SHINE Technologies’ headquarters building in Janesville, Wis. (Photo: SHINE)
The Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration has issued a cooperative agreement worth $35 million to SHINE Technologies, based in Janesville, Wis., to support the commercial production of molybdenum-99, a critical isotope used in more than 40,000 medical procedures in the United States each day, including the diagnosis of heart disease and cancer.
ORNL’s Benjamin Manard places a swipe on the extraction stage of Advion’s Plate Express, a microextraction tool that has been paired with a mass spectrometer. (Photo: Carlos Jones/ORNL, DOE)
International nuclear safeguards verification relies on a precise count of isotope particles collected on swipes during International Atomic Energy Agency inspections of nuclear facilities and isolated through a series of lengthy chemical separations that can take about 30 days to complete. On October 15, Oak Ridge National Laboratory—a member of the IAEA’s Network of Analytical Laboratories (NWAL)—announced that analytical chemists at the site have developed a faster way to measure isotopic ratios of uranium and plutonium collected on swipes, which could help IAEA analysts detect the presence of undeclared nuclear activities or material.
An archive photo of the Nevada National Security Site’s Test Cell C complex, which is being prepared for demolition and closure. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy is preparing to demolish two large, complex facilities at the Nevada Nuclear Security Site with ties to historical nuclear propulsion rocket development and testing programs. The DOE’s Environmental Management (EM) Nevada Program and its environmental program services contractor, Navarro Research and Engineering, have begun characterization and hazard reduction work on the site’s Engine Maintenance, Assembly, and Disassembly (EMAD) and Test Cell C (TCC) complexes.
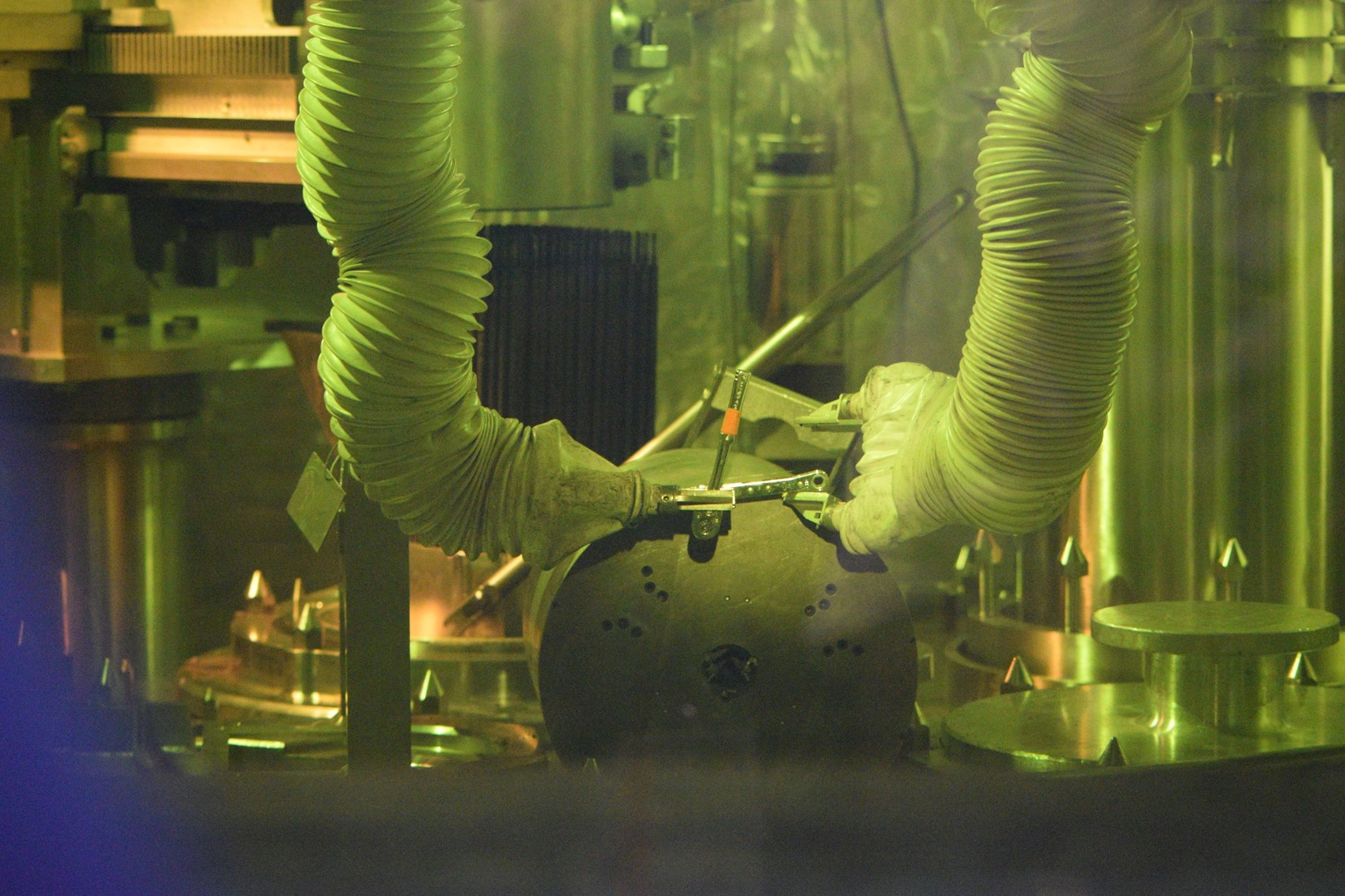
Operators disassemble a cutter head inside a module at the Savannah River's Tritium Extraction Facility using manipulators and hand tools. (Photo: SRNS)
Using basic hand tools and remote manipulators, operators at Savannah River Nuclear Solutions (SRNS) were able to reduce radiation exposure to workers performing cutter head maintenance in the Savannah River Site’s Tritium Extraction Facility (TEF).
According to SRNS, the innovative procedure proved to be an excellent example of real-world application of As Low As Reasonably Achievable (ALARA) principles of time, distance, and shielding.
NorthStar’s RadioGenix system produces the medical radioisope Mo-99 without the use of uranium. (Photo: NorthStar)
NorthStar Medical Technologies of Beloit, Wis., will receive $37 million under two cooperative agreements with the National Nuclear Security Administration for the production of molybdenum-99 without the use of high-enriched uranium. Considered a critical medical radioisotope, Mo-99 is used in more than 40,000 medical procedures in the United States each day, including the diagnosis of heart disease and cancer.
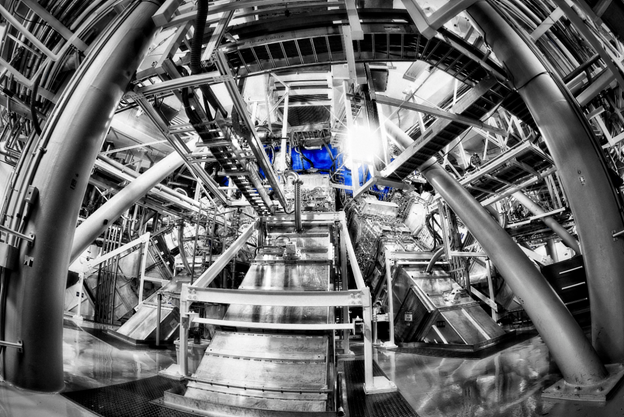
A color-enhanced photograph of the NIF target bay. (Photo: LLNL/Damien Jemison)
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory is celebrating the yield from an experiment at the National Ignition Facility (NIF) of more than 1.3 megajoules of energy—eight times more than the yield from experiments conducted this spring and 25 times more than NIF’s 2018 record yield.
Left: The University of Texas at Austin SBD Challenge team: from left, Michael Butero, Matthew Frangos, Daniel Gutierrez, and John (Jack) Whelan. Right: The University of Rhode Island team: from left, Jay Macchia, Sean Babin, and Peter Tillinghast. (Photo: NNSA)
The National Nuclear Security Administration's Office of Nonproliferation and Arms Control has been partnering with national laboratories and universities to introduce engineering students to the field of international safeguards. Safeguards ensure that nuclear material and facilities are not used to illicitly manufacture nuclear weapons, the NNSA noted in a July 27 article.
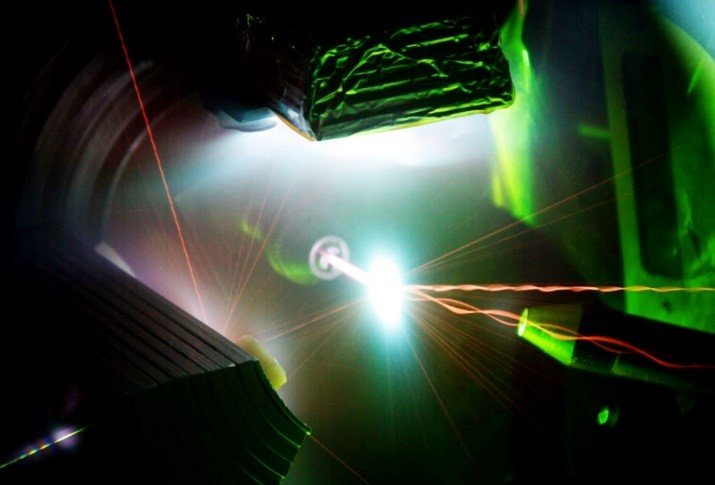
Invisible infrared light from the 200-trillion-watt Trident Laser at Los Alamos National Laboratory interacts with a 1-micrometer thick foil target (in the center of the photo) to generate a high-energy-density plasma. (Photo: Joseph Cowan and Kirk Flippo, LANL)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Science (DOE-SC) and the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) on July 27 announced $9.35 million for 21 research projects in high-energy-density laboratory plasmas. High-energy-density (HED) plasma research, originally developed to support the U.S. nuclear weapons program, has applications in astrophysics, fusion power plant development, medicine, nuclear and particle physics, and radioisotope production.