Focus on Ukraine
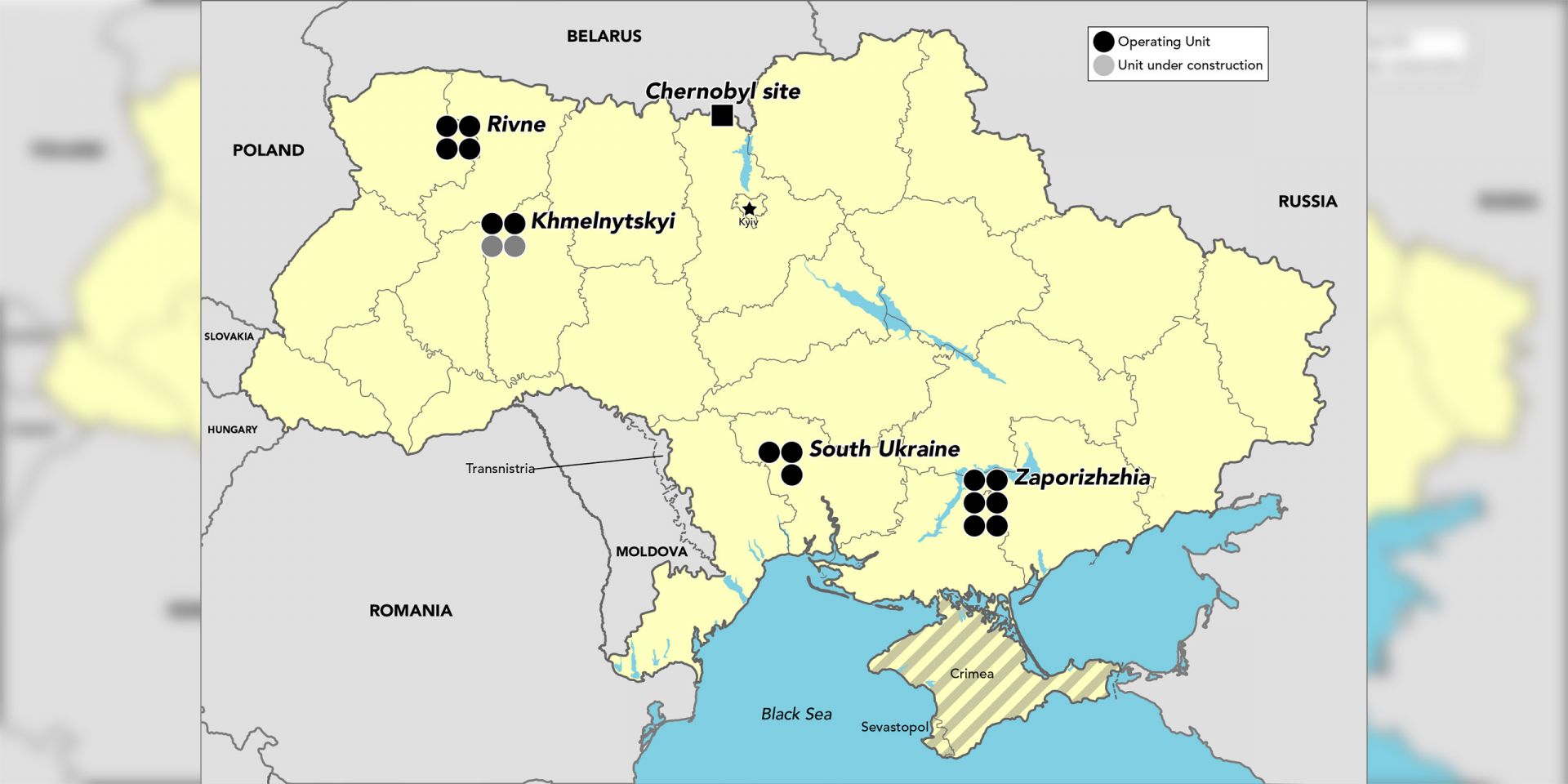
We’ve sifted through facts and statistics on nuclear power in Ukraine to offer some choice insights here. Want more international nuclear data? Check out the March 2022 Nuclear News Reference Issue.


We’ve sifted through facts and statistics on nuclear power in Ukraine to offer some choice insights here. Want more international nuclear data? Check out the March 2022 Nuclear News Reference Issue.
The Leningrad nuclear power plant’s Unit I-2, a 925-MWe RBMK-1000 light-water–cooled graphite-moderated reactor, was permanently shut down on November 10, according to Rosatom, Russia’s state atomic energy corporation. The shutdown occurred at 12:30 a.m. Moscow time.
The unit was the oldest operating reactor at the plant, having achieved initial criticality in May 1975 and entered commercial operation in February 1976. Two additional RBMK-1000s remain in operation at Leningrad—Units I-3 and I-4, both of which have been in operation for about 40 years.
The retired reactor is to be replaced by Unit II-2, one of two 1,085-MWe Generation III+ VVER-1200 pressurized water reactors at the Leningrad site. The new unit was connected to the Russian grid in October, and on November 6 it received regulatory approval to begin pilot operation. (Leningrad’s other VVER-1200, Unit II-1, started commercial operation in 2018.) Following the trial operation, Unit II-2 will be shut down for an additional equipment inspection by a state commission before being put into commercial operation early next year, according to Rosenergoatom, Rosatom’s electric power division.