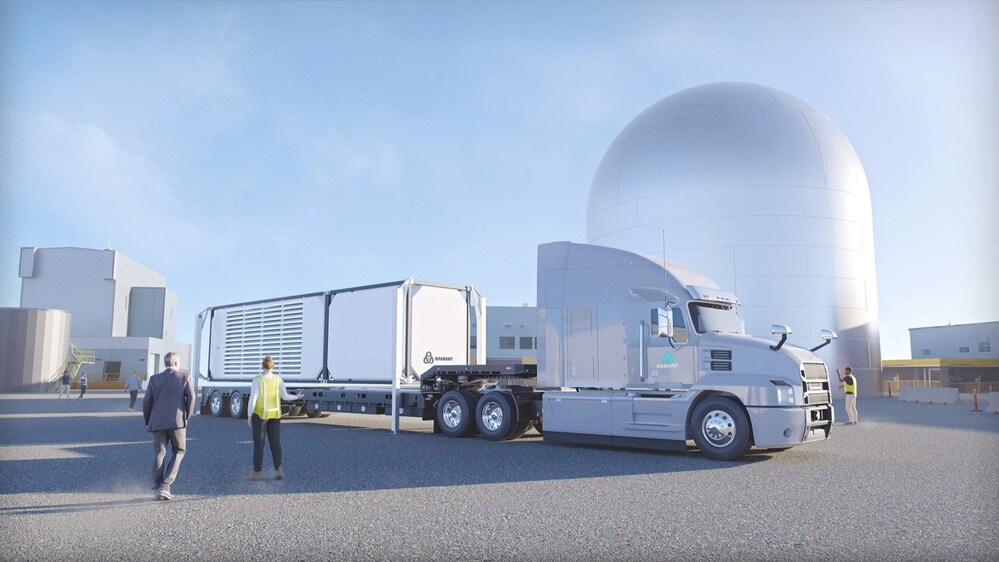
Concept art showing the delivery of Radiant’s Kaleidos to the DOME test bed. (Image: Radiant Industries/Ryan Seper)
Radiant Industries announced on June 4 that the safety design strategy (SDS) for a test of its Kaleidos microreactor in the National Reactor Innovation Center’s DOME test bed at Idaho National Laboratory now has approval from the Department of Energy. Radiant hopes to test Kaleidos—a 1-MW high-temperature, gas-cooled reactor—by 2026 and then market portable commercial reactors to power remote locations and provide backup or primary power for critical applications in hospitals or for disaster relief.
The Materials and Fuels Complex at INL. (Photo: INL)
The Department of Energy will enter into lease negotiations with two solar energy developers for 400 megawatts of solar electricity generation within the Idaho National Laboratory site. Announced on June 5, the projects are the first proposed projects selected under the department’s Cleanup to Clean Energy initiative, an effort to repurpose parts of DOE-owned lands—portions of which were previously used in the nation’s nuclear weapons program—into sites of clean-energy generation, including for solar, geothermal, wind, and nuclear.
ANEEL fuel experiment capsules being staged at the ATR. (Photo: Clean Core)
Clean Core Thorium Energy (Clean Core) has announced that its ANEEL fuel is ready to begin irradiation testing and qualification at Idaho National Laboratory. The fuel, made of thorium and HALEU, was developed by Clean Core for use in pressurized heavy water reactors, including CANDU (Canadian deuterium-uranium) reactors. Irradiation of the fuel samples in INL’s Advanced Test Reactor (ATR) is set to begin this month.
The primary system of THETA at Argonne’s Mechanisms Engineering Test Loop Facility, where Oklo is conducting sodium thermal-hydraulic testing with support from a GAIN award announced in 2021. (Image: Argonne National Laboratory)
The Department of Energy and the Gateway for Accelerated Innovation in Nuclear (GAIN) on March 19 announced the second round of fiscal year 2024 voucher awards to three companies: Element Factory, Kanata America, and Oklo.
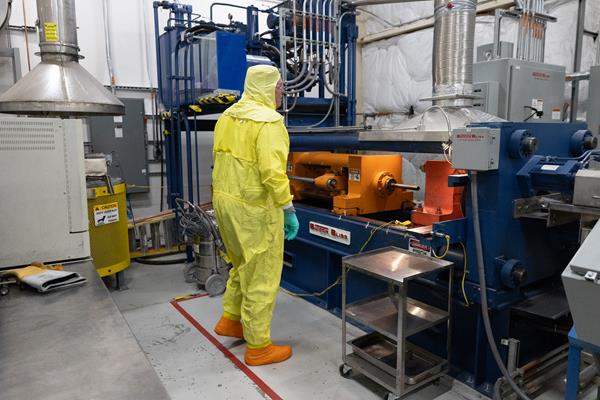
The extrusion in progress. (Photo: INL/Lightbridge)
Lightbridge Corporation announced today that it has reached “a critical milestone” in the development of its extruded solid fuel technology. Coupon samples using an alloy of zirconium and depleted uranium—not the high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU) that Lightbridge plans to use to manufacture its fuel for the commercial market—were extruded at Idaho National Laboratory’s Materials and Fuels Complex.
From left: Piercy, Hart, Iyengar, Tobey
The latest virtual event produced by the American Nuclear Society brought together experts from the forefront of the global nuclear industry to discuss strategies for ensuring a safe, secure, and healthy expansion in the face of a rapidly changing energy and geopolitical landscape.
The webinar, moderated by ANS Executive Director/CEO Craig Piercy, featured J’Tia Hart, chief science officer for the National and Homeland Security Directorate at Idaho National Laboratory; Anagha Iyengar, deputy program director for analytics and innovation at the National Nuclear Security Administration’s Office of International Nuclear Security; and William Tobey, former NNSA deputy administrator for defense nuclear nonproliferation.
Concept art of the MARVEL microreactor (Image: INL)
The Department of Energy announced February 7 that fuel for the MARVEL microreactor, which Idaho National Laboratory plans to host inside the Transient Reactor Test (TREAT) facility, is now being fabricated by TRIGA International, with the first fuel delivery expected in spring 2025. MARVEL operation was expected “by the end of 2024” as recently as May 2023, but that timeline had shifted by October, when the DOE said MARVEL “is expected to be completed in early 2025.” Now, according to the DOE’s latest announcement, “Fuel loading for MARVEL is anticipated to occur in 2026, with the microreactor expected to be on line by 2027.”
A still from a video on Westinghouse Electric Company’s eVinci microreactor, one of seven advanced reactor technologies that received support in GAIN’s latest round of nuclear energy vouchers. (Image: Westinghouse)
The Gateway for Accelerated Innovation in Nuclear (GAIN) announced December 19 that seven firms will get vouchers to access the nuclear research facilities and expertise of the national laboratory complex in the first round of fiscal year awards. Each company is paired with one or more national laboratories to work on concepts from advanced reactor fueling to fuel recycling to climate forecasting.
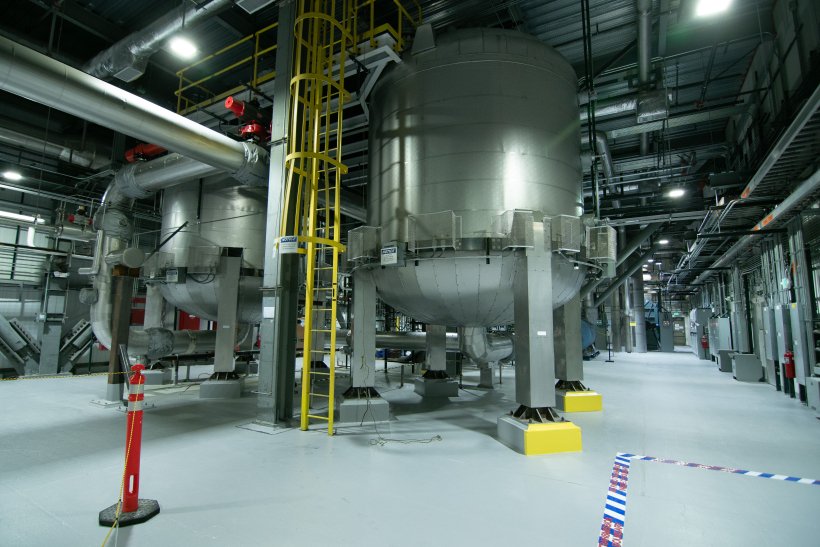
A view of two vessels that each contain approximately 30,000 pounds of granulated activated carbon, used to remove mercury from process off-gas during IWTU operations. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management said Idaho’s Integrated Waste Treatment Unit (IWTU) is set to resume radioactive liquid waste treatment operations early next year after crews replaced carbon material from two plant vessels. The IWTU was shut down for an unplanned outage on September 6 to address elevated mercury concentrations in the plant’s granulated activated carbon (GAC) beds, according to Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board (DNFSB) reports.
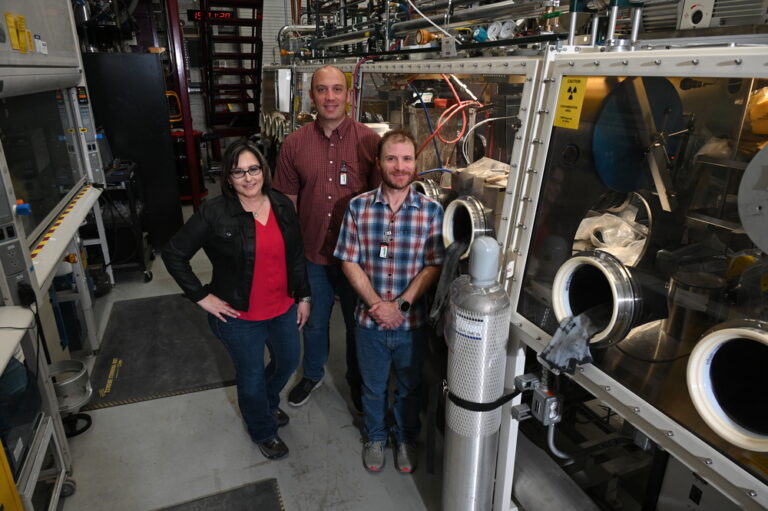
The project team included (from left to right) Jennifer Watkins, Seth Ashby, and Adrian Wagner. (Photo: INL)
Researchers at Idaho National Laboratory in early 2023 manufactured commercial-grade high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU) fuel pellets to the specifications of a General Electric accident tolerant fuel design, INL announced November 21. A team working at INL’s Experimental Fuels Facility at the Material and Fuels Complex fabricated about two dozen uranium dioxide pellets using HALEU enriched up to 15 percent U-235.
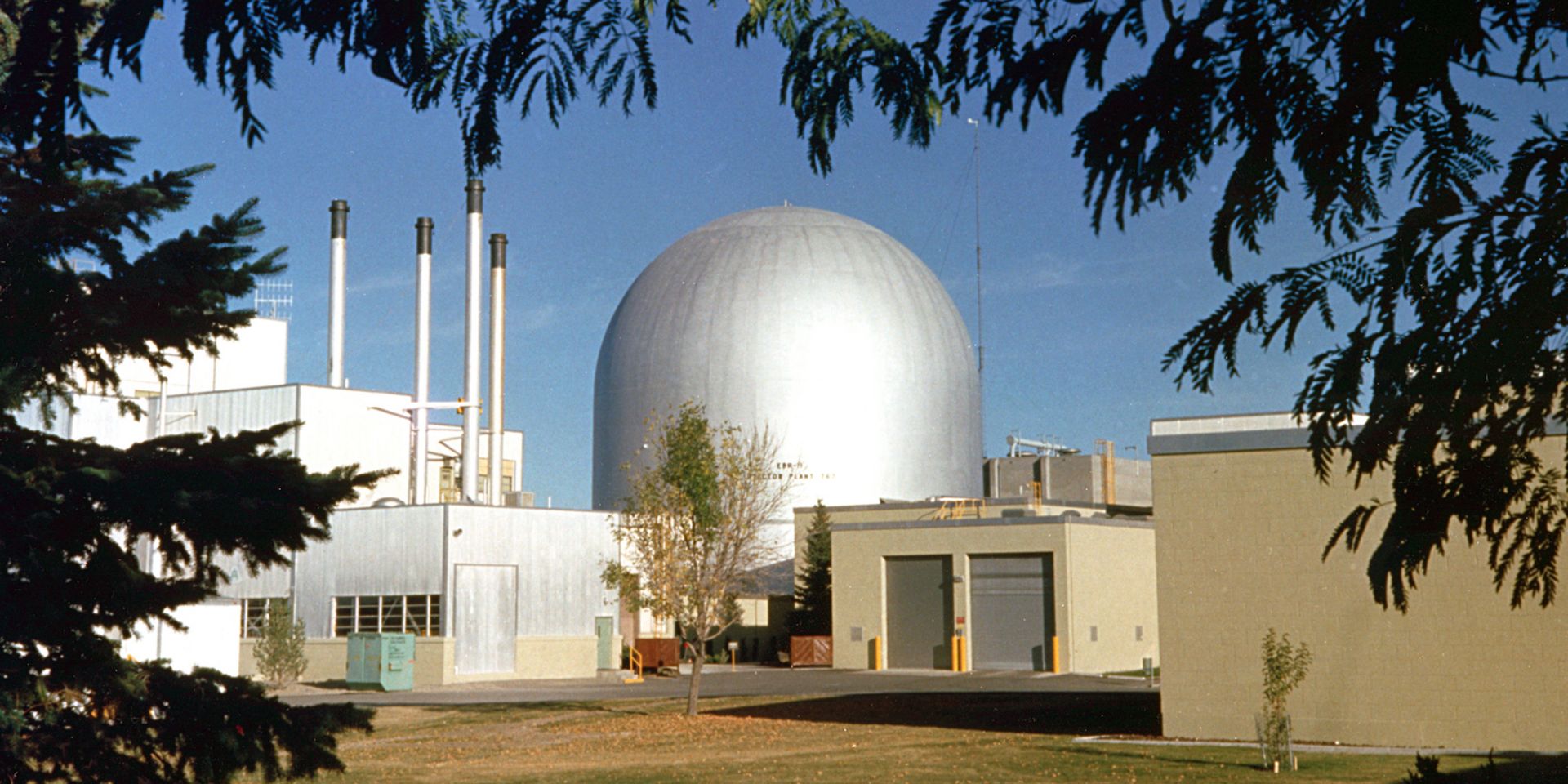
Experimental Breeder Reactor-II (Photo: ANL)
If you head west out of Idaho Falls on U.S. Highway 20 and make your way across the Snake River Plain, it won’t be long before you’ll notice a silver dome in the distance to the north. One of the most recognizable structures in the history of nuclear energy, Experimental Breeder Reactor-II stands out from the desert landscape. The 890-square-mile site on which EBR-II is located is the former National Reactor Testing Station, now known as Idaho National Laboratory.
The 2F Evaporator at SRS. (Photo: Savannah River Site Photography)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management is responsible for roughly 90 million gallons of radioactive liquid waste at Idaho National Laboratory, the Hanford Site in Washington state, and the Savannah River Site in South Carolina. About 900,000 gallons of waste are stored at INL, 56 million gallons at Hanford, and roughly 36 million at SRS. A further 400,000 gallons of waste from various operations are being stored at the Oak Ridge Site in Tennessee.






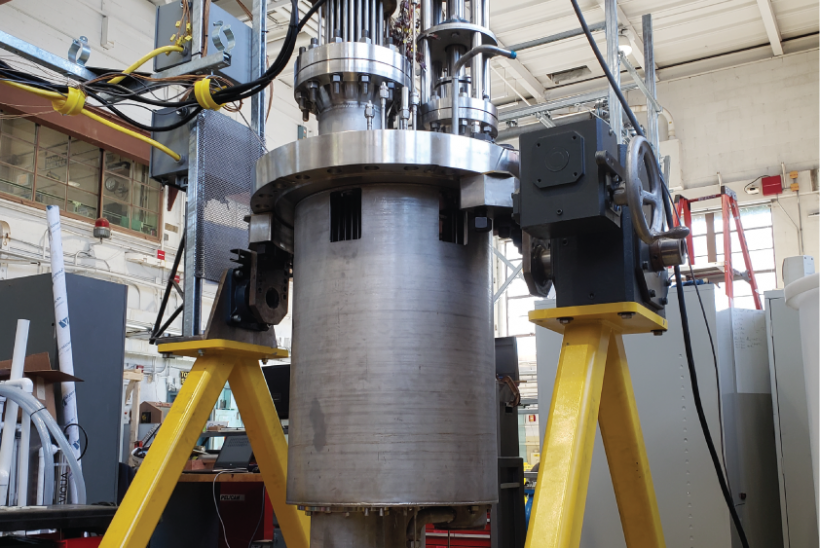



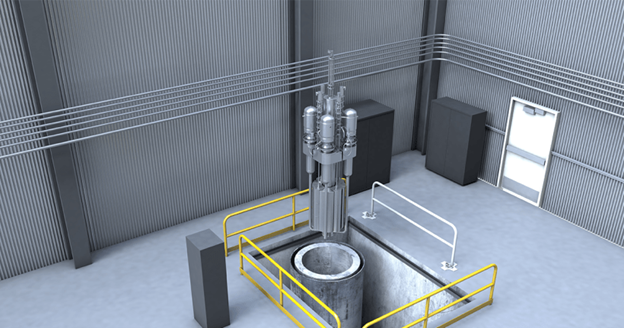


 Two teams of guest editors from Idaho National Laboratory have announced plans for special issues of the American Nuclear Society's Nuclear Science and Engineering, the nuclear community’s longest-running technical journal. Abdalla Abou Jaoude and Abderrafi M. Ougouag are leading the NSE issue Technical Challenges and Opportunities in the Development and Deployment of Microreactors, while Joseph Nielsen and Piyush Sabharwall are organizing the NSE issue Irradiation Experiments Supporting Advanced Nuclear Technologies.
Two teams of guest editors from Idaho National Laboratory have announced plans for special issues of the American Nuclear Society's Nuclear Science and Engineering, the nuclear community’s longest-running technical journal. Abdalla Abou Jaoude and Abderrafi M. Ougouag are leading the NSE issue Technical Challenges and Opportunities in the Development and Deployment of Microreactors, while Joseph Nielsen and Piyush Sabharwall are organizing the NSE issue Irradiation Experiments Supporting Advanced Nuclear Technologies.



