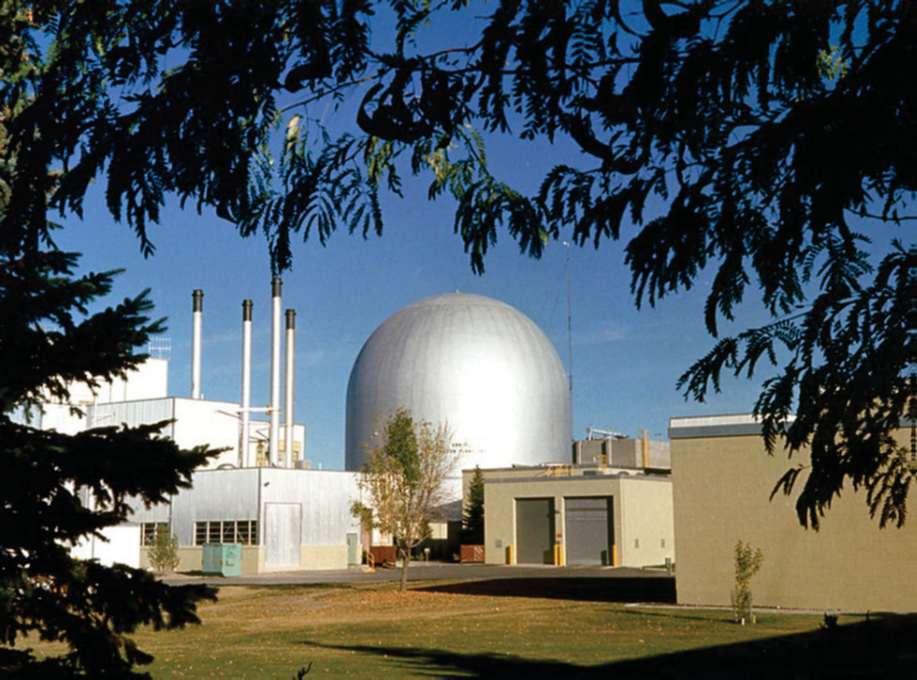
The EBR-II dome, site of the DOME advanced reactor test bed. (Photo: INL)
Heat pipes transfer heat out of the eVinci microreactor’s core and allow for air cooling without using water or pressurized gas. (Photo: DOE)
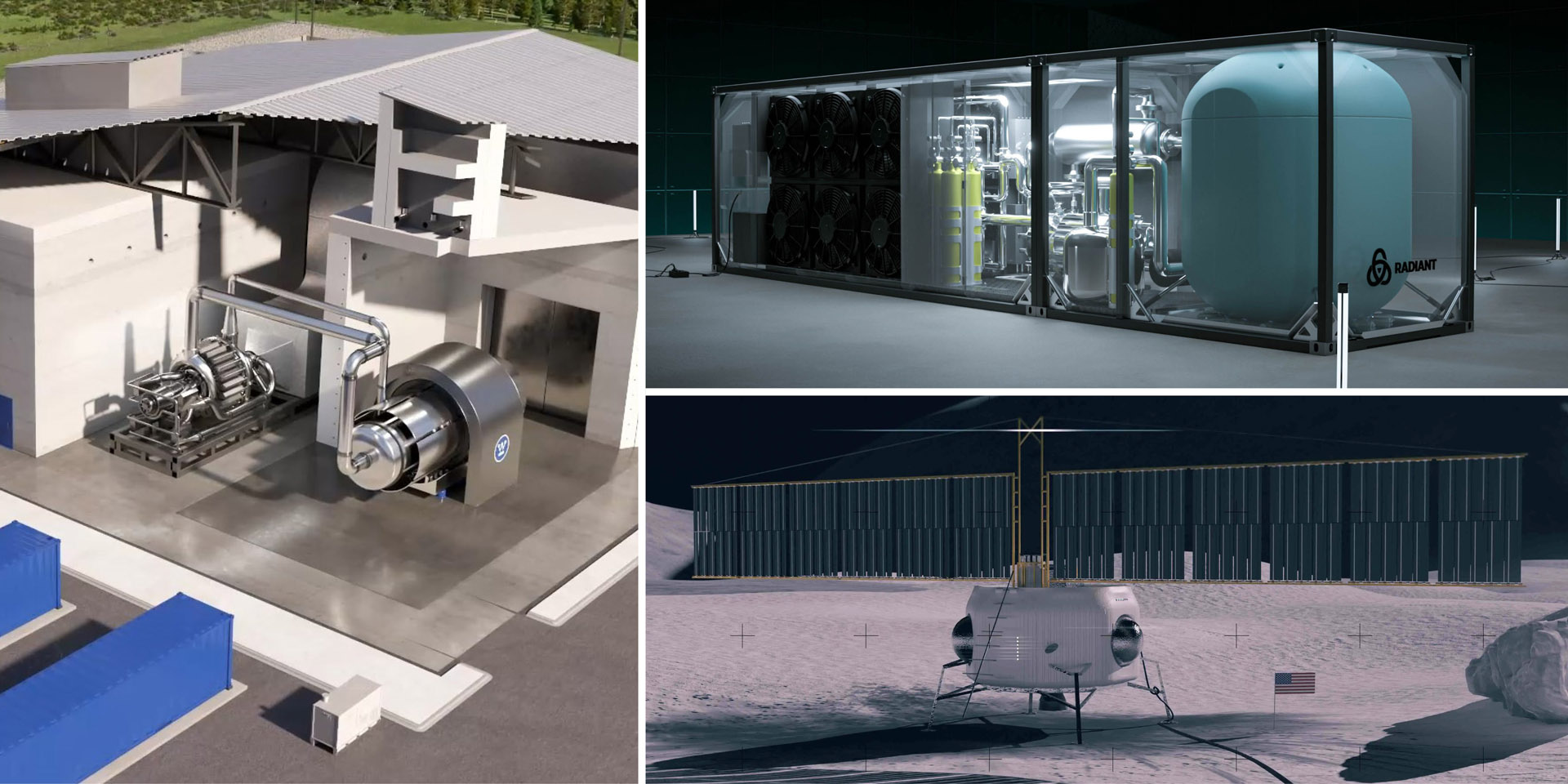
Westinghouse Electric Company has completed the front-end engineering and experiment design (FEEED) for a prototype microreactor at Idaho National Laboratory, the Department of Energy recently announced. The one-fifth scale version of eVinci, Westinghouse’s 5-MWe sodium-cooled heat pipe design, is one of three reactors that could be tested at the National Reactor Innovation Center’s (NRIC) DOME test bed “as early as 2026,” the DOE said.
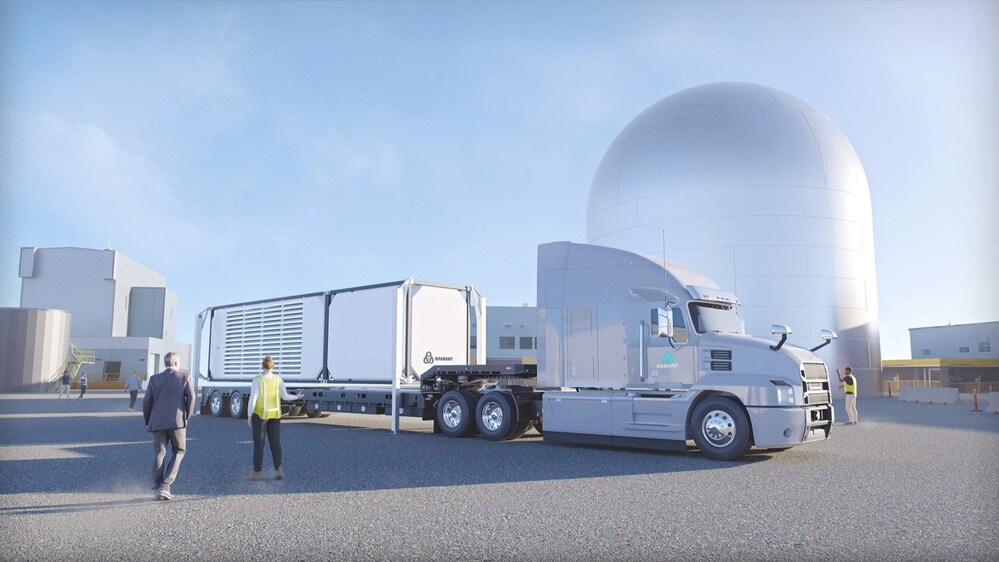
Concept art showing the delivery of Radiant’s Kaleidos to the DOME test bed. (Image: Radiant Industries/Ryan Seper)
Radiant Industries announced on June 4 that the safety design strategy (SDS) for a test of its Kaleidos microreactor in the National Reactor Innovation Center’s DOME test bed at Idaho National Laboratory now has approval from the Department of Energy. Radiant hopes to test Kaleidos—a 1-MW high-temperature, gas-cooled reactor—by 2026 and then market portable commercial reactors to power remote locations and provide backup or primary power for critical applications in hospitals or for disaster relief.
MCRE could be built inside the ZPPR cell (shown here) at INL’s Materials and Fuels Complex. (Photo: INL)
A tiny 200-kWt reactor the Department of Energy says would be the first critical fast-spectrum circulating fuel reactor and the first fast-spectrum molten salt reactor (MSR) could be built and operated inside the Zero Power Physics Reactor (ZPPR) cell at Idaho National Laboratory’s Materials and Fuels Center (MFC). Details included in the Molten Chloride Reactor Experiment (MCRE) draft environmental assessment (EA)—released on March 16 for two weeks of public comment (later extended to four weeks, through April 14)—covered the potential environmental impacts associated with the development, construction, operation, and decommissioning of MCRE at INL, facilitated by the National Reactor Innovation Center (NRIC).
The NS Savannah—the first merchant ship powered by a nuclear reactor.
The American Bureau of Shipping (ABS) has announced the launch of a research project that will look into barriers to the adoption of advanced nuclear propulsion for commercial vessels.
The $794,000 project, awarded to ABS last year by the Department of Energy’s Office of Nuclear Energy, is now being formally contracted through the DOE’s U.S. Industry Opportunities for Advanced Nuclear Technology Development funding opportunity, according to ABS’s August 17 announcement. Support is to be provided by Idaho National Laboratory’s National Reactor Innovation Center (NRIC).
The Molten Chloride Reactor Experiment will be built at Idaho National Laboratory to demonstrate criticality in a fast-spectrum salt-cooled reactor within five years. (Image: Southern Company)
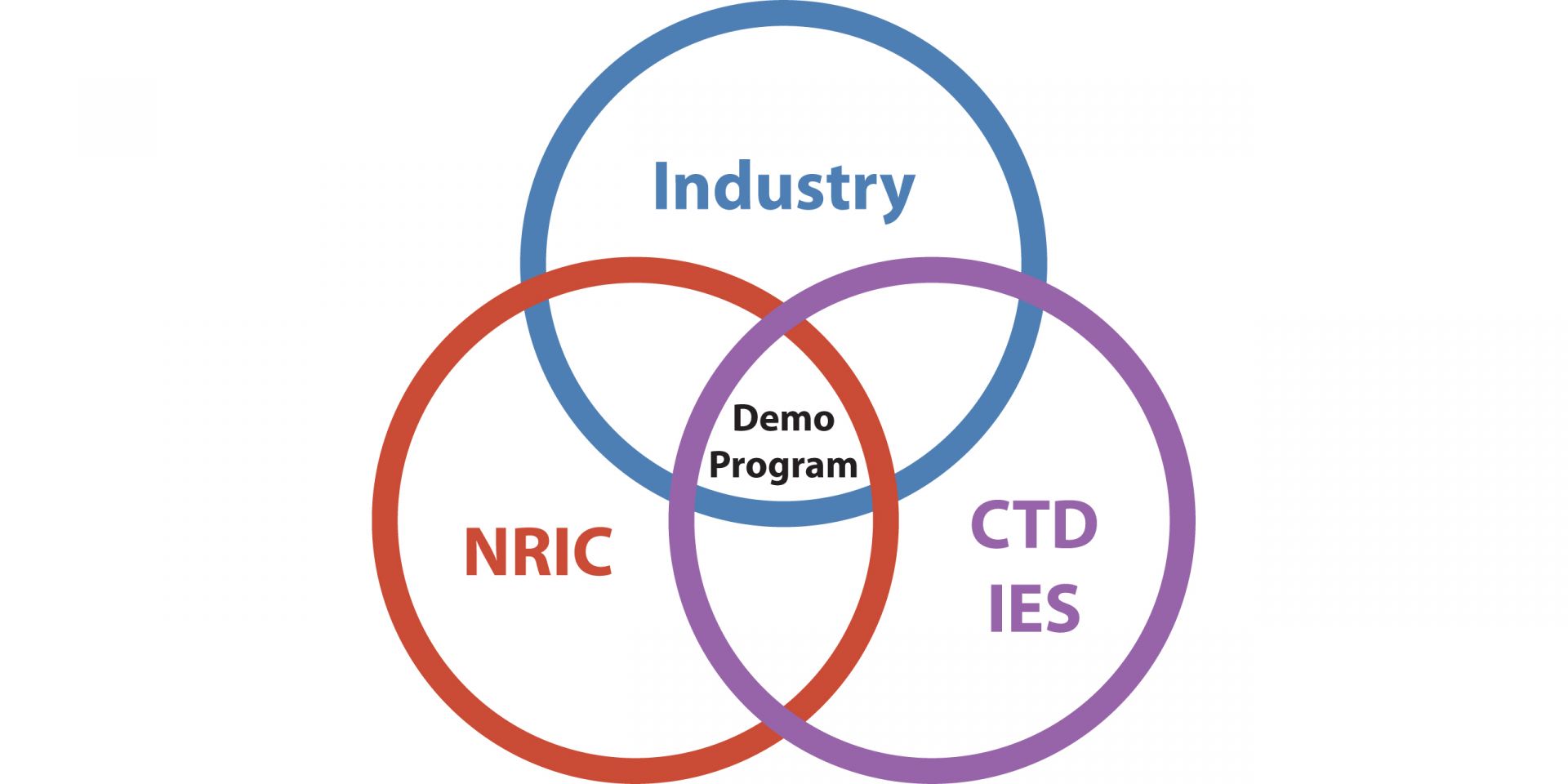
The demonstration program aims to accelerate innovation and deployment of energy concepts at the intersection of industry needs, NRIC’s mission, and the R&D portfolio of CTD IES. (Graphic: BEA)
The National Reactor Innovation Center (NRIC) wants to hear from developers and end users interested in integrated energy systems for advanced reactors. Battelle Energy Alliance (BEA), the managing and operating contractor for Idaho National Laboratory, has issued a call for Expressions of Interest for a potential multi-phase demonstration program for innovative uses of nuclear energy, to be carried out by NRIC and the Crosscutting Technology Development Integrated Energy Systems (CTD IES) program. The final date for responses is May 21.
Advanced reactor demonstration projects on the horizon will challenge the nuclear supply chain in new ways. A vital component that can be east to overlook is the need for skilled construction, trades, and craft workers. That's why Idaho National Laboratory is forging valuable networks to address these needs.
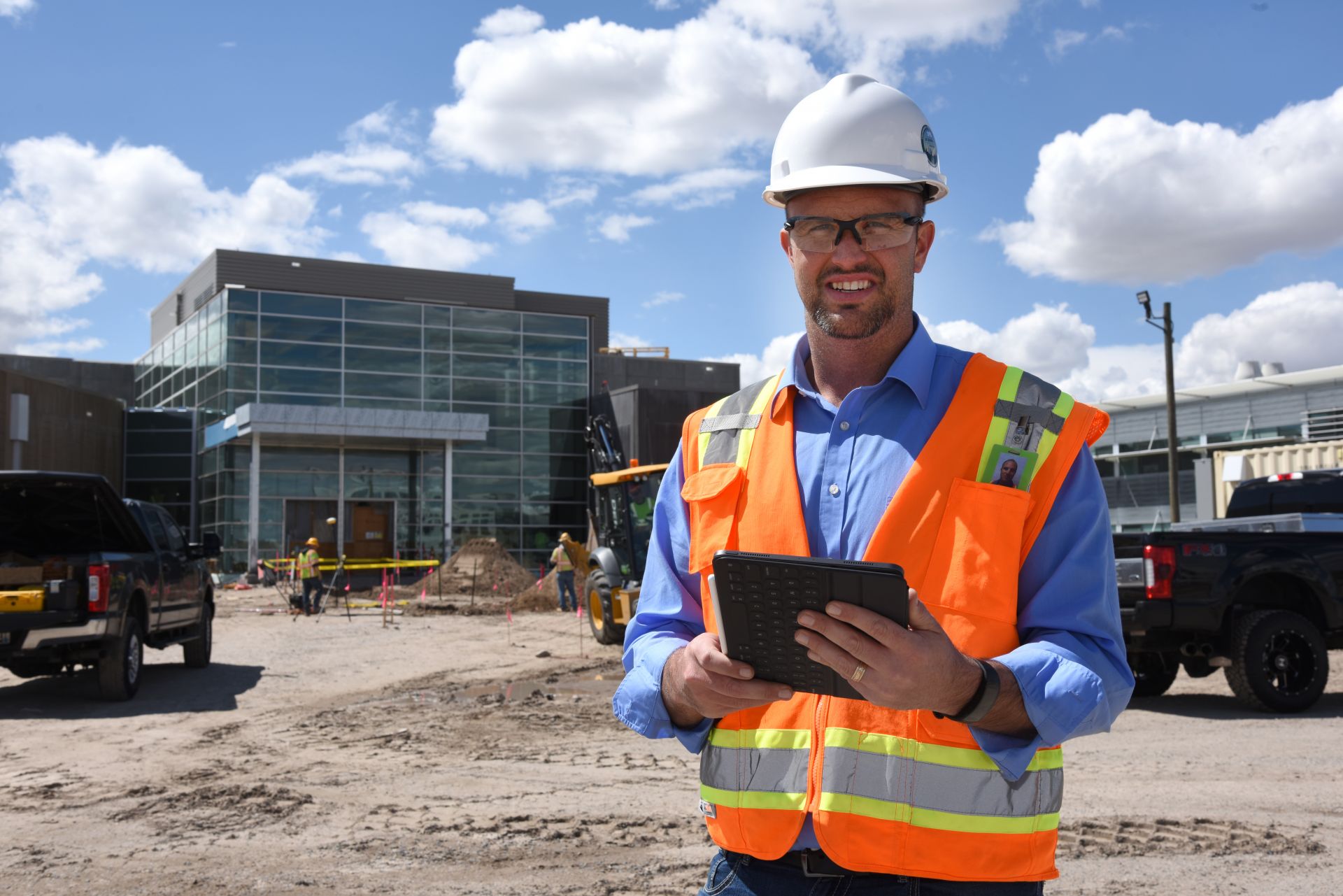

INL will need technical, innovative, and safety-minded construction personnel for the advanced nuclear projects ahead. Photo: INL
Around the world, researchers in the energy industry are engaging in the work of studying, testing, and developing carbon-free energy solutions. Throughout these circles, many scientists and engineers are embracing the possibilities of advanced nuclear technologies, including small modular reactors and microreactors. While these innovative technologies are poised to address some of the nation’s biggest concerns, they also present their own unique challenges, including the need for a large and talented workforce within the construction industry.
Fortunately, the state of Idaho and its key nuclear players are well-equipped for this challenge. In southeastern Idaho, home of Idaho National Laboratory, strong partnerships throughout the region have forged networks between the lab and the educational institutions, employers, trades, and unions that are working to establish this highly specialized nuclear talent pipeline.