
The radiochemistry laboratory, nicknamed the McCluskey Room, in the Hanford Site’s Plutonium Finishing Plant is where Harold McCluskey was contaminated in 1976, and where workers reentered more than 40 years later to clean up the mess left over from that accident. Health physics technician Clay Rowan is shown here taking radiological measurements near racks of glove boxes similar to one that exploded onto McCluskey. (Photo: DOE)
In 1976 at the Hanford Site in Washington state, a 64-year-old chemical operations technician named Harold McCluskey was working on columns filled with special exchange resins in a glove box at the Plutonium Finishing Plant.
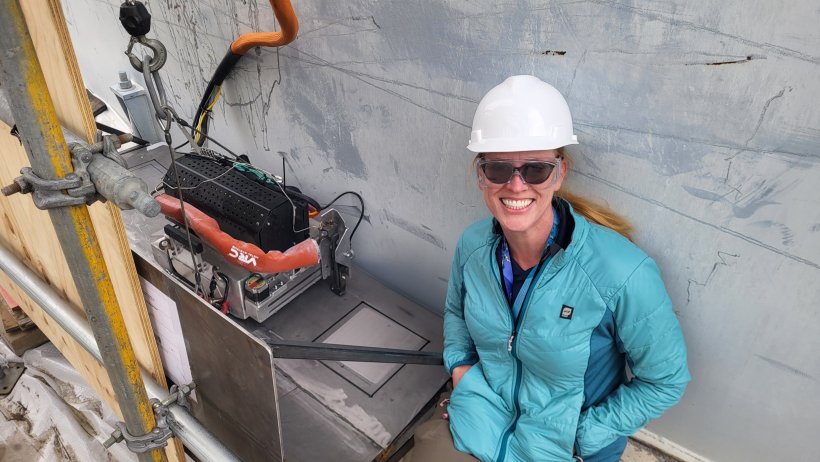
Stephanie Doll of WRPS poses next to the metal patch applied during the demonstration. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management and its contractor Washington River Protection Solutions (WRPS) recently demonstrated the use of cold spray technology as a means of refurbishing double-shell waste tanks at the Hanford Site in Washington state. The tanks store liquid radioactive and chemical waste that was created during Hanford’s plutonium production era.
Lourdes Legaspi, engineering automation supervisor (center) and her team are designing pipe and equipment components for the Hanford Site’s partially completed HLW Facility. A collaboration between the DOE and Bechtel National set a foundation for requirements engineers will follow in continuing the design of the facility. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management announced that its Office of River Protection (ORP) recently created a plan with contractor Bechtel National for completing the High-Level Waste Facility at the Hanford Site’s Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant, also known as the Vit Plant.
Hanford’s Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant, also known as the Vit Plant. (Photo: Bechtel National)
Researchers at the Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory are investigating the details of plutonium chemistry with the goal of aiding the cleanup of the Hanford Site in Washington state. For more than 40 years, reactors located at Hanford produced plutonium for America’s defense program, resulting in millions of gallons of liquid radioactive and chemical waste.
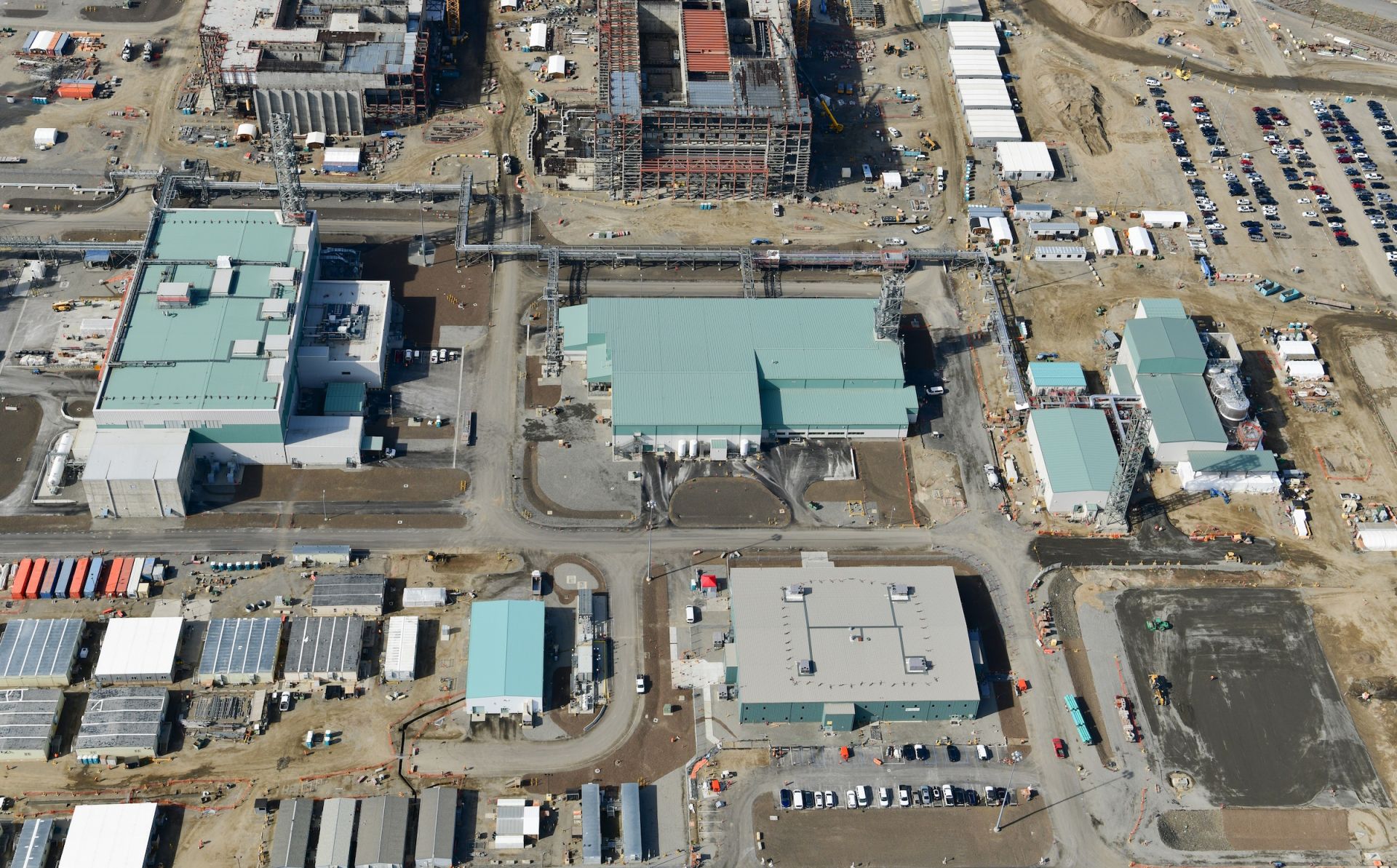
An aerial view of the Hanford Site’s 200 Area and the Waste Treatment and Immobilization Plant, also known as the Vit Plant. (Photo: DOE)
The U.S. Department of Energy, Washington State Department of Ecology, and U.S. Environmental Protection Agency have reached an agreement on revised plans for managing millions of gallons of radioactive and chemical liquid waste stored in 177 underground tanks at the Hanford Site near Richland, Wash.
A partnership between Washington River Protection Solutions (WRPS) and Washington State University has resulted in the development of a device to measure radioactive and chemical tank waste at the Hanford Site. WRPS is the contractor at Hanford for the Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management.

The mission of the Department of Energy’s Office of River Protection (ORP) is to complete the safe cleanup of waste resulting from decades of nuclear weapons development. One of the most technologically challenging responsibilities is the safe disposition of approximately 56 million gallons of radioactive waste historically stored in 177 tanks at the Hanford Site in Washington state.
ORP has a clear incentive to reduce the overall mission duration and cost. One pathway is to develop and deploy innovative technical solutions that can advance baseline flow sheets toward higher efficiency operations while reducing identified risks without compromising safety. Vitrification is the baseline process that will convert both high-level and low-level radioactive waste at Hanford into a stable glass waste form for long-term storage and disposal.
Although vitrification is a mature technology, there are key areas where technology can further reduce operational risks, advance baseline processes to maximize waste throughput, and provide the underpinning to enhance operational flexibility; all steps in reducing mission duration and cost.
Upgrades are under way at the Hanford Site's 222-S Laboratory, including replacing the Cold War-era windows in the labs hot cells. Photo: DOE)