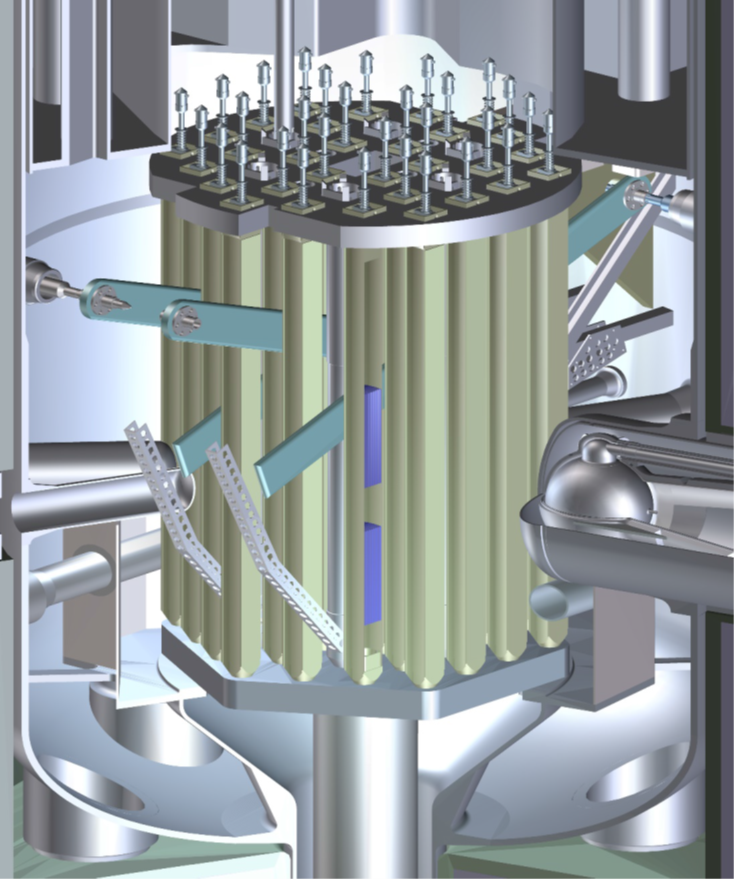
A rendering of the core of the NBSR, which consists of 30 aluminum-cladded plate-type U3O8 fuel elements with a 17.8-cm gap between elements. (Image: NCNR Technical Working Group, Root Cause Investigation of February 2021 Fuel Failure)
(CLICK IMAGE TO ENLARGE)
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has submitted two reports and supplemental information to the Nuclear Regulatory Commission after conducting a root cause analysis of the February 2021 fuel failure and resultant alert at the NIST Center for Neutron Research (NCNR) in Gaithersburg, Md. While the 20-MWt NCNR research reactor remains shut down, scuttling the plans of researchers who rely on it as a source of both cold and thermal neutrons, NIST states in an October 4 update that it has requested permission to restart the reactor, contingent upon meeting all 18 corrective actions identified.
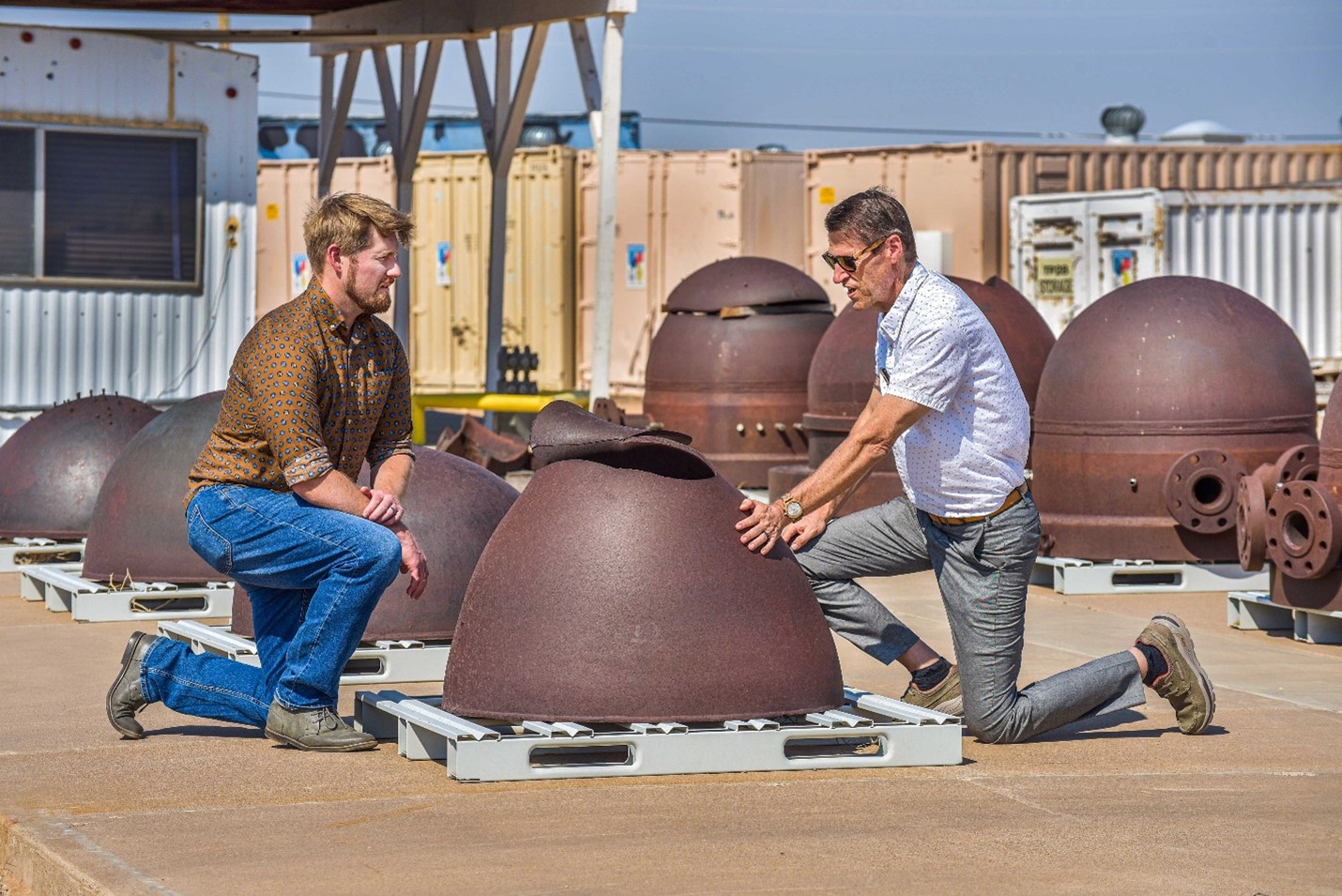
Having completed three separate decommissioning projects, EnergySolutions takes the final steps in restoring the sites to a natural state.
For any nuclear power plant that has been permanently shut down, site restoration is the ultimate decommissioning goal when contracting with a utility to demolish a facility. The task, however, is not as simple as mobilizing heavy equipment and waving a wrecking ball or planting explosives to implode the facility, then loading up the debris and sending it to a landfill.
There is a real science and engineering approach necessary to safely restore the land to its original state. That has been the goal for EnergySolutions over the past decade as the company works to safely decommission shuttered nuclear power plants—packaging, transporting, and disposing of the waste, and restoring the sites for whatever reuse the owners and host communities see fit.
Click to open full graphic
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission has issued a license to Interim Storage Partners (ISP), a joint venture of Waste Control Specialists and Orano USA, to construct and operate a consolidated interim storage facility for spent nuclear fuel in Andrews, Texas. Issued on September 13, the license comes just four days after Texas governor Greg Abbott signed a bill to block such a facility from being built in the state.
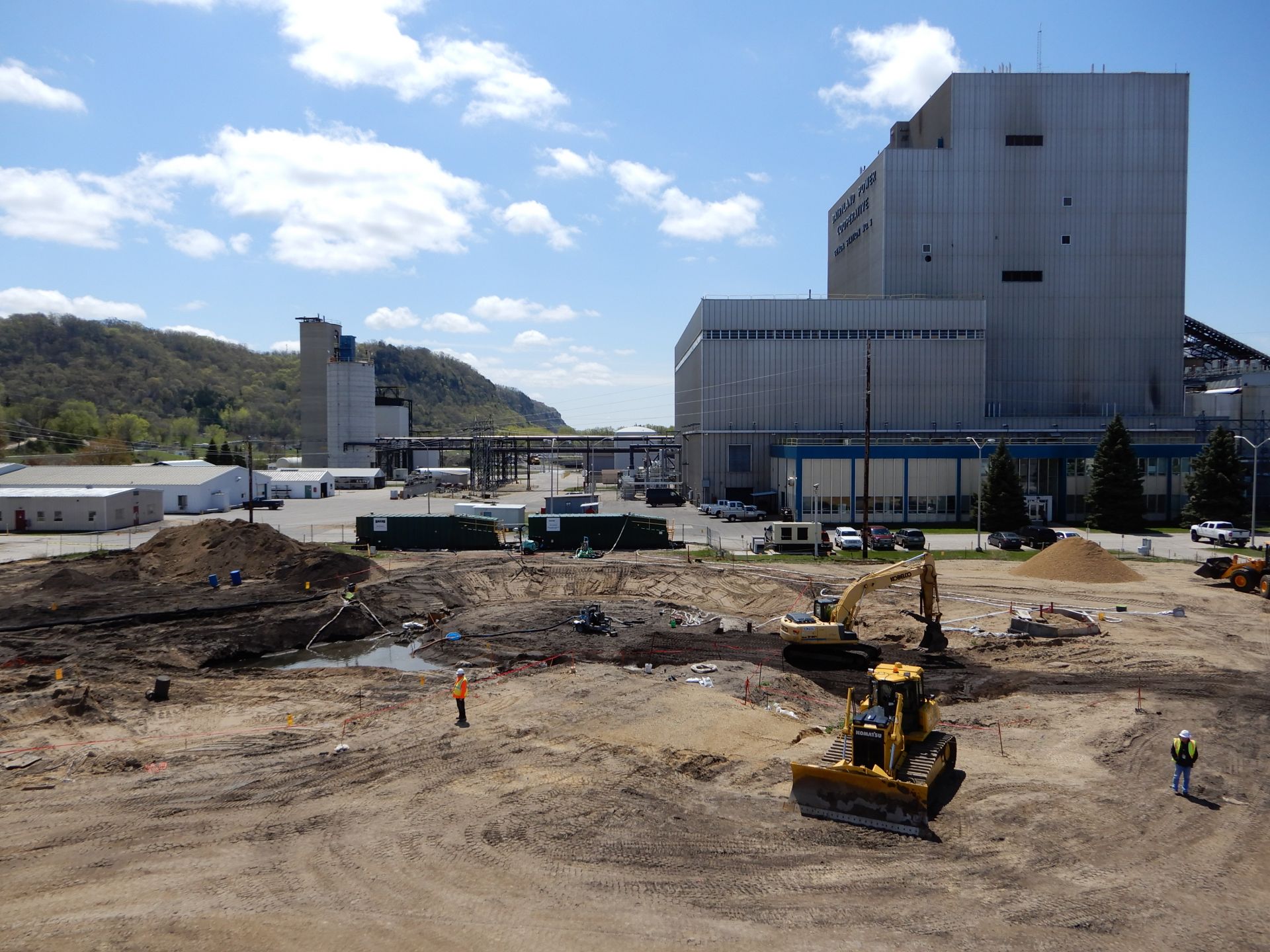
The La Crosse site in 2019 with major decommissioning completed. The coal-fired Genoa plant is in the background. (Photo: EnergySolutions)
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission has extended its orders transferring the licenses for the La Crosse and Zion nuclear power plants from EnergySolutions back to the plant owners until late 2022. This is the third time the NRC has extended the effectiveness of the license transfer orders for the decommissioned plants since approving them in 2019.
Hurricane Ida knocked out all transmission lines into New Orleans, leaving more than a million people without power. (Photo: Entergy)
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission said it was monitoring events at three nuclear power reactors in Louisiana and Mississippi after Hurricane Ida made landfall on August 29. With winds of 150 miles per hour, the Category 4 storm left more than 1 million people without power in the two states. Ida has since weakened to a tropical storm.
Sandia's Brad Beeny (left) and Larry Humphries examine remnants from a series of lower head failure experiments. Results from these and other experiments are used to inform nuclear accident modeling computer code. (Photo: Randy Montoya)
Researchers at Sandia National Laboratories have been expanding MELCOR—the severe accident modeling computer code used by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission to evaluate the safety of light water reactors—to study the small modular reactors and non-light-water advanced reactors that are under development. An article published in Sandia Lab News on August 27 describes in detail how MELCOR is being expanded to work with different reactor geometries, fuel types, and coolant systems.
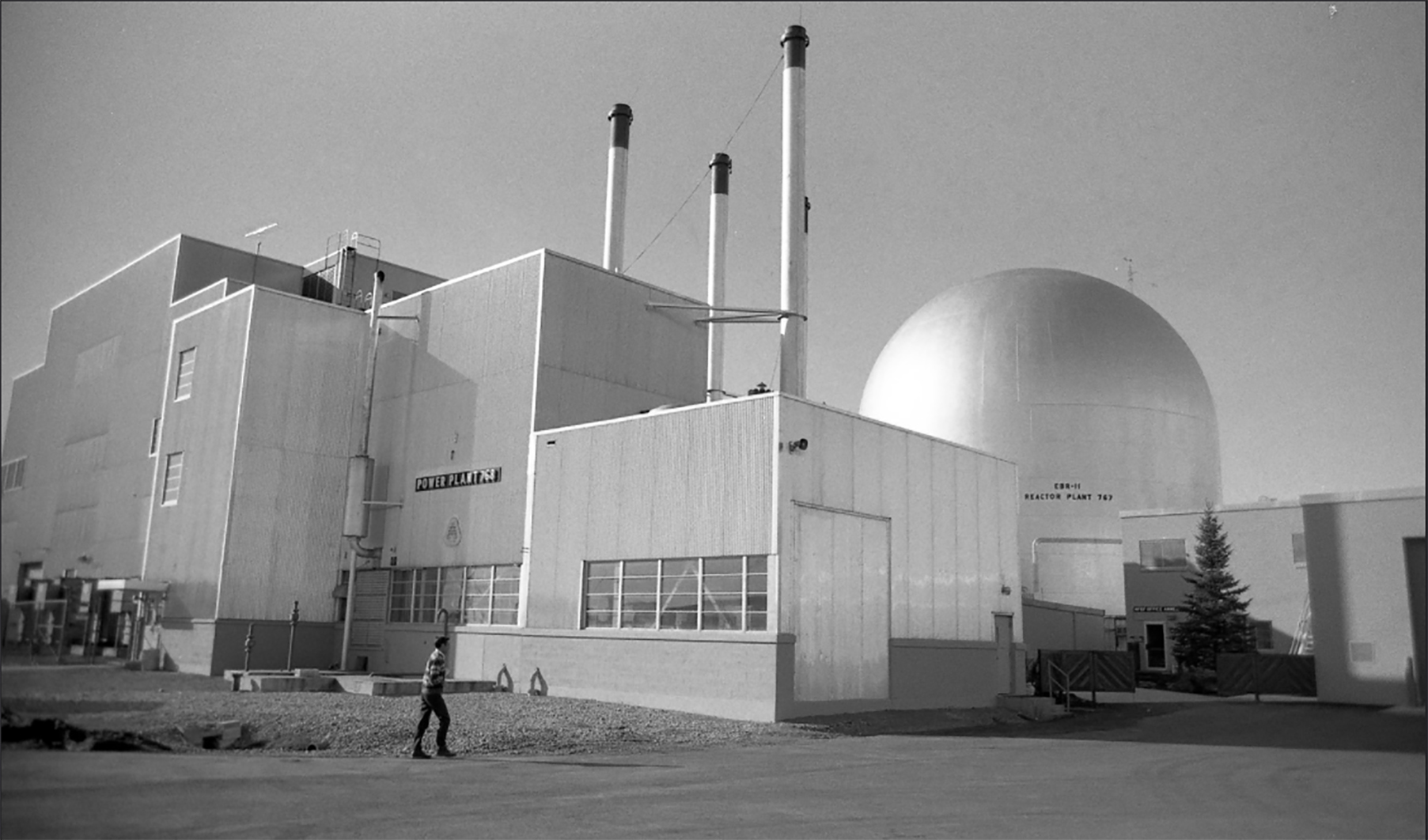
The EBR-II sodium fast reactor at Idaho National Laboratory began operations in 1964 and generated electricity for decades. Soon it will serve as a National Reactor Innovation Center test bed for future advanced reactor demonstrations. (Source: ANL)
At the box office or streaming at home, it’s fear, not truth, that sells. The laws of physics are swept aside, apocalypse is inevitable, and superpowered heroes wait until the last possible second to save the universe. It can make for great entertainment, but in the real world we need to stick with science over science fiction and be wowed by engineering, not special effects.
The truth is, science and innovation are incredible in their own right. From communications and machine learning to space travel and medical advances, technology is evolving in hyperdrive to solve real problems. With climate change and global warming here on earth, we don’t have to go looking for trouble in a galaxy far, far away.
Irradiated lead test rods are delivered to Oak Ridge National Laboratory for examination. (Photo: ORNL)
Several lead test rods of Westinghouse’s EnCore accident tolerant fuel recently arrived at Oak Ridge National Laboratory for post-irradiation examination over the next year in support of the Nuclear Regulatory Commission’s licensing process. The rods were installed in 2019 in Exelon’s Byron-2, a 1,158-MWe pressurized water reactor, and were removed in fall 2020 and prepared for shipment to ORNL.
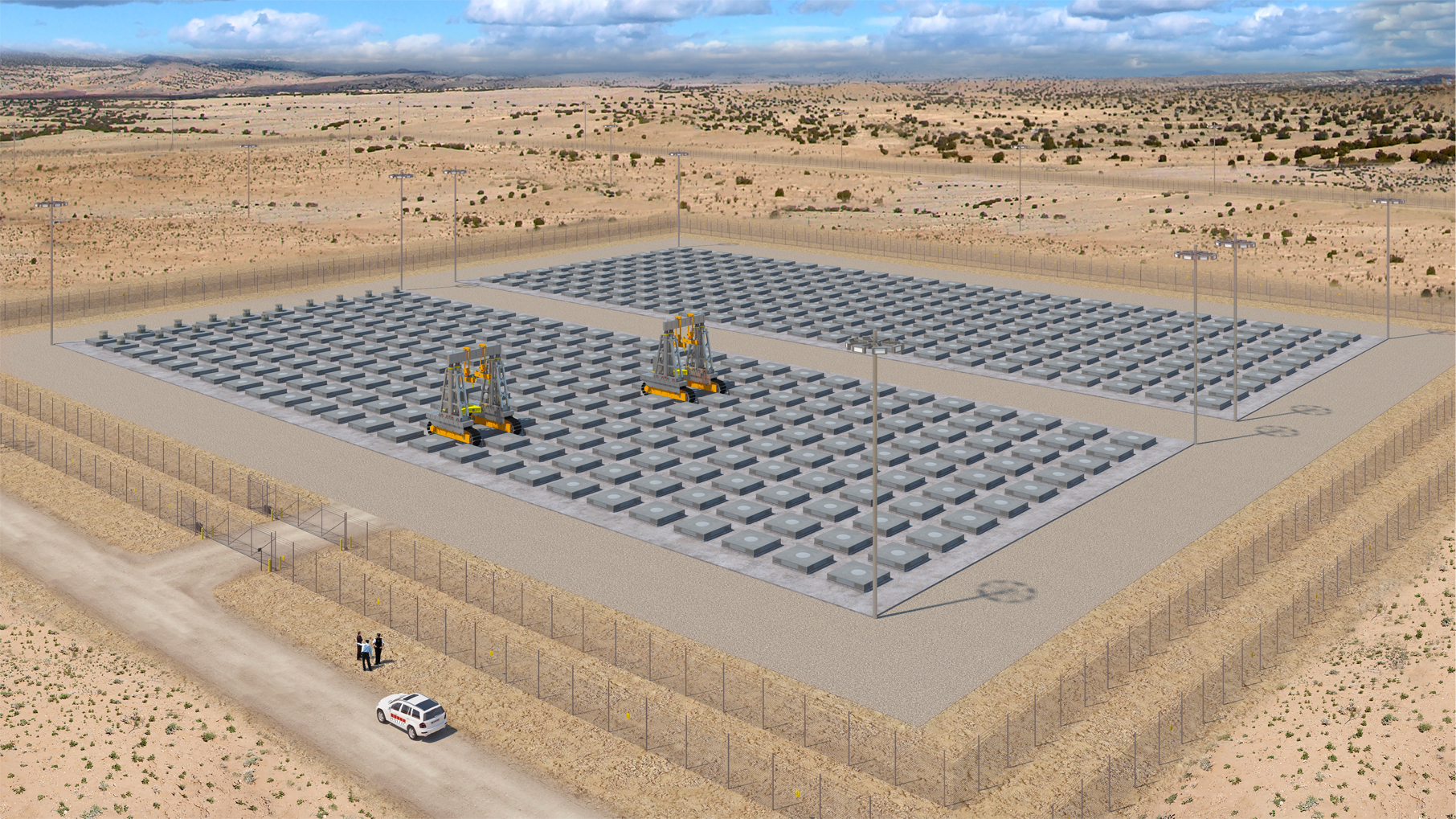
(Source: Interim Storage Partners)
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission has issued its final environmental impact statement on an application by Interim Storage Partners for a license to construct and operate a consolidated interim storage facility for spent nuclear fuel in Andrews County, Texas. After considering the environmental impacts of the proposed action, the NRC announced today that its staff has recommended granting the proposed license.
Chuck Metz Jr. discusses his collaboration with Harold Denton, whose memoir interweaves a retelling of the Three Mile Island accident events with stories of his career-long advocacy for nuclear safety.

Metz
A number of years ago, historian and writer Chuck Metz Jr. was at the Bush’s Visitor Center in Tennessee’s Great Smoky Mountains when he ran into former Nuclear Regulatory Commission official Harold Denton and his wife. Metz was at the visitor center, which opened in 2010 and is now a tourist hotspot, because, as he explained to the Dentons at the time, he had overseen the development of its on-site museum and had written a companion coffee-table history book.

The chance meeting turned into a friendship and a fruitful collaboration. Denton, who in 1979 was the public spokesperson for the NRC as the Three Mile Island-2 accident unfolded, had been working on his memoir, but he was stuck. He asked Metz for help with the organization and compilation of his notes. “I was about to retire,” Metz said, “but I thought that exploring the nuclear world might be an interesting change of pace.”
Denton passed away in 2017, but by then Metz had spent many hours with his fast friend and was able to complete the memoir, Three Mile Island and Beyond: Memories of a Life in Nuclear Safety, which was published recently by ANS. Metz shared some of his thoughts about Denton and the book with Nuclear News. The interview was conducted by NN’s David Strutz.
Former commissioner Annie Caputo left the NRC when her term expired at the end of June.
In a July 1 letter to President Biden, ANS President Steven Nesbit and ANS Executive Director/CEO Craig Piercy stated that a full complement of five commissioners is essential to the effectiveness of the Nuclear Regulatory Commission in protecting public health and safety while enabling the deployment and applications of nuclear technology.
An artist's rendering of the HI-STORE facility (Image: Holtec)
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission plans to complete its safety review of Holtec International’s proposed HI-STORE consolidated interim storage facility by January 2022. A final licensing decision on the facility will be made in conjunction with the release of the agency’s final safety evaluation report, the NRC said in a July 2 letter to Holtec.
U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission headquarters (photo: U.S. NRC)
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission has halted efforts to consider allowing U.S. nuclear power plant owners to request 40-year license renewals for their facilities, the agency announced on Facebook and Twitter on July 2. Currently, the maximum potential operating lifespan for a plant is 80 years: 40 years with the original license, 20 more with an initial license renewal, and another 20 with a second renewal.
Aerial view of the Morris Operation in Illinois. (Image: GE Hitachi)
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission has begun its review of GE Hitachi’s application to renew the license of its Morris Operation, the spent nuclear fuel storage facility in Grundy County, Ill. Notice of the 20-year license renewal application, along with an opportunity to request a hearing or petition for leave to intervene by August 30 was published in the June 30 Federal Register.
Vacancies undermine the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission’s mission
The American Nuclear Society (ANS) requests President Biden restore the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) to five commissioners by naming and expediting nominees to the agency. The impending vacancy of Commissioner Annie Caputo’s seat after June 30 will reduce the five-member NRC to three commissioners. NRC commissioners are appointed by the president and confirmed by the Senate for staggered five-year terms.














.jpg)

 2x1.jpg)