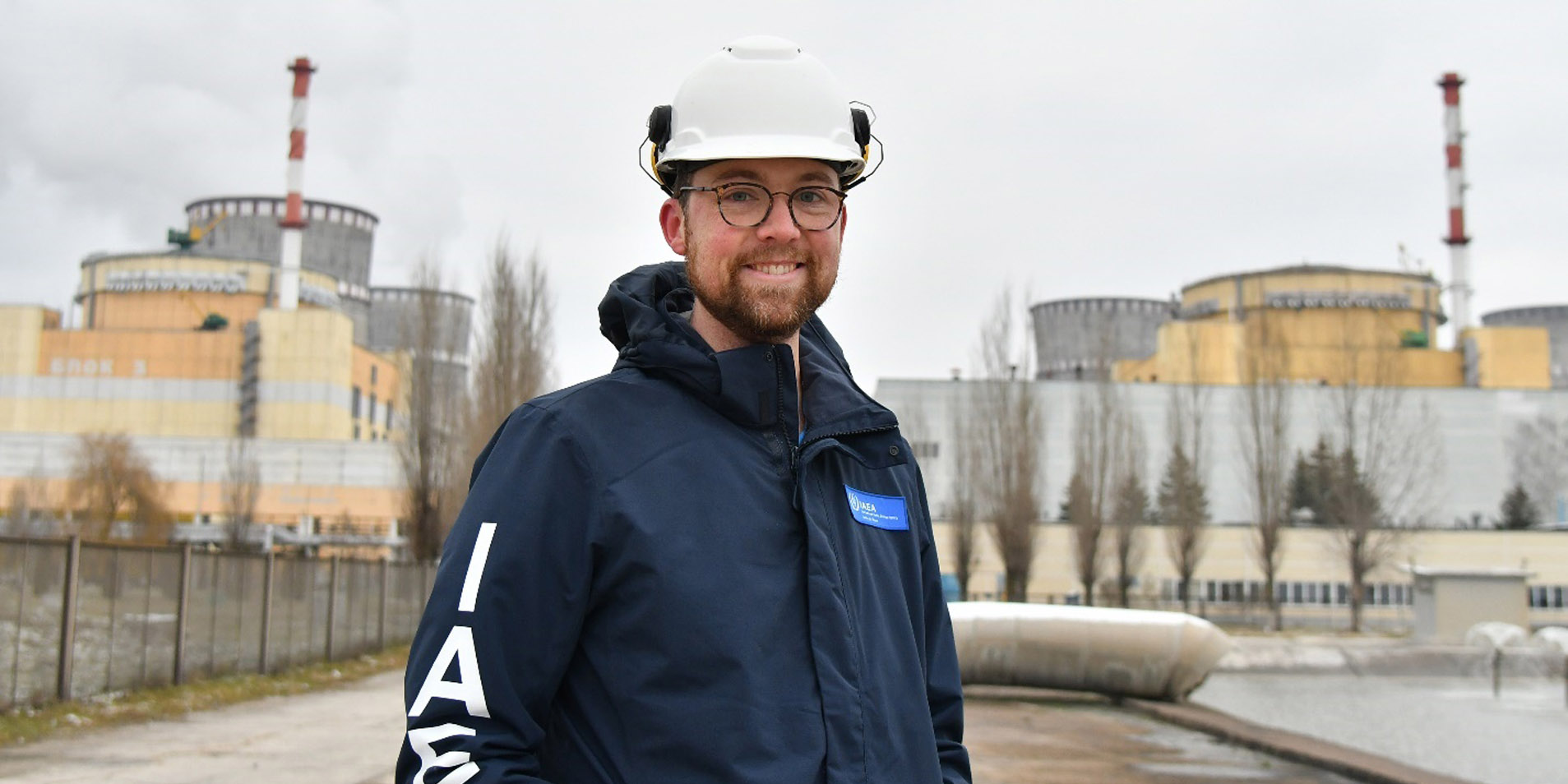
Olsen was part of the IAEA team that inspected the Rivne nuclear power plant in Ukraine last year. (Photo: IAEA)
Student members are the future of the American Nuclear Society, and ANS believes in the importance of supporting students those who have shown academic, service, and leadership excellence as they navigate their early careers. Robert Olsen, now a nuclear security officer with the International Atomic Energy Agency in Vienna, Austria, was one such beneficiary.
The ministers representing their respective nations as the statement on civil nuclear fuel cooperation was announced were (from left) Jonathan Wilkinson, minister of natural resources of Canada; Yasutoshi Nishimura, Japan’s minister of economy, trade, and industry; Jennifer Granholm, U.S. energy secretary; Grant Shapps, U.K. energy security secretary; and Agnes Pannier-Runacher, French minister for energy transition.
A civil nuclear fuel security agreement between the five nuclear leaders of the G7—announced on April 16 on the sidelines of the G7 Ministers’ Meeting on Climate, Energy and Environment in Sapporo, Japan—establishes cooperation between Canada, France, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States to flatten Russia’s influence in the global nuclear fuel supply chain.
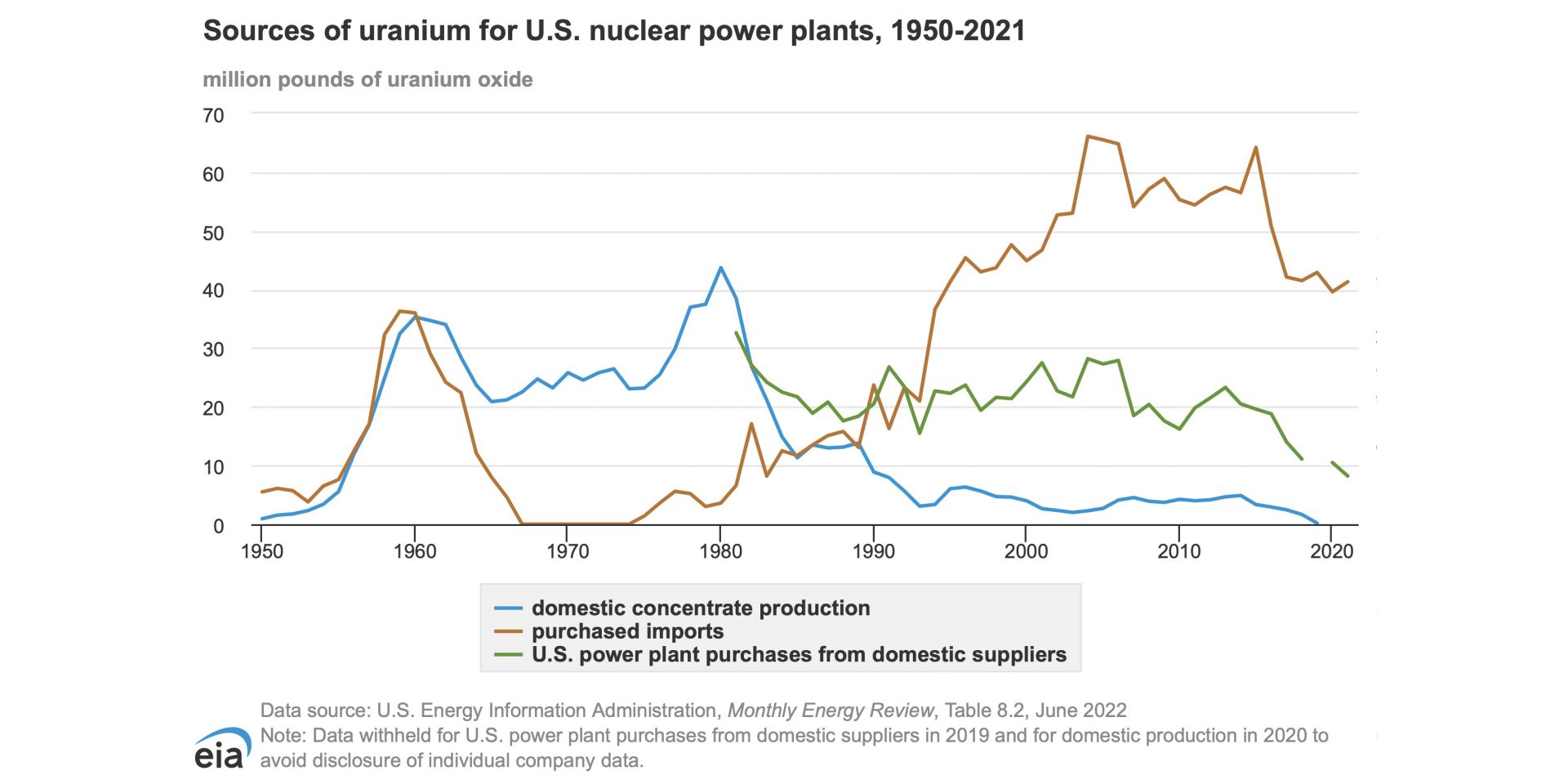
This chart from the EIA shows sources of uranium for U.S. nuclear power plants, 1950-2021. In 2020, according to the chart, 39.60 million pounds of uranium oxide was imported for the domestic nuclear power plant fleet. (Credit: Energy Information Agency)
The naturalist John Muir is widely quoted as saying, “When we try to pick out anything by itself, we find it hitched to everything else in the Universe.” While he was speaking of ecology, he might as well have been talking about nuclear fuel.
At the moment, by most accounts, nuclear fuel is in crisis for a lot of reasons that weave together like a Gordian knot. Today, despite decades of assertions from nuclear energy supporters that the supply of uranium is secure and will last much longer than fossil fuels, the West is in a blind alley. We find ourselves in conflict with Russia with ominous implications for uranium, for which Russia holds about a 14 percent share of the global market, and for two processes that prepare uranium for fabrication into reactor fuel: conversion (for which Russia has a 27 percent share) and enrichment (a 39 percent share).
The Zaporizhzhia plant (Image: Energoatom)
As if being stuck in the middle of a combat zone isn’t sufficiently nerve-racking, workers at Ukraine’s Zaporizhzhia nuclear power plant—under Russian occupation since last March—must now concern themselves with having access to enough water to keep the facility safe.
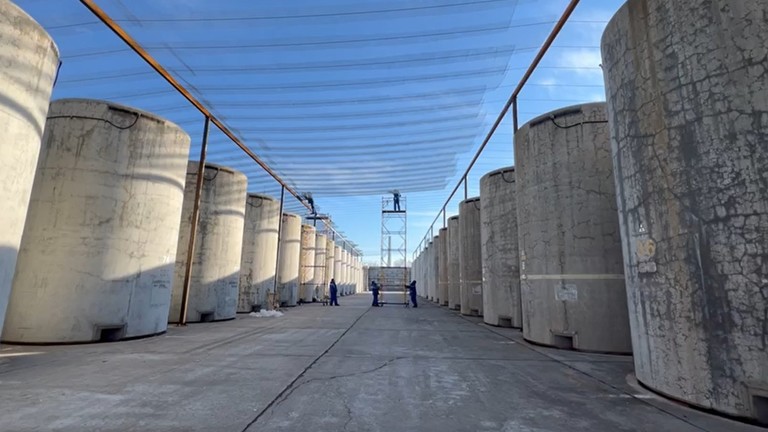
This image from a video reportedly shows the start of installation of a protective covering over spent fuel storage tanks at the Zaporizhzhia nuclear power plant in Ukraine. (Image: Telegram/Vladimir Rogov)
Russia has begun construction of protected covering at Ukraine’s Zaporizhzhia nuclear power plant, according to a December 17 report from Russian news outlet RT. The story has been picked up in the West by some news agencies but has not been widely circulated.
Vladimir Rogov, a Russian-appointed official in Zaporizhzhia Oblast, said, “Russia is constructing a protective dome over spent radioactive fuel stores at the [Zaporizhzhia] nuclear power plant as Ukrainian forces continue to target the facility.”
The Yakutia awaits launch at St. Petersburg’s Baltic Shipyard on Nov. 22. (Photo: TASS/Valentin Yegorshin)
Advancing its efforts to develop the Arctic and establish new energy markets, Russia launched a new nuclear-powered icebreaker, the Yakutia, in St. Petersburg during a November 22 ceremony. At the launching in the northern Russian port city, the Russian flag was raised on another nuclear icebreaker, the Ural. Overseeing the events via video link from the Kremlin, Russian president Vladimir Putin said that the icebreakers “were laid down as part of a large serial project and are part of our large-scale, systematic work to reequip and replenish the domestic icebreaker fleet, to strengthen Russia's status as a great Arctic power.”