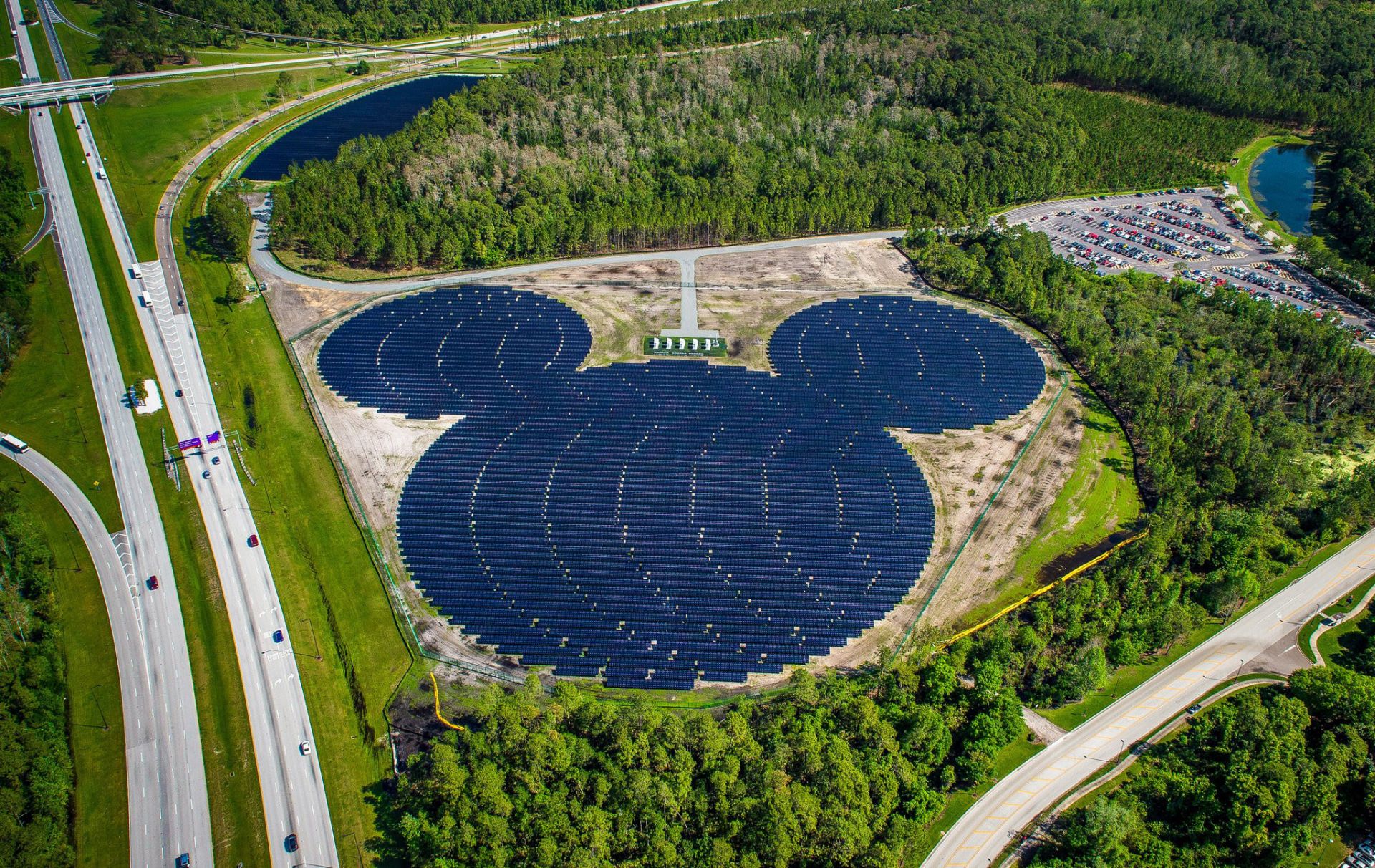
The Mickey Mouse–shaped solar array near Epcot is made of 48,000 solar panels and is operated by Duke Energy. (Photo: Duke Energy)
There is extra significance to the American Nuclear Society holding its annual meeting in Orlando, Florida, this past week. That’s because in 1967, the state of Florida passed a law allowing Disney World to build a nuclear power plant.
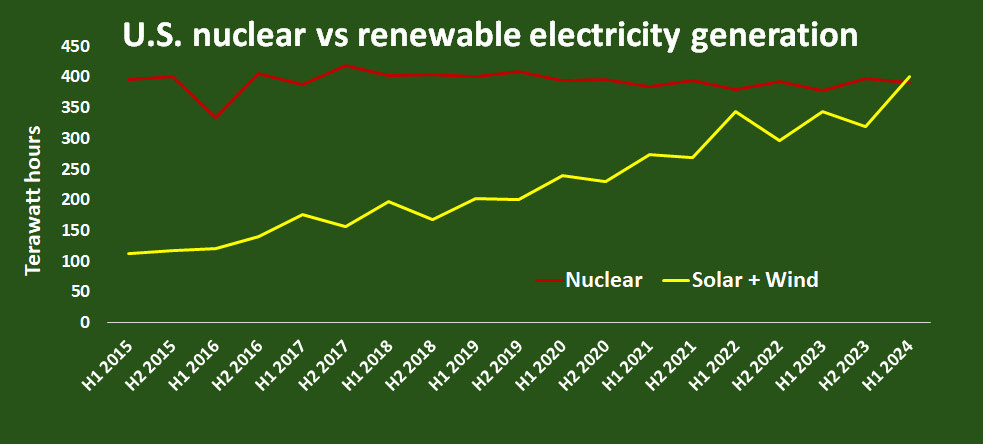
U.S. nuclear vs. renewable electricity generation. (Image: Ember)
The combined energy generation in the United States from solar and wind during the first half of the year was more than that of nuclear plants for the first time, according to data from energy think tank Ember.
Electricity generation from utility-scale solar and wind assets during the first half of 2024 was a record 401.4 terawatt-hours, compared with 390.5 TWh from nuclear reactors
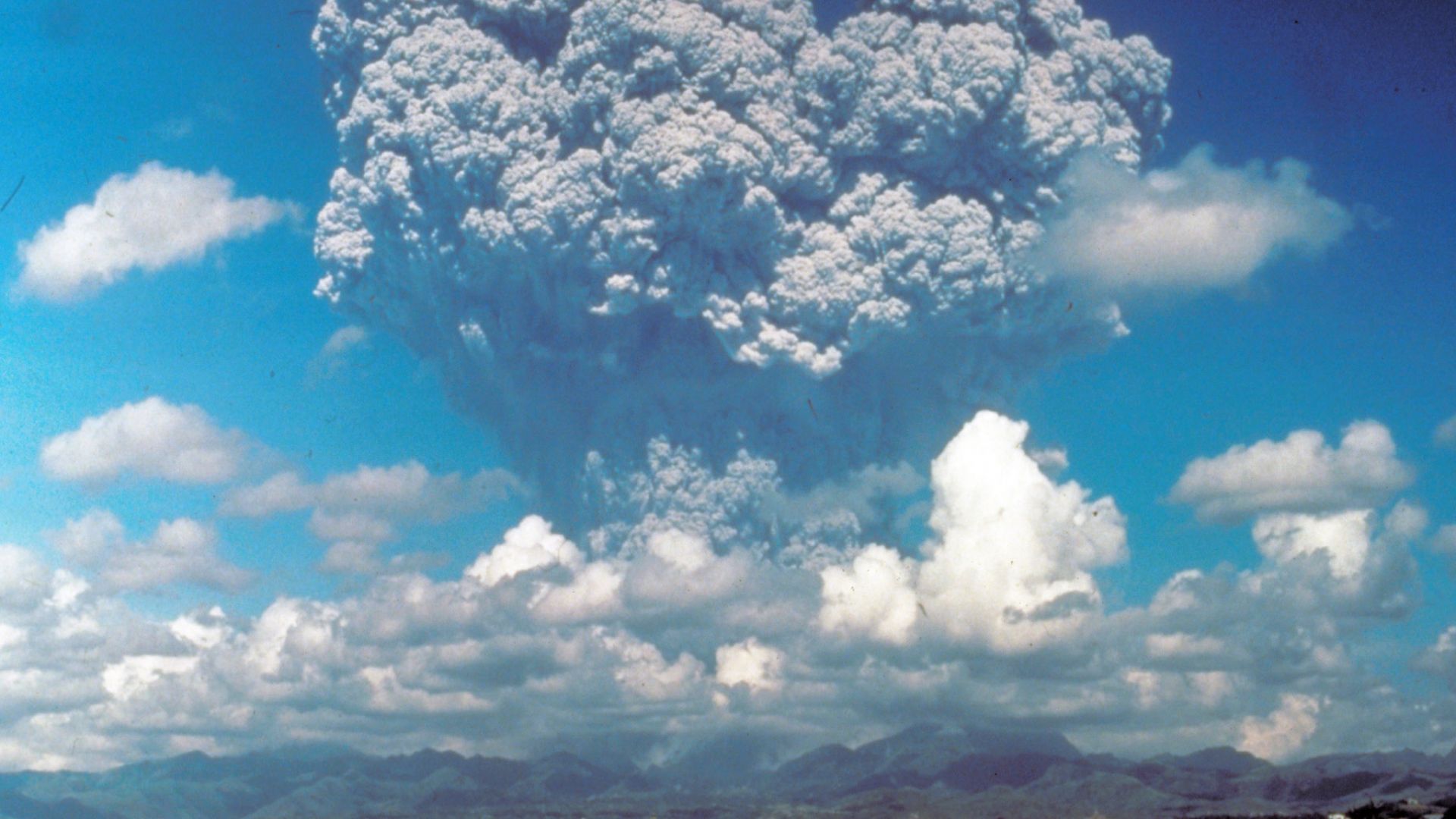
Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines, as it began its cataclysmic eruption in 1991. Millions of tons of particulates were blown into the stratosphere, causing global cooling, similar to what solar geoengineering would do in a controlled way. (Photo: U.S. Geological Survey)
We’re failing.
We’re failing to decarbonize the world in any significant way. Global greenhouse gas emissions are still rising and appear on track to continue rising until at least 2040—the result of energizing the developing world.
Comanche Peak nuclear power plant. (Photo: Meranda Cohn/Vistra)
When a technical problem with a feedwater pump at Unit 1 of the Comanche Peak nuclear power plant caused the unit to shut down temporarily on June 16, a new backup system was employed by grid operator Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT) to make up for the electricity loss.
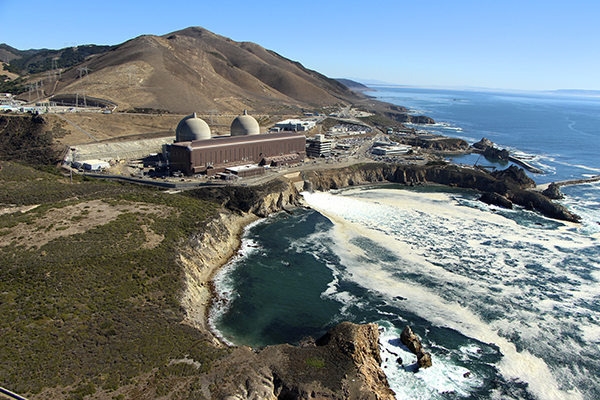
The Diablo Canyon nuclear power plant.
There is still a chance for California’s last remaining nuclear power plant to stay open.
Last Friday, more than 50 nuclear advocates testified in support of the Diablo Canyon nuclear power plant at a California Energy Commission workshop. Many spoke of the need for California to shore up its electricity grid in the face of coming heat waves and power outages. Others emphasized that closing the plant, which generates 2.2 GW of electricity and currently provides 8.6 percent of the state’s total supply and about 15 percent of its low-carbon electricity, would be devastating to California’s emission-reduction goals.
The electric power transmission grid of the U.S. consists of thousands of miles of lines operated by hundreds of companies.
To do big things, like building the interstate highway system, or going to the moon, government usually has a plan. Electric companies and grid operators, which are responsible for keeping the lights on, always have a plan. But something unusual has happened in the past few months. About four dozen U.S. utilities, plus the federal government and many states, have promised to do something extremely big: to eliminate carbon dioxide emissions, or cut them drastically. But they are not clear on how.
A statement from Steven P. Nesbit, president of the American Nuclear Society, and Lonnie R. Stephenson, international president of the International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers.
September 8, 2021, 6:59AMANS Nuclear CafeSteven P. Nesbit and Lonnie R. Stephenson America’s electric utility workers and nuclear engineers are ready to work together to help rapidly decarbonize and electrify the economy. We welcome provisions in the bipartisan infrastructure bill that aim to prevent premature closures of our nuclear power plants. Through measures such as production tax credits, President Biden can safeguard America’s largest carbon-free energy source by recognizing the clean-air contributions of nuclear energy.











 A recent article from
A recent article from 