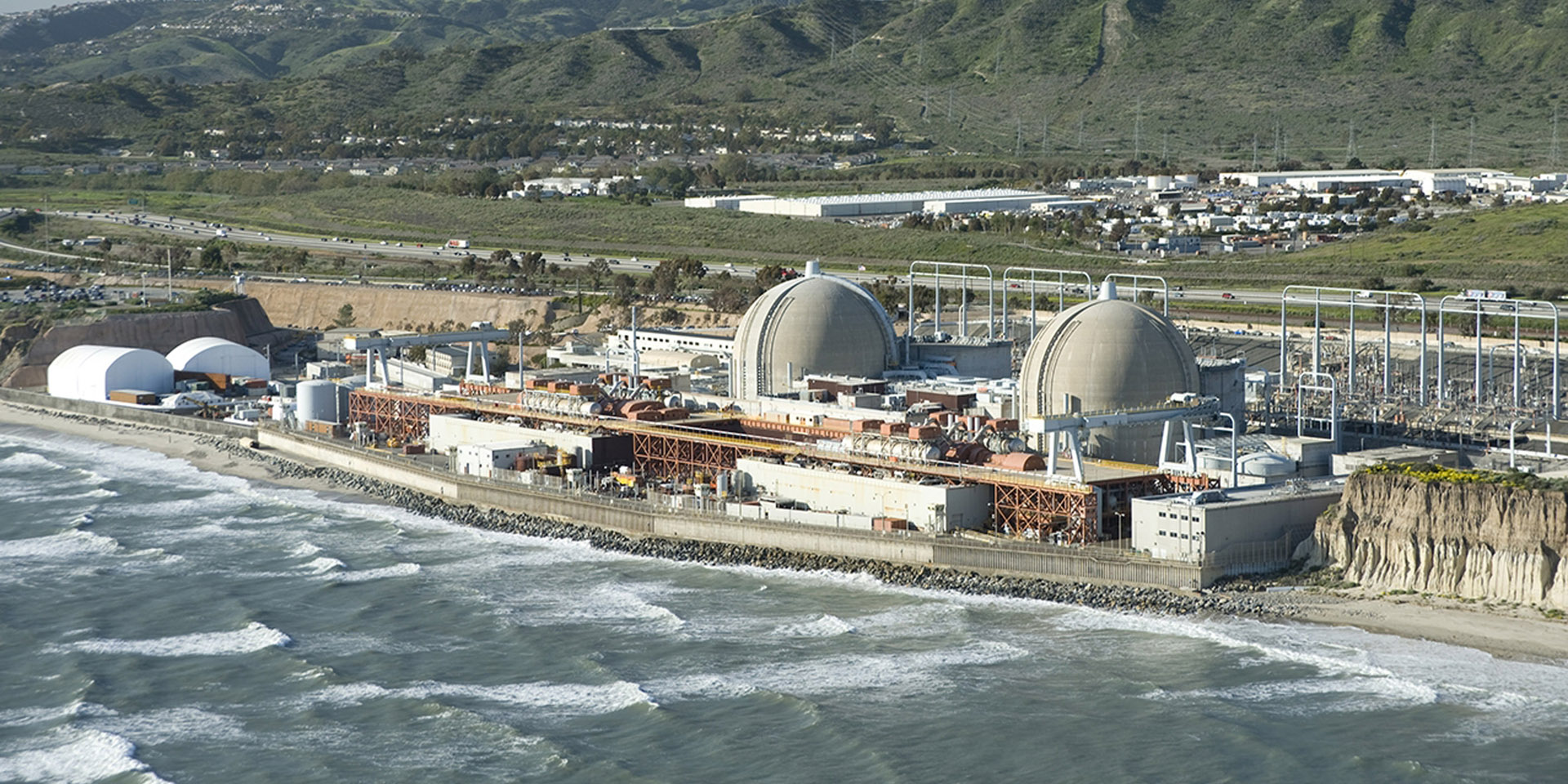
San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station. (Photo: Southern California Edison)
Ten years ago this month, on June 7, 2013, Southern California Edison (SCE) communicated the decision to permanently shutter the San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station (SONGS). The decision set in motion the decommissioning of a plant that had provided steady baseload power for the region since 1968 during a period of tremendous growth in the western United States. In the end, issues presented by the planned replacement steam generators that were intended to support future plant operations proved too large of a hurdle, and the plant was forced to retire.
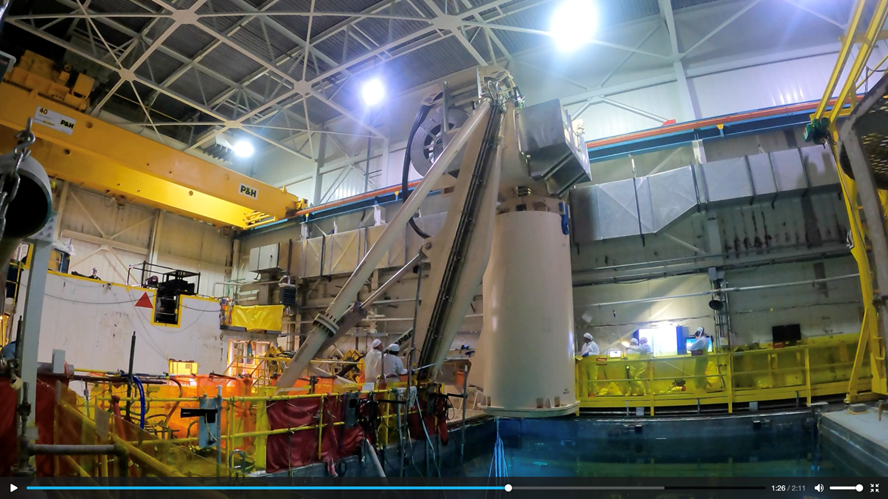
The Holtec HI-LIFT at Indian Point-3. (Image: Holtec)
Holtec International has said its patented HI-LIFT crane technology, being installed at the Indian Point-3 nuclear power plant, will speed the defueling of the spent nuclear fuel pool and avoid millions in excess decommissioning costs.
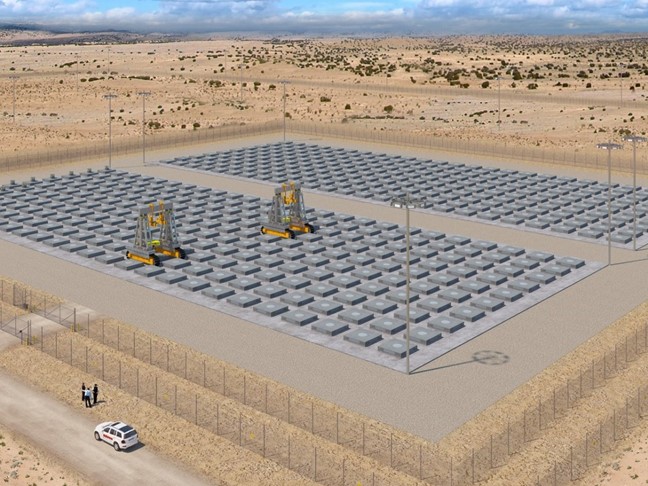
A rendering of Holtec’s proposed HI-STORE CISF in New Mexico. (Image: Holtec)
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission has issued a license to Holtec International to construct and operate a consolidated interim storage facility (CISF) for spent nuclear fuel in southeastern New Mexico. Holtec is proposing building the facility, called the HI-STORE CISF, between the cities of Carlsbad and Hobbs in Lea County on land provided by the Eddy Lea Energy Alliance (ELEA).
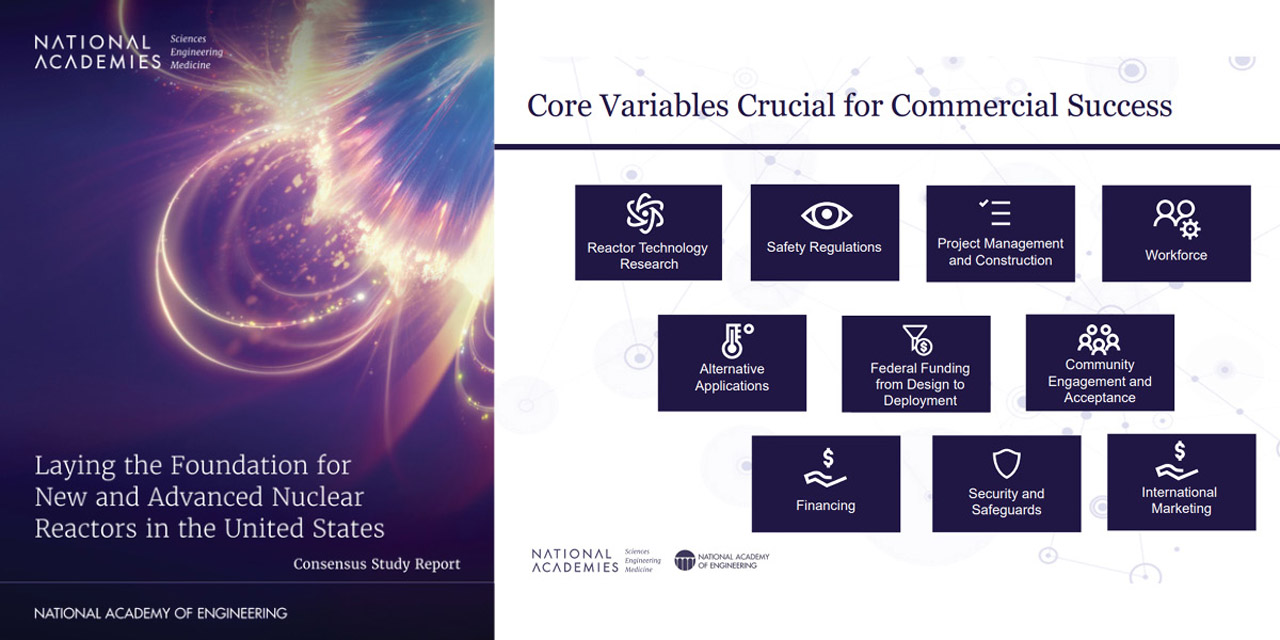
This slide on the right from the consensus committee’s public briefing identifies 10 core variables that are important to the success of advanced reactor deployments. (Image: NASEM, Laying the Foundation for New and Advanced Nuclear Reactors in the United States)
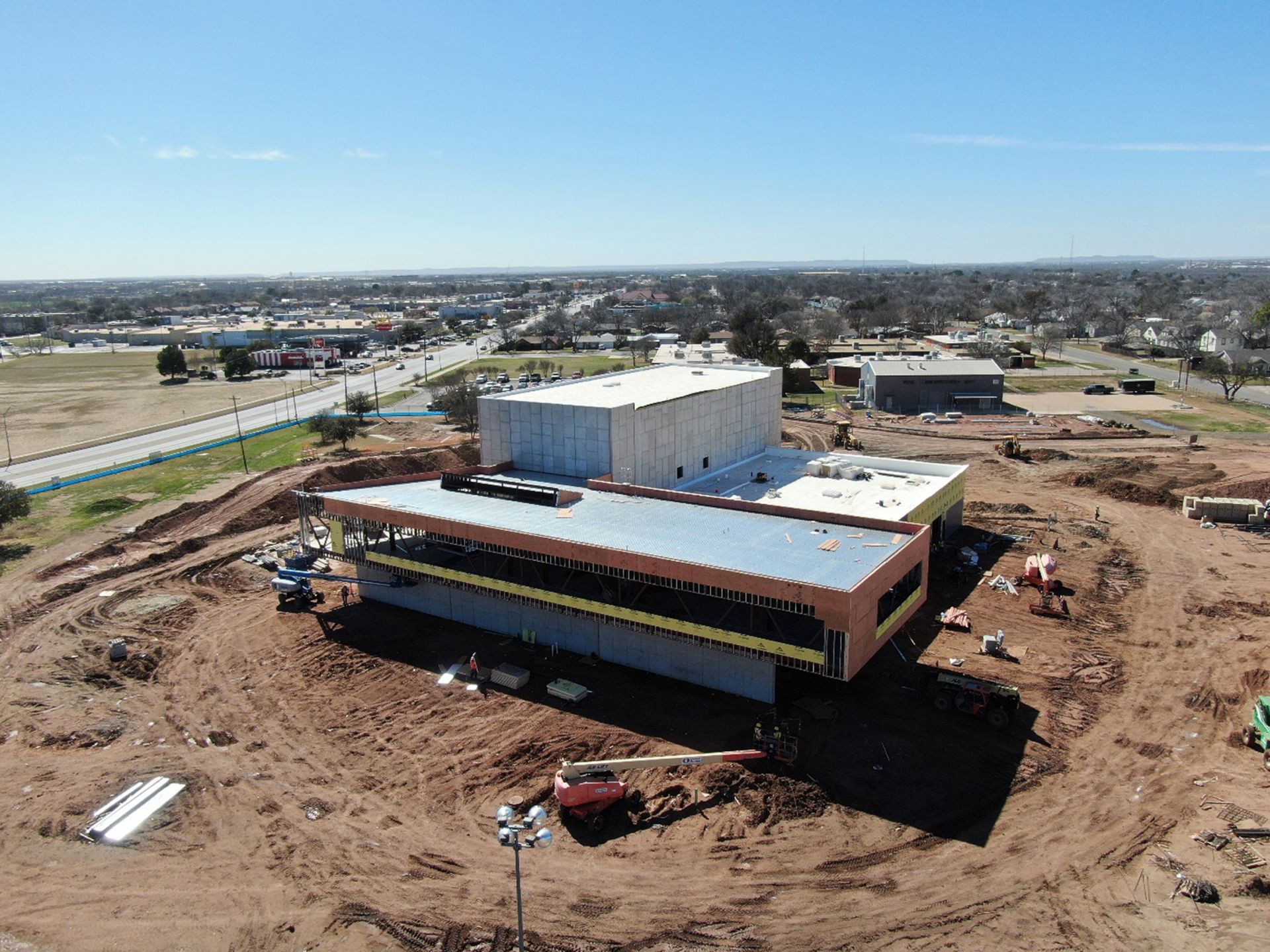
A south-facing view of the Dillard Science and Engineering Research Center at Abilene Christian University, scheduled for completion in the summer of 2023. The new facility will provide space for ACU’s NEXT Lab, as well as for research in chemistry, physics, and engineering.
Abilene Christian University’s Nuclear Energy eXperimental Testing (NEXT) Lab continues to make progress toward building a molten salt research reactor (MSRR) on the university’s campus. NEXT Lab submitted an application for a construction permit to the Nuclear Regulatory Commission last August, and in November the agency announced it had docketed the application—the first for a new research reactor in more than 30 years.
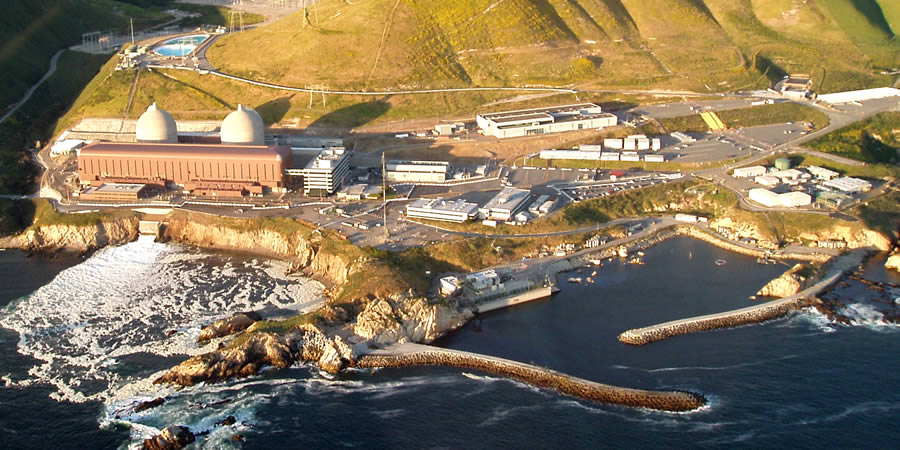
The Diablo Canyon nuclear power plant.
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission announced that an agency licensing board will hold oral arguments in a challenge to Pacific Gas and Electric’s application to renew its license for the Diablo Canyon independent spent fuel storage installation in California.
The arguments, which will be open to the public, will be heard by an NRC Atomic Safety and Licensing Board on May 24 beginning at 1 p.m. eastern time.
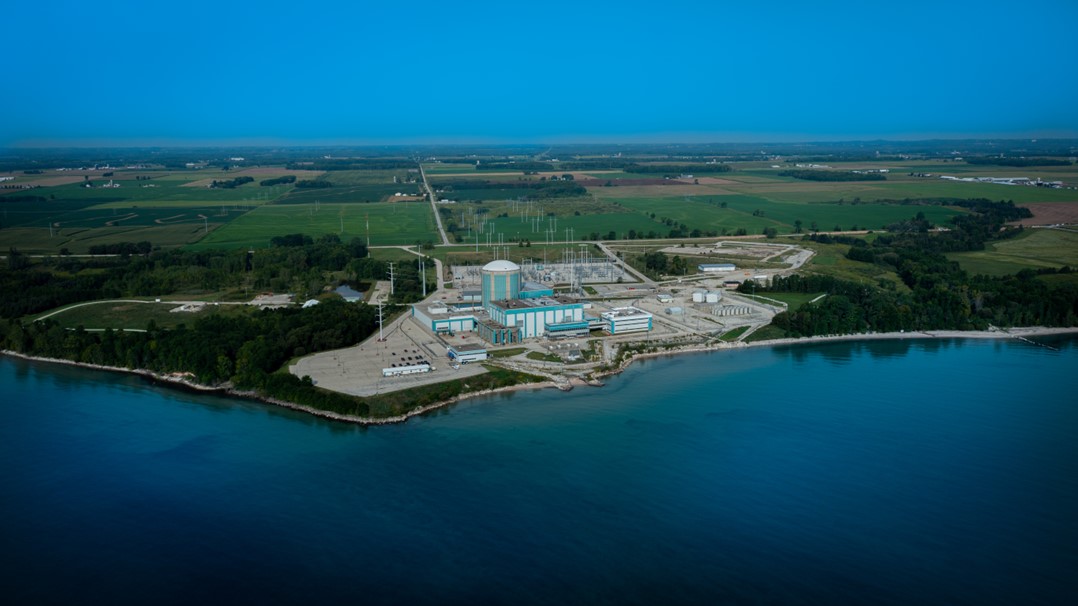
The Kewanee nuclear power plant is located along the shore of Lake Michigan. (Photo: EnergySolutions)
EnergySolutions subsidiary KewauneeSolutions is hoping to begin site restoration work at the closed Kewaunee nuclear power plant in Wisconsin later this year and has submitted a request to the Nuclear Regulatory Commission to use the plant’s decommissioning trust fund to do so.
The University of North Texas, one of the NRC grant recipients. (Photo: Michael Barera)
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission has announced its Minority-Serving Institutions Grants Program (MSIG) awards for fiscal year 2023. Four institutions were granted a total of $997,943: University of North Texas ($400,000 for fellowships), University of Central Florida ($397,943 for fellowships), University of Nevada–Las Vegas ($100,000 for scholarships), and Virginia Commonwealth University ($100,000 for scholarships).
More details about the grants for this year will be posted on the NRC’s grant awards website, where recipients of awards from previous years can also be seen.
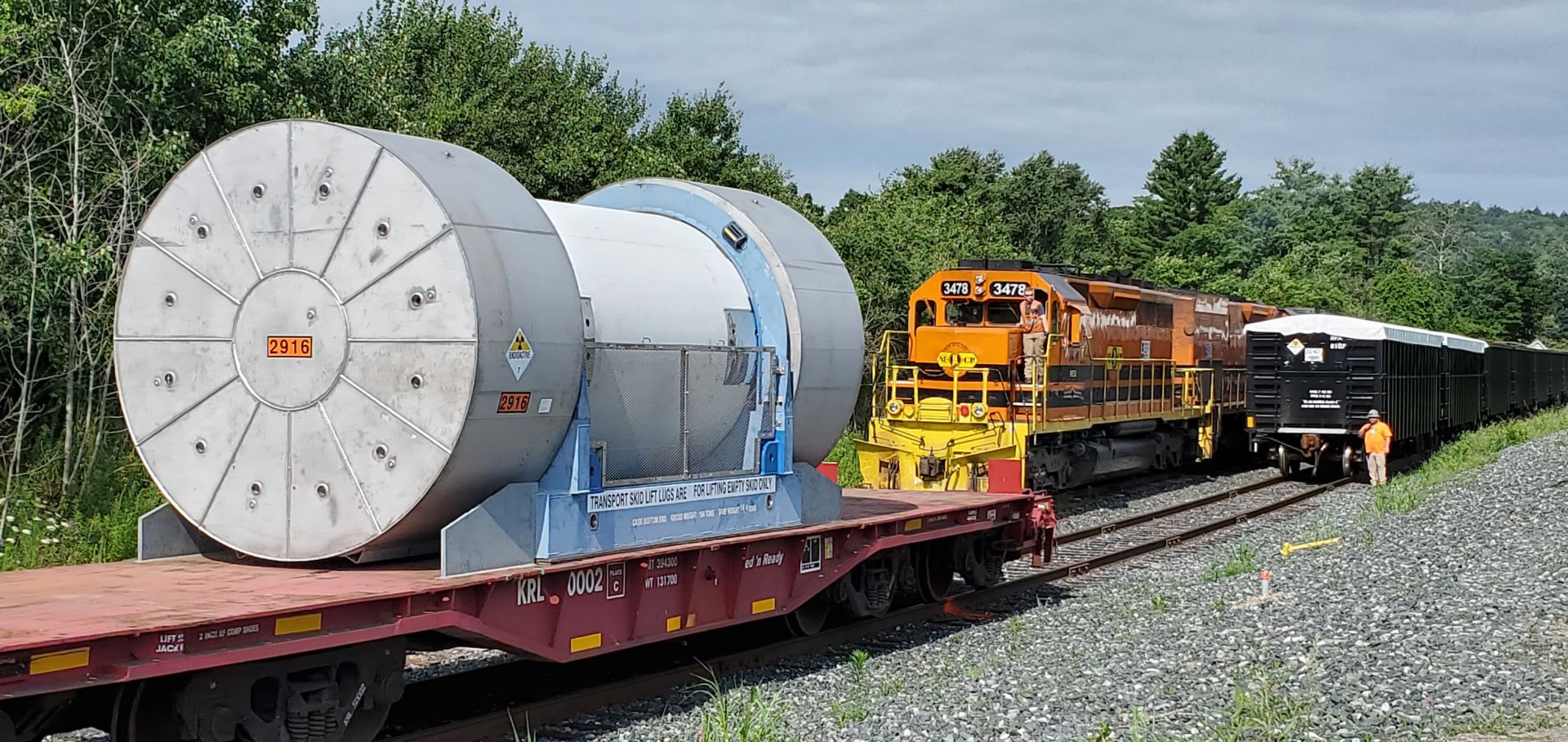
A loaded MP197HB cask is prepared for departure from the Vermont Yankee decommissioning site to West Texas. (Photos: Orano TN)
The rapid changes in the nuclear energy industry over the last decade, driven in part by fluctuating energy market prices and an aging fleet of reactors, have led to the closure of multiple reactors in the United States and other countries. These closures have increased the need for larger and more efficient ways to manage low-level radioactive waste processing and transport capacities. The safe transport of radioactive material is a key component of the overall nuclear industry reliability. Though sometimes perceived as a bottleneck and costly, it is necessary to send waste material to disposal.









.jpg)
