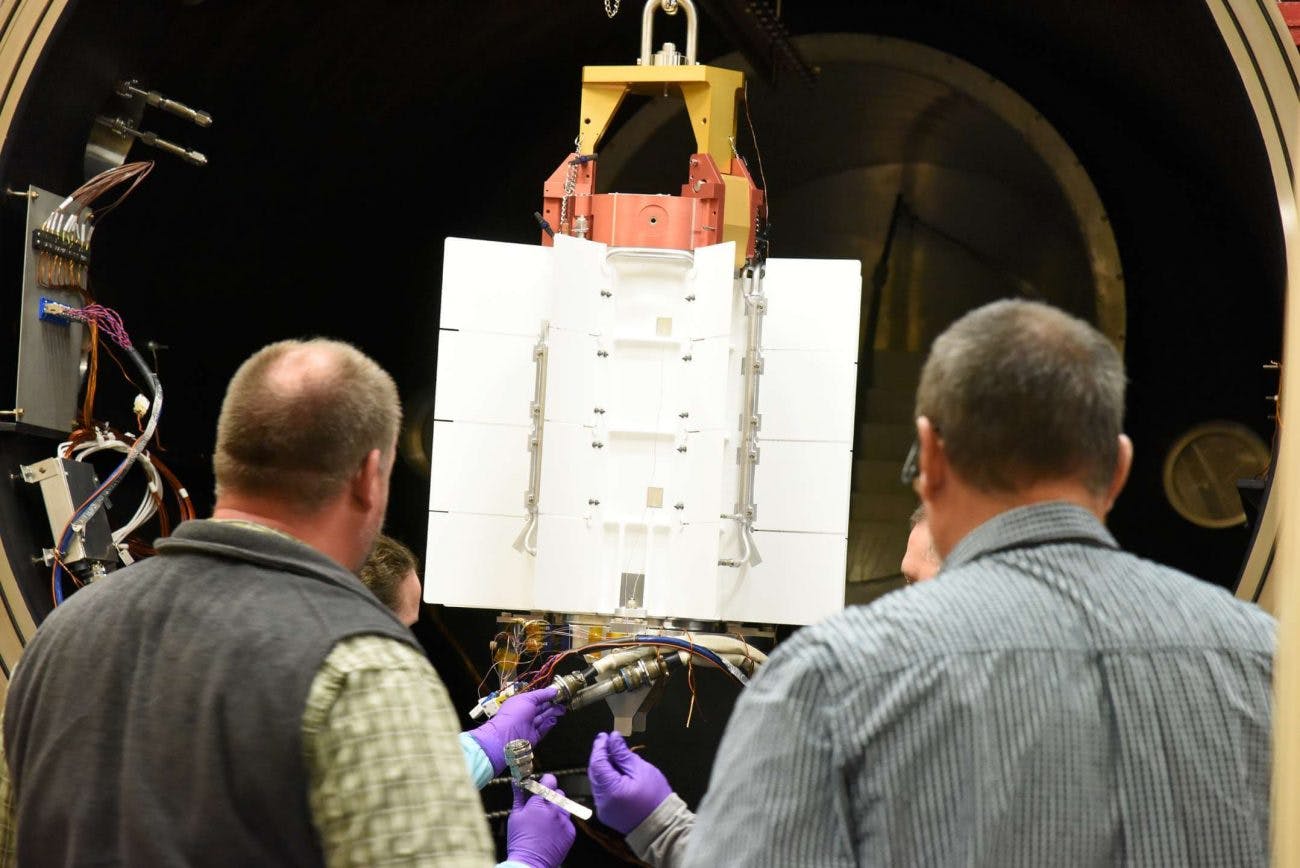
The EBR-II sodium fast reactor at Idaho National Laboratory began operations in 1964 and generated electricity for decades. Soon it will serve as a National Reactor Innovation Center test bed for future advanced reactor demonstrations. (Source: ANL)
At the box office or streaming at home, it’s fear, not truth, that sells. The laws of physics are swept aside, apocalypse is inevitable, and superpowered heroes wait until the last possible second to save the universe. It can make for great entertainment, but in the real world we need to stick with science over science fiction and be wowed by engineering, not special effects.
The truth is, science and innovation are incredible in their own right. From communications and machine learning to space travel and medical advances, technology is evolving in hyperdrive to solve real problems. With climate change and global warming here on earth, we don’t have to go looking for trouble in a galaxy far, far away.
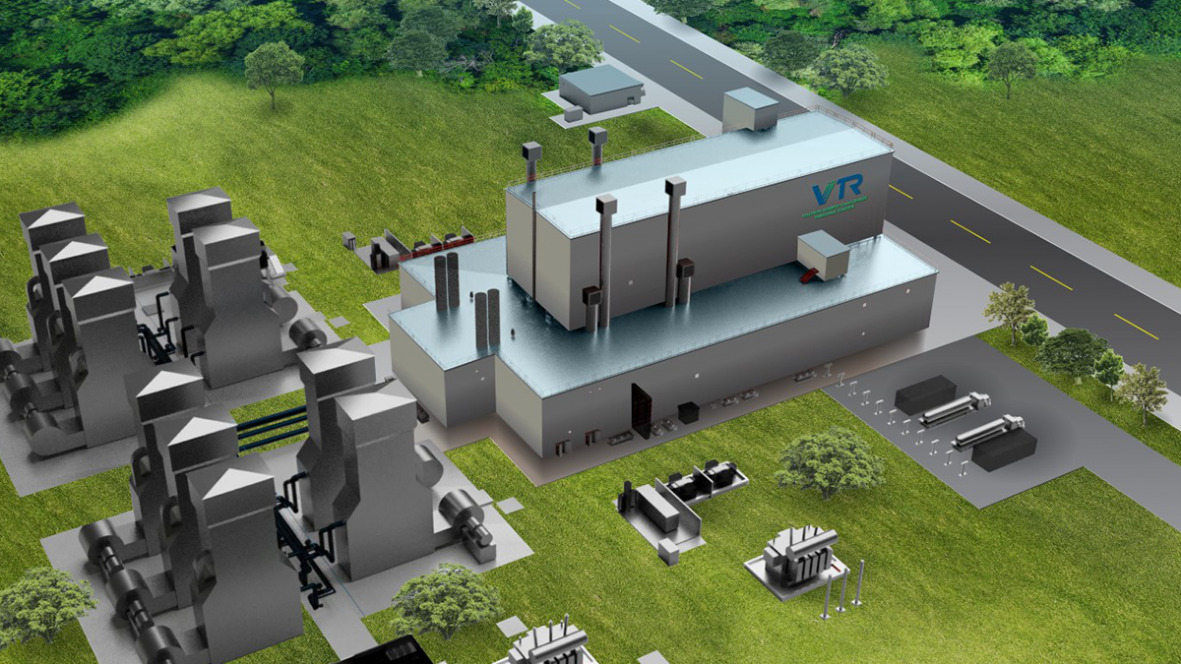
A rendering of the VTR facility. (Image: INL)
The Department of Energy announced in 2020 its approval of Critical Decision 1 for the Versatile Test Reactor (VTR) project, a one-of-a-kind scientific user facility that would support research and development of innovative nuclear energy and other technologies. The decision was well received by the nuclear energy community—after all, the DOE’s Nuclear Energy Advisory Committee had studied and reported on the need for the VTR and found strong support for the project among reactor developers, federal agencies and national laboratories, and university researchers.
Irradiated lead test rods are delivered to Oak Ridge National Laboratory for examination. (Photo: ORNL)
Several lead test rods of Westinghouse’s EnCore accident tolerant fuel recently arrived at Oak Ridge National Laboratory for post-irradiation examination over the next year in support of the Nuclear Regulatory Commission’s licensing process. The rods were installed in 2019 in Exelon’s Byron-2, a 1,158-MWe pressurized water reactor, and were removed in fall 2020 and prepared for shipment to ORNL.
A rendering of the VTR facility. (Image: INL)
Kathryn Huff, the Department of Energy’s acting assistant secretary for nuclear energy, asserted in an article published online by the Office of Nuclear Energy (DOE-NE) on July 30 that demonstration reactors, such as the Natrium and Xe-100 reactors being built as full-size power producers with cost-shared funding from the DOE, and test reactors, such as the Versatile Test Reactor, are both necessary for nuclear innovation. Both are also line items in the DOE budget request, and Huff’s article sends a clear message to appropriators about the need to fund both the Advanced Reactor Demonstration Program (ARDP) and the VTR.
Hot-fire test at Blue Origin’s West Texas launch facility in July 2019. (Photo: Blue Origin)
In July 1969, the public’s attention was fixated on NASA’s Apollo 11 mission—a “giant leap for mankind” that was memorably marked by Neil Armstrong as he stepped onto the surface of the moon. This July, the possibilities of spaceflight are once again capturing the public’s imagination and news headlines. While NASA invests in nuclear propulsion research and development to stretch the limits of U.S. space missions, private companies Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin are stretching the definition of “astronaut” and proving they can offer a high-altitude thrill to paying customers.
A still image from a three-part video tour of NuScale’s facilities. (Photos: NuScale Power)
When Utah Associated Municipal Power Systems (UAMPS) in 2015 announced its plan to develop the Carbon Free Power Project (CFPP) using NuScale Power’s modular light water reactor design, it envisioned the construction of a dozen 50-MWe modules for a plant that could produce a total of 600 MWe. The CFPP’s target output later rose to 720 MWe, when UAMPS opted to scale up to 60-MWe modules. In late June, the plans changed once again, as UAMPS participants chose to build 77-MWe modules but downsize the plant from 12 units to six, which would yield 462 MWe—about 64 percent of the 720 MWe that could have been generated from 12 of the 60-MWe modules.
An artist's rendition of Oklo’s Aurora powerhouse. (Image: Gensler)
California-based Oklo has received a $2 million cost-share award from the Department of Energy for the commercialization of advanced fuel recycling capabilities by using electrorefining technology. Oklo is matching $1 million in funds and is partnering with the DOE and Argonne National Laboratory on this public-private partnership, which is intended to help reduce fuel costs for advanced reactor designs while reducing waste by turning used fuel into advanced reactor fuel.
The MARVEL reactor concept with Stirling engines. (Image: DOE)
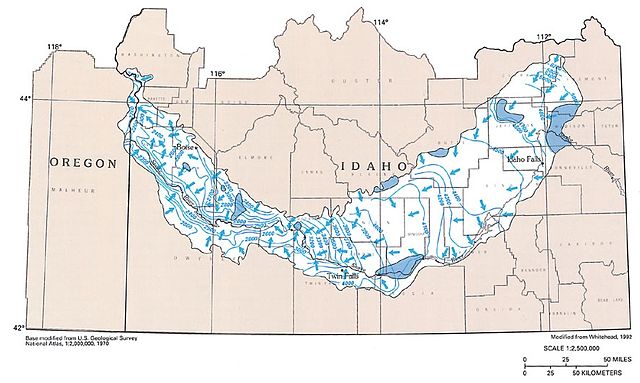
The Snake River Plain Aquifer
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management will award the Idaho Cleanup Project contract for the Idaho National Laboratory site to Idaho Environmental Coalition (IEC), of Tullahoma, Tenn. The contract has an estimated ceiling of approximately $6.4 billion over 10 years, with cost reimbursement and fixed-price task orders to define the contract performance.
A photo of a prototype Lightbridge fuel assembly. (Photo: Lightbridge)
Operators at the Advanced Test Reactor at Idaho National Laboratory have begun a nine-month outage to perform a core internals changeout. When the ATR is restarted in early 2022, the top head closure plate of the pressurized water test reactor will have new access points that could permit the irradiation of more fuel and material samples in the reactor’s high-flux neutron conditions.
Operations personnel working above the Advanced Test Reactor on the reactor top area. The small cylindrical section in the center of the platform has access ports for refueling and experiment loading and unloading during routine outages. (Photo: INL)
The Advanced Test Reactor (ATR) at Idaho National Laboratory is getting an overhaul that will keep it off line for nine months. When the ATR is restarted in early 2022, the one-of-a-kind pressurized water test reactor—which is operated at low pressures and temperatures as a neutron source—will be ready for another decade or more of service, with the potential for more experimental capacity in years to come.
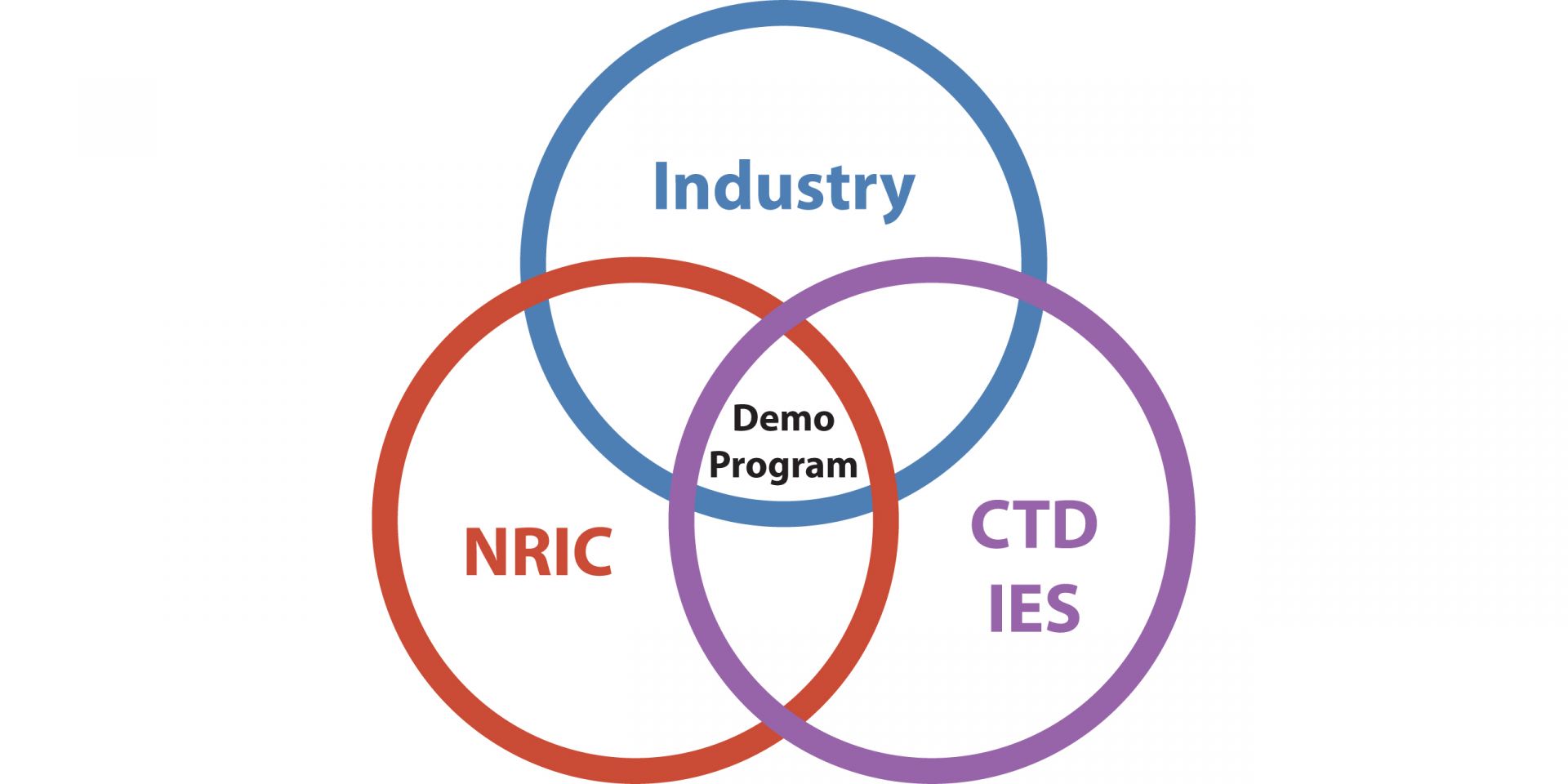
The demonstration program aims to accelerate innovation and deployment of energy concepts at the intersection of industry needs, NRIC’s mission, and the R&D portfolio of CTD IES. (Graphic: BEA)
The National Reactor Innovation Center (NRIC) wants to hear from developers and end users interested in integrated energy systems for advanced reactors. Battelle Energy Alliance (BEA), the managing and operating contractor for Idaho National Laboratory, has issued a call for Expressions of Interest for a potential multi-phase demonstration program for innovative uses of nuclear energy, to be carried out by NRIC and the Crosscutting Technology Development Integrated Energy Systems (CTD IES) program. The final date for responses is May 21.
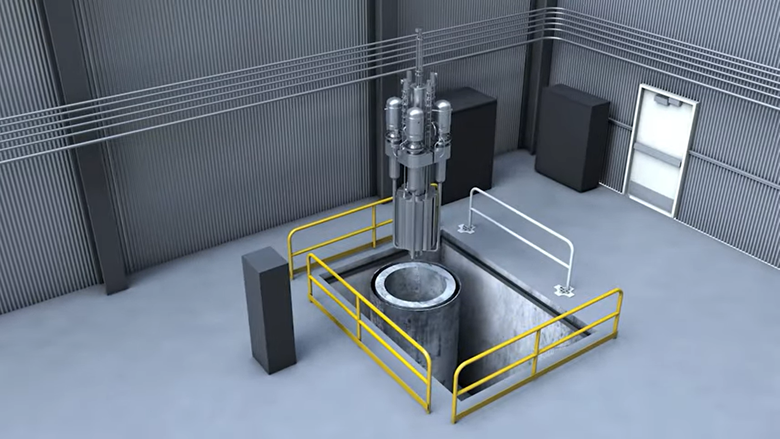
An image from a video released by INL shows MARVEL, to be installed in a concrete pit within the TREAT reactor building. Source: INL
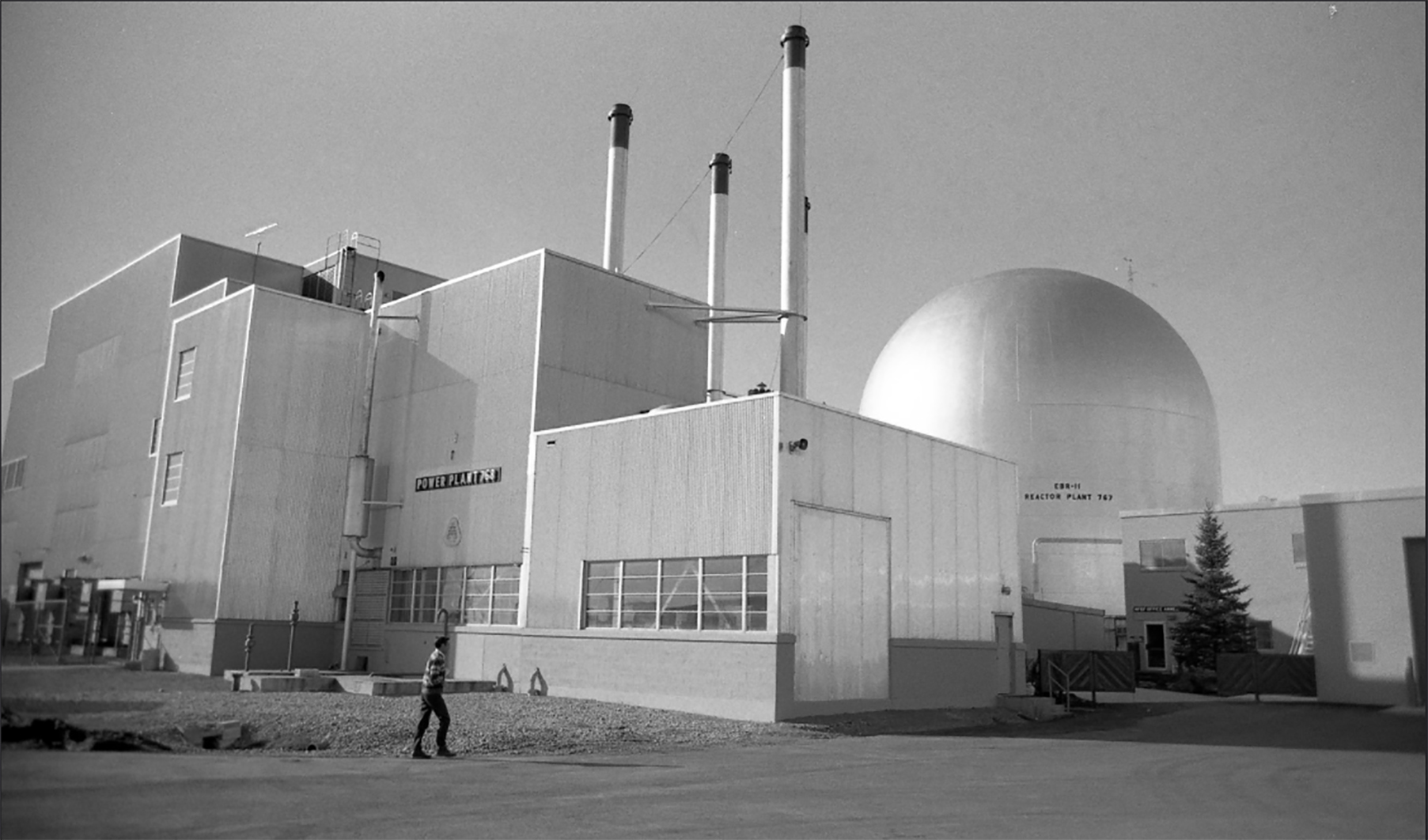





 A recently released technical report from Idaho National Laboratory finds “significant potential” for deploying microreactors on a global scale, but also “significant challenges in achieving the technical capacities, meeting regulatory requirements and international accords, achieving competitive costs, and for gaining public acceptance.”
A recently released technical report from Idaho National Laboratory finds “significant potential” for deploying microreactors on a global scale, but also “significant challenges in achieving the technical capacities, meeting regulatory requirements and international accords, achieving competitive costs, and for gaining public acceptance.”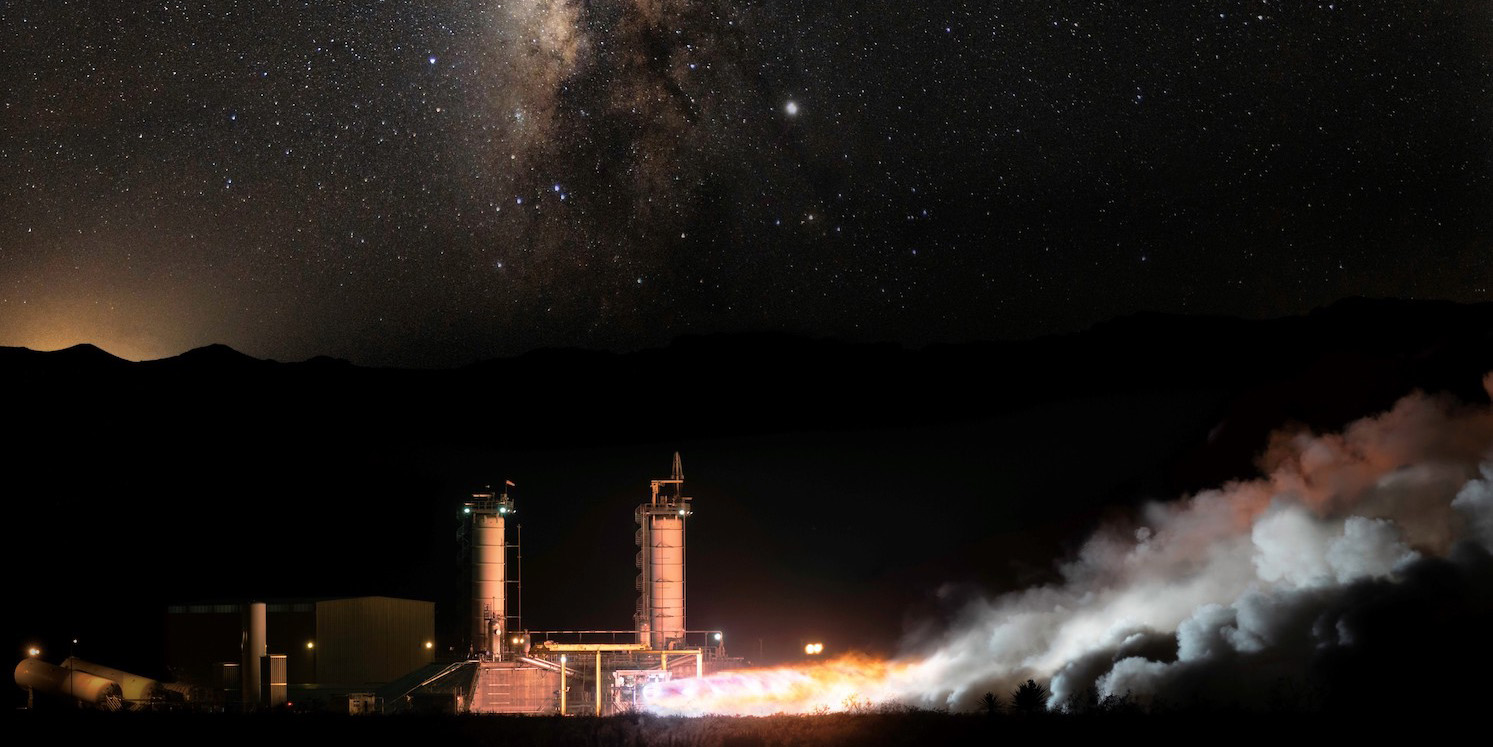
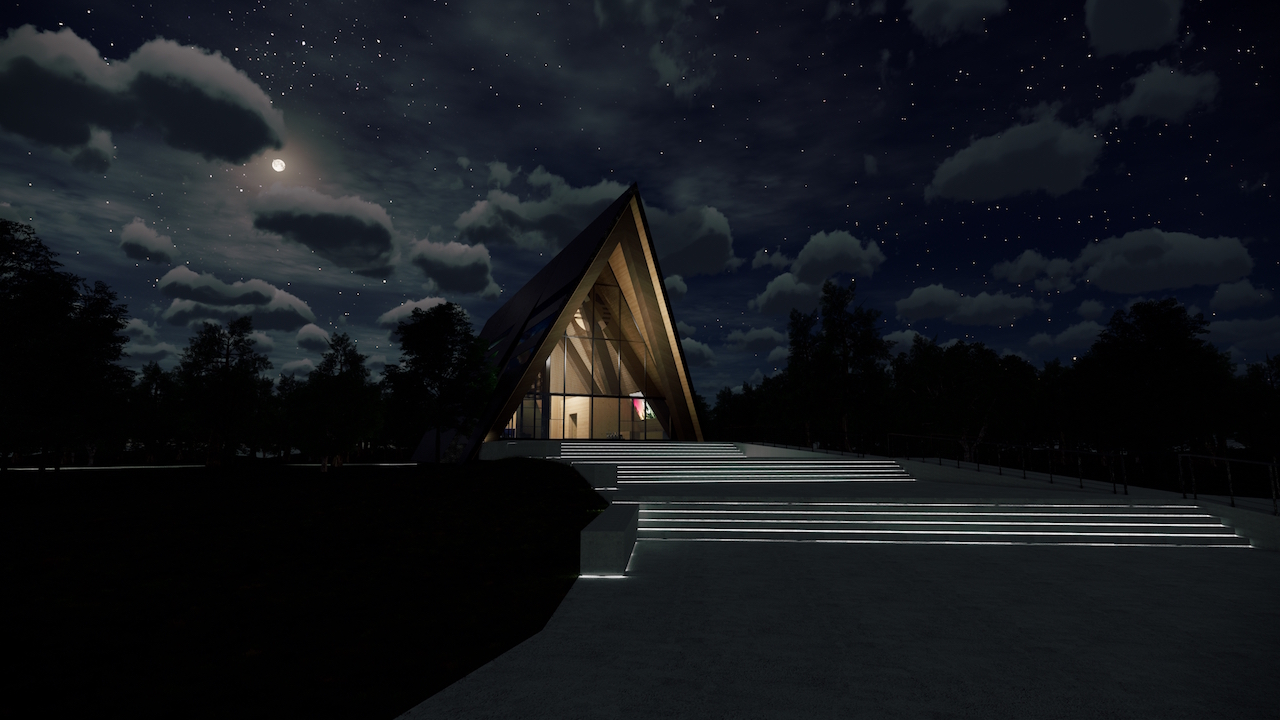
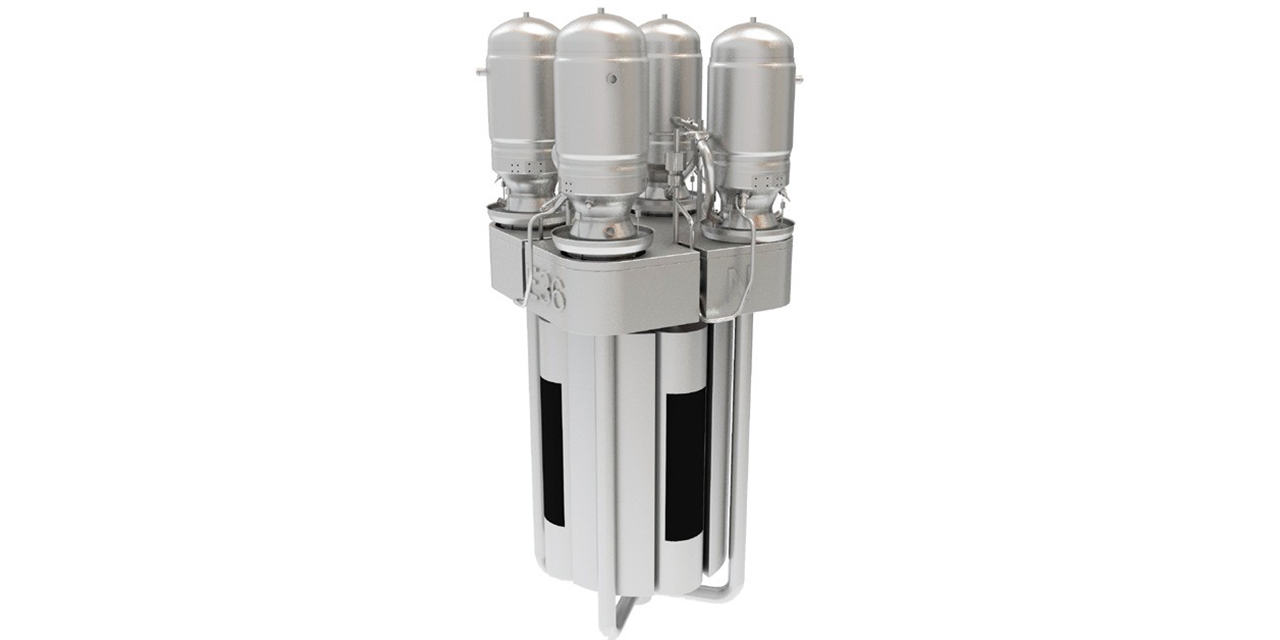
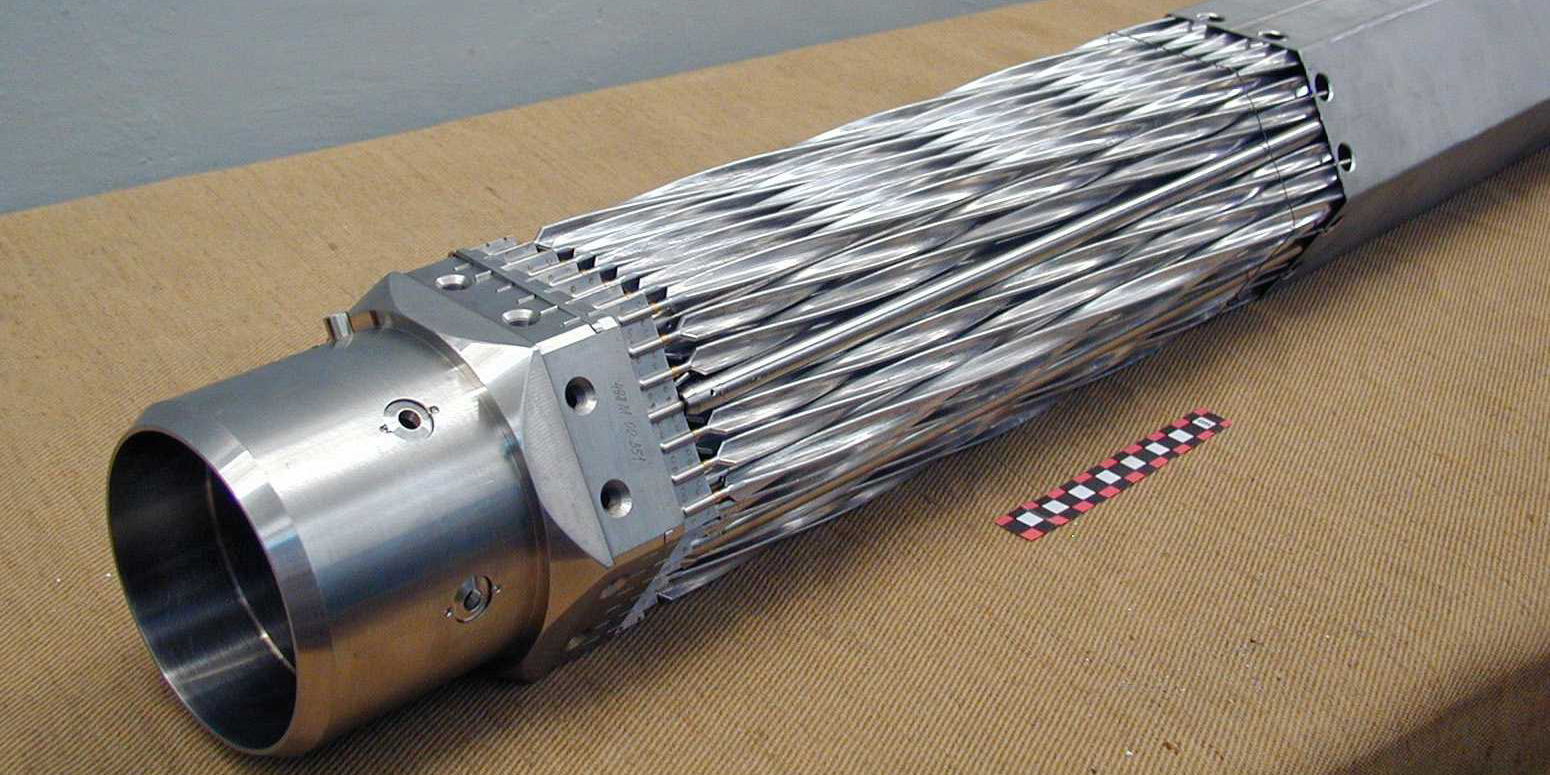
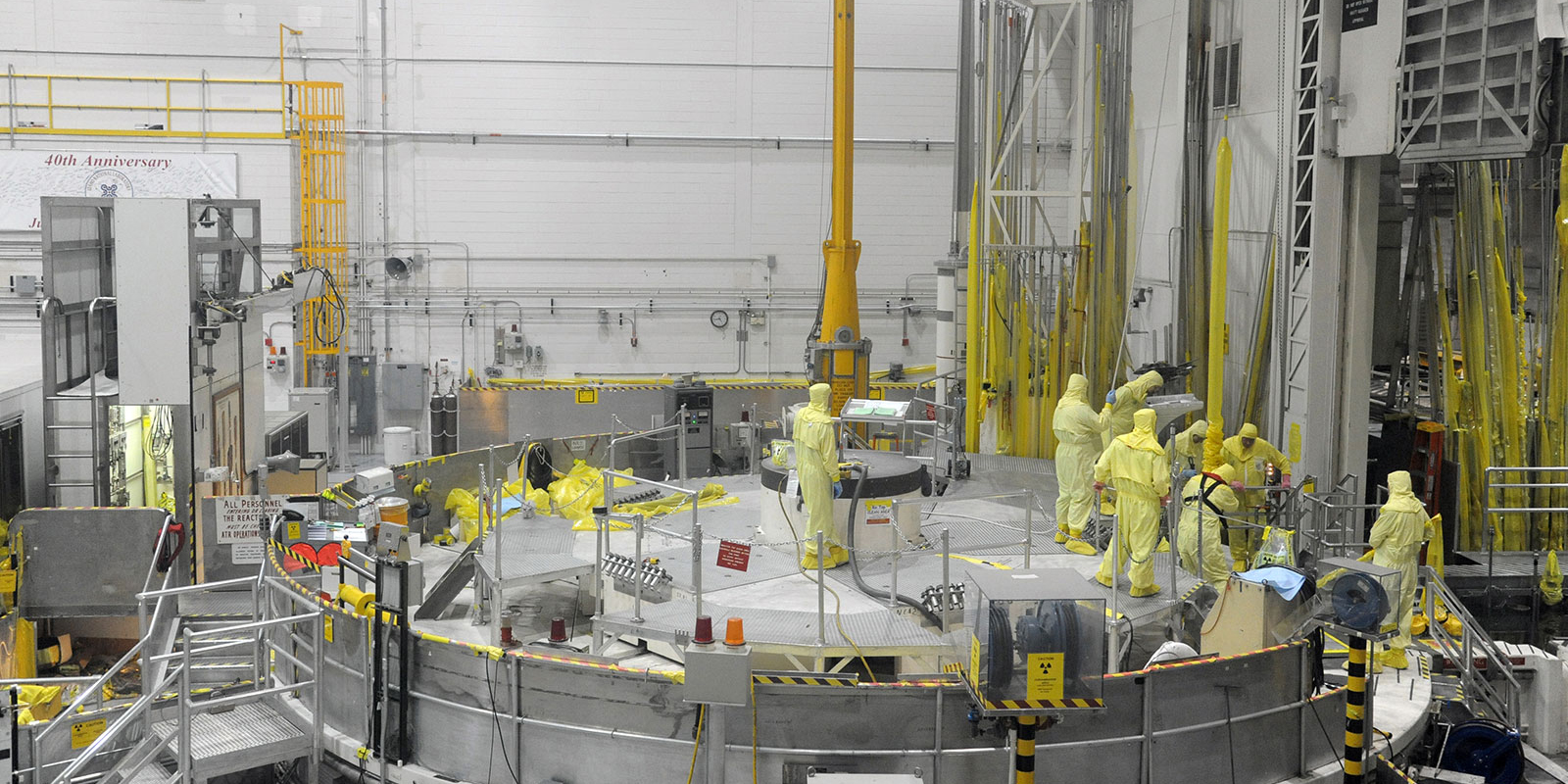





 The Gateway for Accelerated Innovation in Nuclear (GAIN) announced that three nuclear technology companies—Radiant, Oklo, and Lightbridge—will receive GAIN nuclear energy vouchers to accelerate the innovation and application of advanced nuclear technologies.
The Gateway for Accelerated Innovation in Nuclear (GAIN) announced that three nuclear technology companies—Radiant, Oklo, and Lightbridge—will receive GAIN nuclear energy vouchers to accelerate the innovation and application of advanced nuclear technologies. 



