ANS Standards Committee publishes new standard for light water reactor risk-informed, performance-based design
The new standard ANSI/ANS-30.3-2022, Light Water Reactor Risk-Informed, Performance-Based Design, has just been issued by the American Nuclear Society. Approved by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) on July 21, 2022, the standard provides requirements for the incorporation of risk-informed, performance-based (RIPB) principles and methods into the nuclear safety design of commercial light water reactors. The process described in this standard establishes a minimum set of process requirements the designer must follow in order to meet the intent of this standard and appropriately combine deterministic, probabilistic, and performance-based methods during design development.
Rethinking seismic design may be key for making nuclear plant construction affordable.
Nuclear power plants not only provide the nation’s largest source of carbon-free electricity, they also can operate 24 hours a day, 365 days a year to augment intermittent renewables such as wind and solar. Further, studies show that nuclear energy is among the safest forms of energy production, especially when considering factors such as industrial accidents and disease associated with fossil fuel emissions. All said, nuclear has the potential to play a key role in the world’s energy future. Before nuclear can realize that potential, however, researchers and industry must overcome one big challenge: cost.
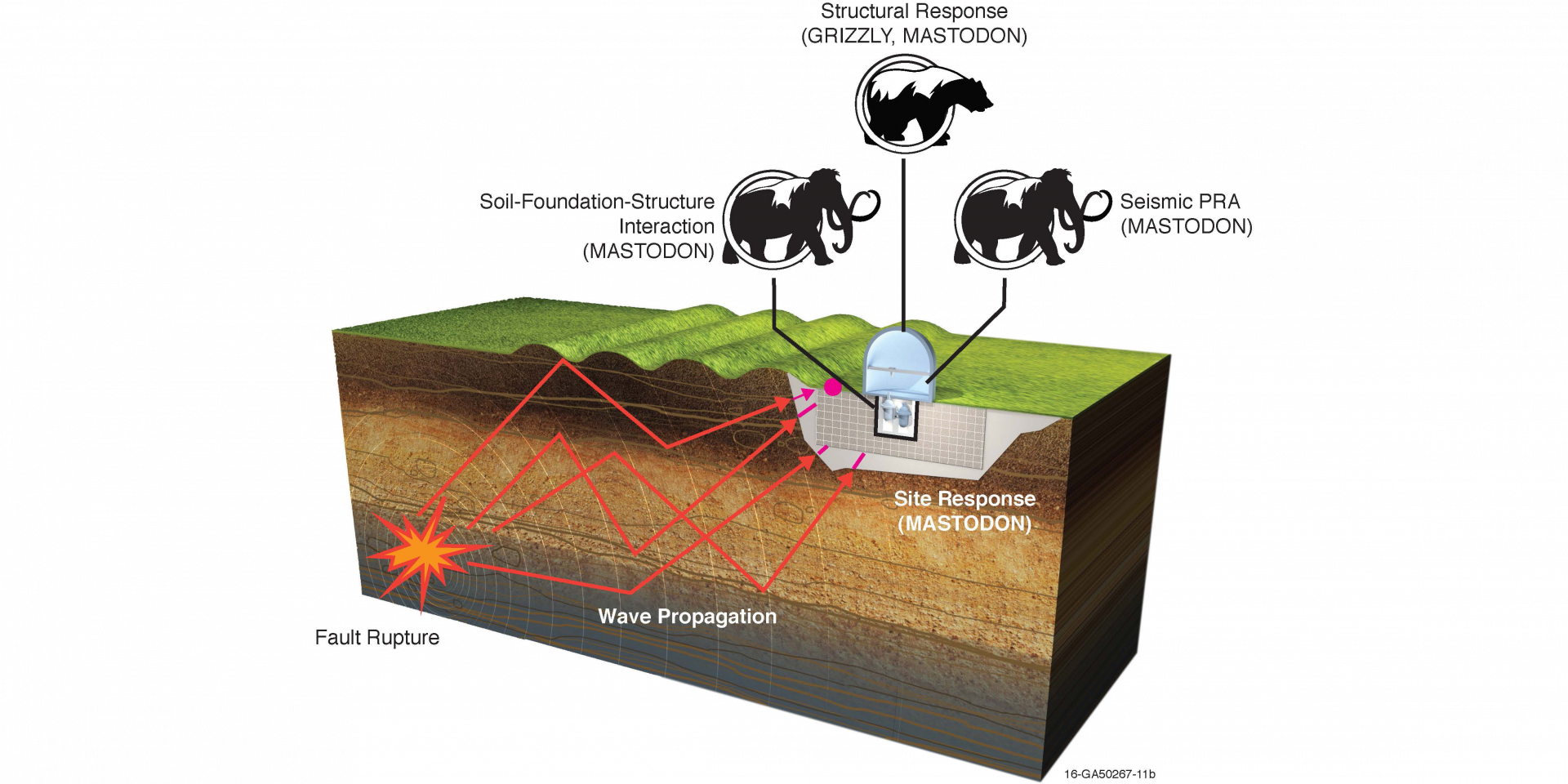
A team at Idaho National Laboratory is collaborating with experts around the nation to tackle a major piece of the infrastructure equation: earthquake resilience. INL’s Facility Risk Group is taking a multipronged approach to reduce the amount of concrete, rebar, and other infrastructure needed to improve the seismic safety of advanced reactors while also substantially reducing capital costs. The effort is part of a collaboration between INL, industry, the Department of Energy’s Advanced Research Projects Agency–Energy (ARPA-E), and the State University of New York–Buffalo (SUNY Buffalo).
Risk-informed and performance-based approaches to nuclear safety have saved money and improved safety for current reactors and have the potential to offer even greater benefits for advanced reactors.
June 26, 2020, 3:05PMNuclear NewsN. Prasad Kadambi, Edward Wallace, James O’Brien, and Robert Youngblood Since the 1980s, the nuclear power industry in the United States has worked to enhance the regulatory framework for nuclear facilities by making it more risk-informed and performance-based (RIPB). This has had some success in improving safety and reducing regulatory burden by focusing resources on the most risk--significant areas and allowing greater flexibility in choosing ways to achieve desired safety outcomes. However, there are further opportunities for the use of RIPB approaches in addressing current regulations and applying implementation tools, and in developing new RIPB regulations and advanced tools to further sharpen the focus on risk and performance outcomes.





