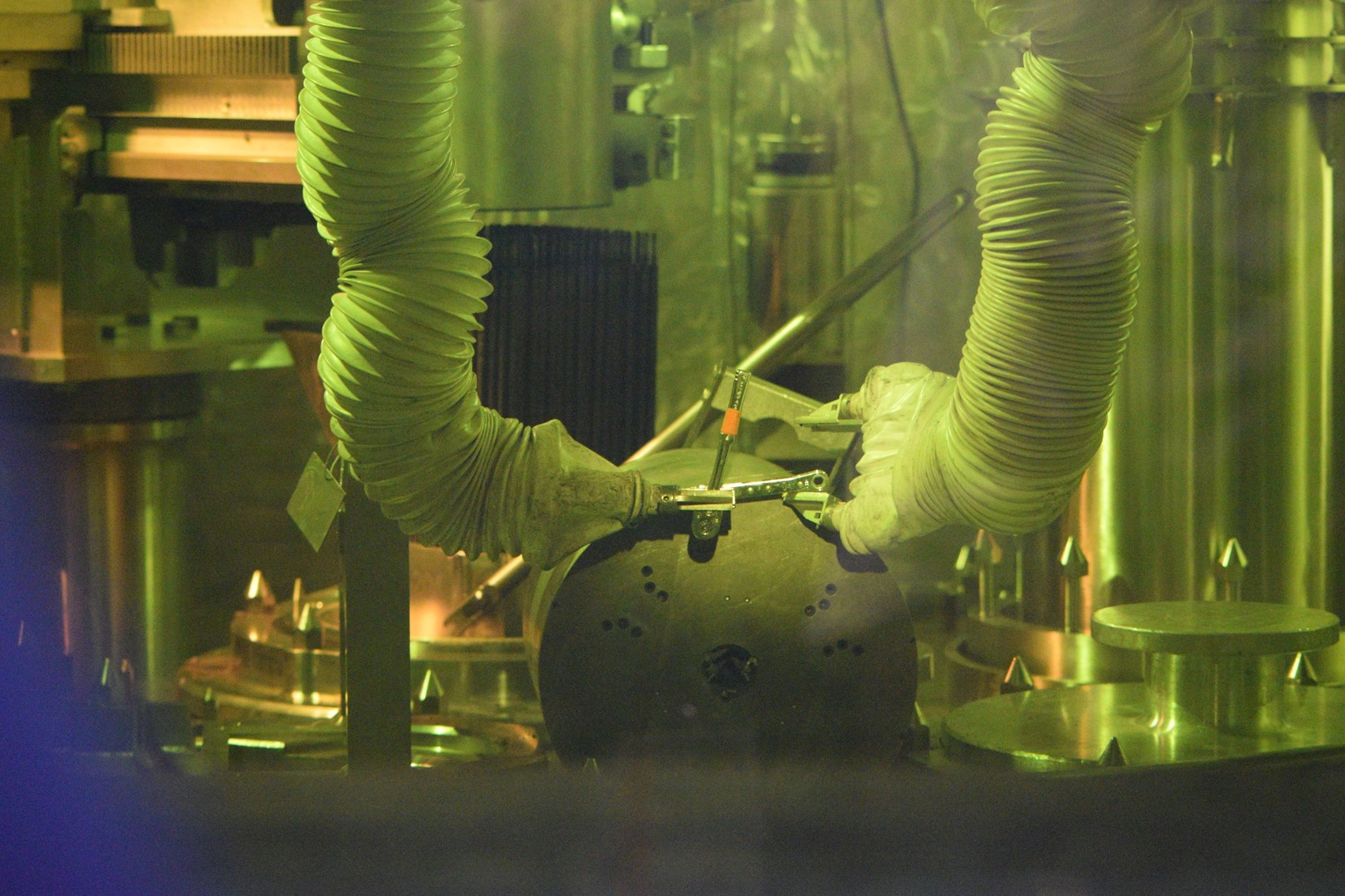
Operators disassemble a cutter head inside a module at the Savannah River's Tritium Extraction Facility using manipulators and hand tools. (Photo: SRNS)
Using basic hand tools and remote manipulators, operators at Savannah River Nuclear Solutions (SRNS) were able to reduce radiation exposure to workers performing cutter head maintenance in the Savannah River Site’s Tritium Extraction Facility (TEF).
According to SRNS, the innovative procedure proved to be an excellent example of real-world application of As Low As Reasonably Achievable (ALARA) principles of time, distance, and shielding.
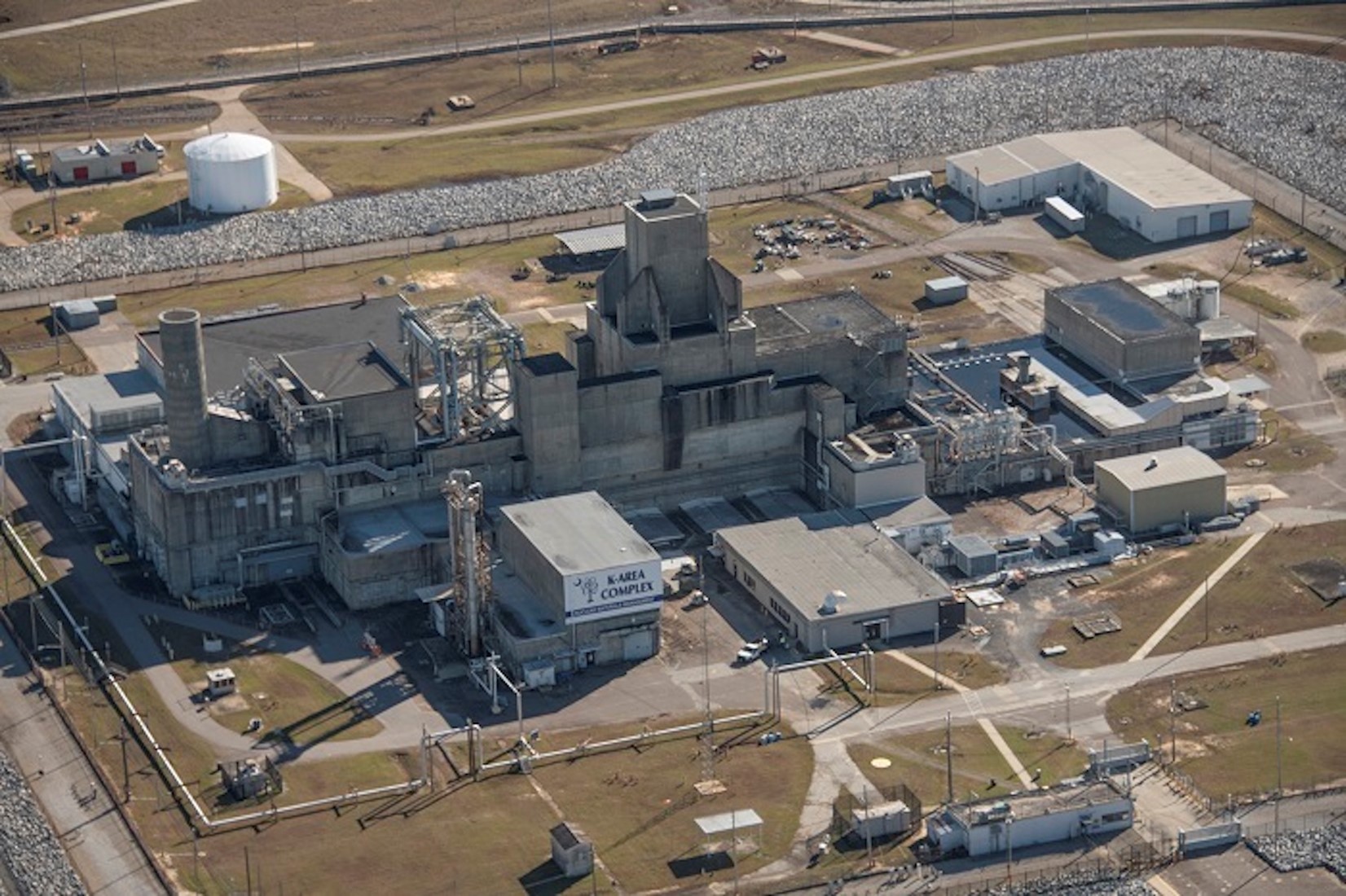
A view of Savannah River’s K Area Complex, where plutonium downblending operations take place. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management has doubled the number of work shifts for employees in glove box operations at its Savannah River Site in South Carolina. The increased work pace will help the department meet its commitment to South Carolina to remove surplus plutonium from the state, the DOE said.
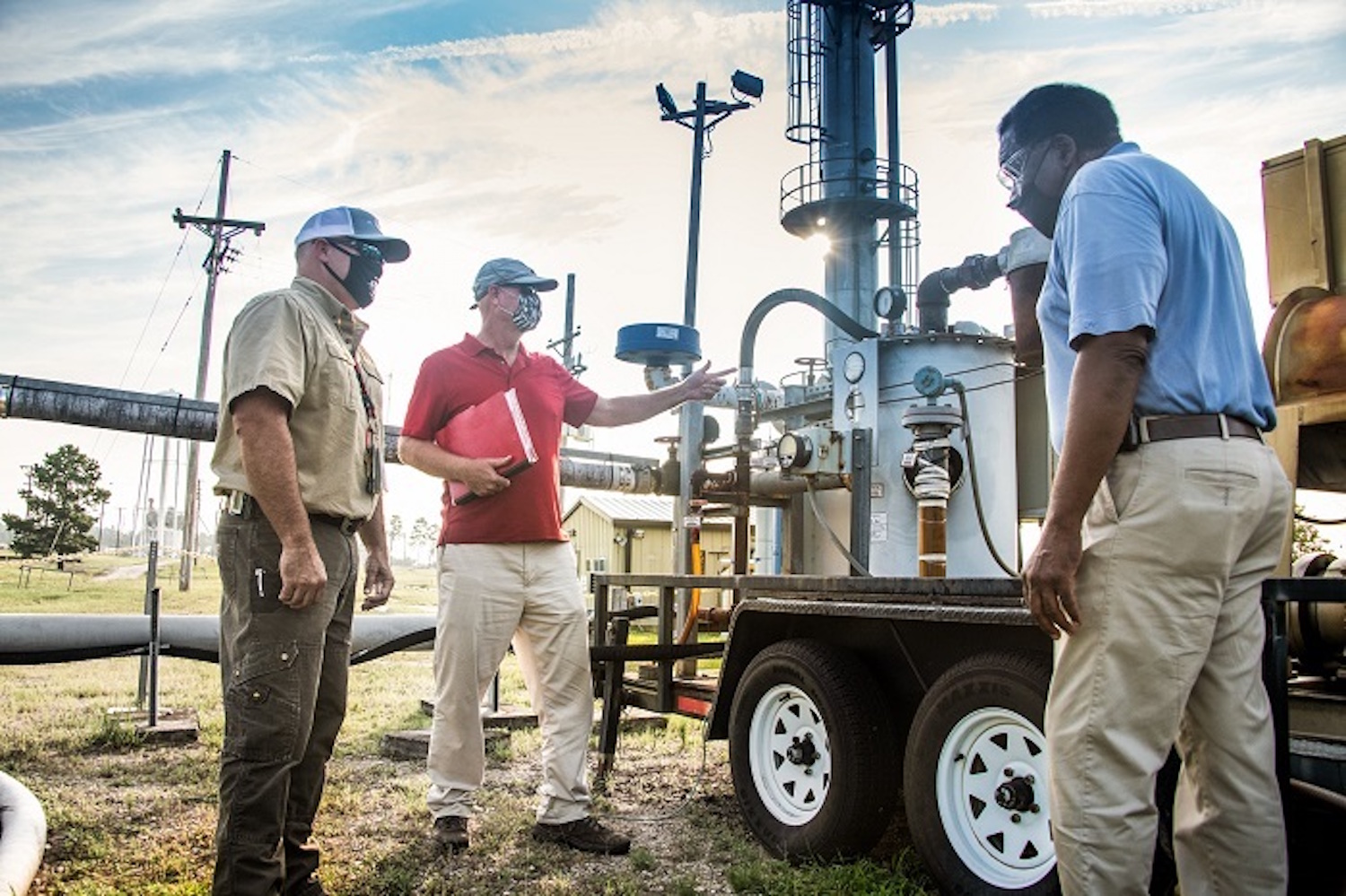
From left, SRNS mechanic Todd Cockrell, engineer John Bradley, and project manager Joao Cardoso-Neto plan the removal of a vapor extraction unit at the Savannah River Site. (Photo: DOE)
Department of Energy site contractors Savannah River Nuclear Solutions and Savannah River Remediation received high marks from a recent independent audit of their environmental management work at the Savannah River Site in South Carolina.
A train pushes a container full of old equipment from H Canyon to a Savannah River Site disposal facility to make way for a new spent nuclear fuel dissolving campaign. (Photo: DOE)
The Department of Energy is preparing for an upcoming campaign to dissolve stainless-steel-clad spent nuclear fuel at its Savannah River Site in South Carolina by installing a new dissolver and an additional double-sized tank for storing dissolved material.
A view of the Savannah River Site’s Salt Waste Processing Facility. (Photo: DOE)
The Salt Waste Processing Facility at the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site has performed largely as expected, processing more than one million gallons of radioactive waste during its first eight months of operation, the DOE reported on June 8. The SWPF is being used to treat the majority of the site’s remaining liquid radioactive waste, generated from the production of nuclear materials.
A salt dissolution campaign in Tank 37 at the Savannah River Site was completed ahead of schedule, creating tank space for evaporator operations and allowing for more feed to the Salt Waste Processing Facility. (Photo: DOE)
Department of Energy contractor Savannah River Remediation (SRR) announced on May 11 that it has completed a salt dissolution campaign in Tank 37, one of the underground tanks storing high-level radioactive liquid waste at the Savannah River Site (SRS) in South Carolina.
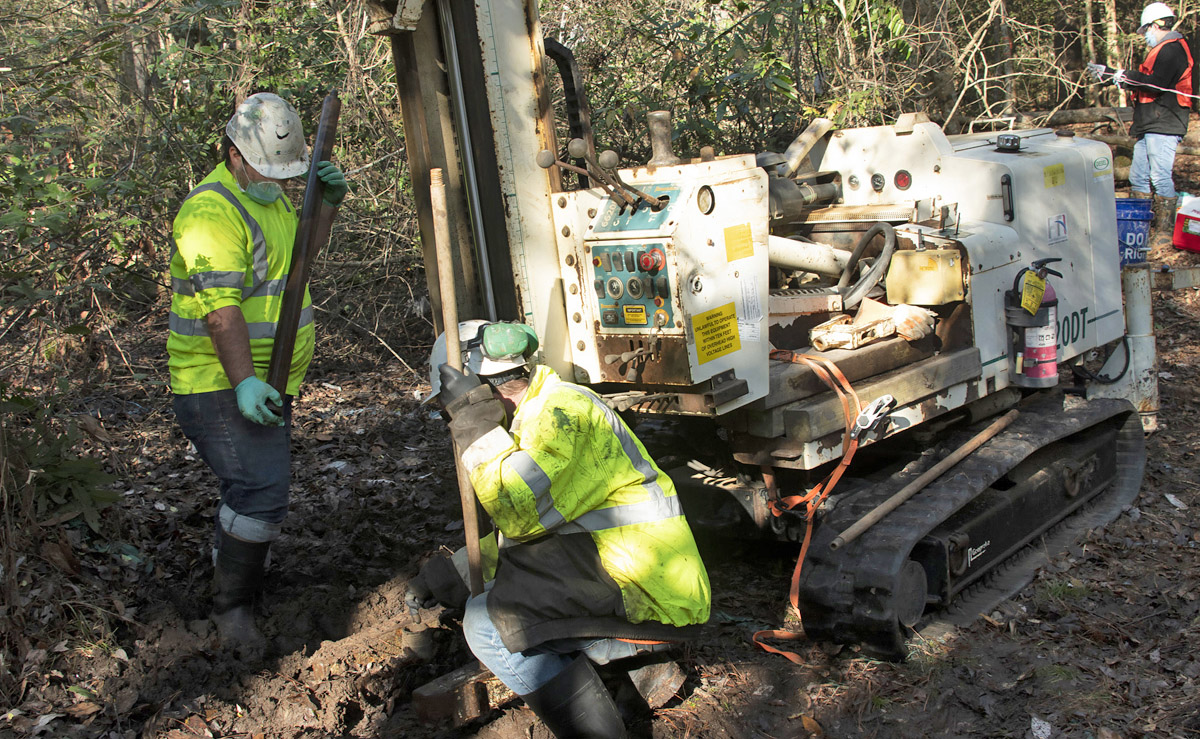
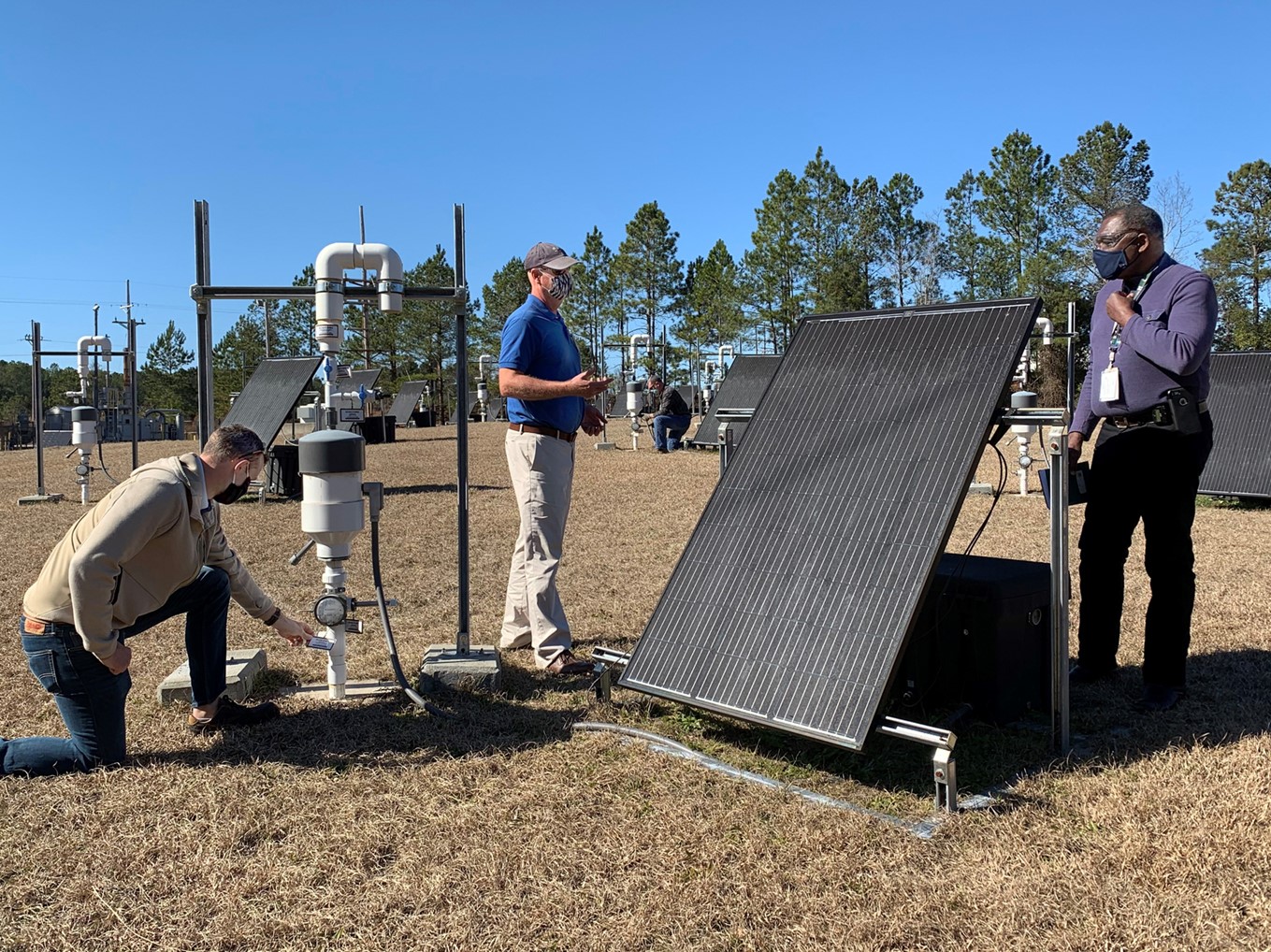
SRNS subcontractors Donald Miles and Richard Mooney drill for soil samples as part of a project to immobilize I-129 in the groundwater and soil at the Savannah River Site. Photo: DOE/SRNS
A silver chloride–based cleanup technology is expected to reduce radioactive iodine-129 contamination found in soil and groundwater near the center of the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site in South Carolina to levels well below regulatory limits. The I-129 was created during the production of plutonium and tritium at the site throughout the Cold War era.
SRNS engineers (from left) Will Jolin, John Bradley, and Joao Cardoso-Neto discuss a plan to move and repurpose equipment used at 19 soil cleanup sites. Photo: DOE
A project to passively remove nonradioactive contaminants from the soil and groundwater at the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site in South Carolina is coming to an end, as workers prepare to remove solar-power “plugs” from 19 soil remediation locations at the site.
Crews move equipment used to inspect drums holding diluted plutonium into a storage site in K Area at the Savannah River Site. Photo: DOE
Workers at the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site in South Carolina recently finished transferring equipment to the site’s K Area in preparation of shipping downblended plutonium to the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant in New Mexico for disposal. The plutonium is part of the 34 metric tons of surplus plutonium the National Nuclear Security Administration plans to ship to WIPP under the “dilute and dispose” option the department adopted following the cancellation of the MOX Fuel Fabrication Facility project.
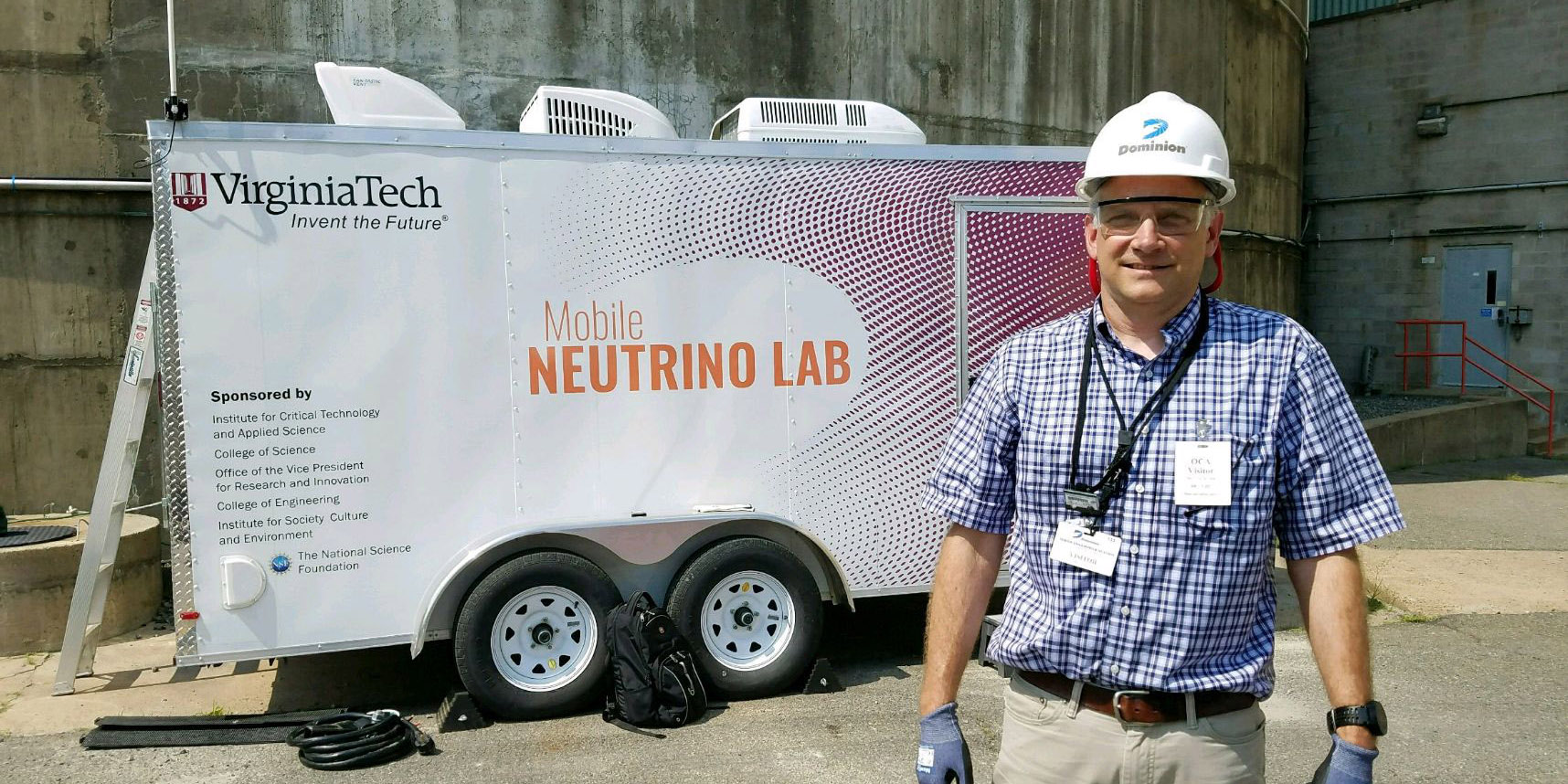
A prototype neutrino detector deployed outside Unit 2 at Dominion Power’s North Anna Generating Station in Mineral, Va. Photo: Steve Mackay, Virginia Tech
Savannah River’s DWPF has been pouring high-level waste canisters for a quarter of a century. Photo: DOE
The month of March marked the 25th year of radiological operations for the Defense Waste Processing Facility (DWPF) at the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site in South Carolina. Radiological operations at DWPF, which is used to treat Savannah River’s high-level radioactive tank waste, began on March 12, 1996, with the first canister of vitrified waste poured on April 29 that year.
To date, more than 4,200 stainless steel canisters of vitrified waste have been poured at DWPF, according to the DOE.
The only operating waste vitrification plant in the nation, DWPF is operated by Savannah River Remediation, the DOE’s liquid waste contractor at the site. According to the DOE, DWPF operations are expected to continue for approximately 15 more years, and about 4,000 more canisters are scheduled to be produced. The DOE expects to begin hot operations at a second waste vitrification plant later this year at its Idaho National Laboratory site.
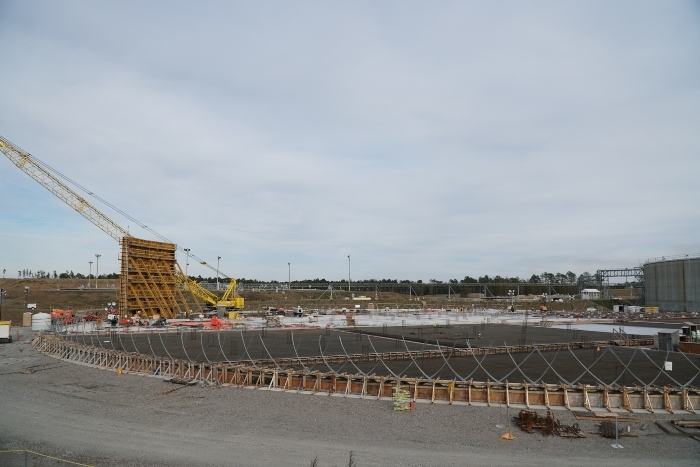
The first wall section of Saltstone Disposal Unit 8 is being constructed at the Savannah River Site. Source: DOE
The first wall section of Saltstone Disposal Unit 8 (SDU 8) at the Department of Energy's Savannah River Site in South Carolina was installed earlier this month.
SDU 8 will stand 43 feet tall and 375 feet in diameter, and have a 33-million-gallon capacity, just like two SDUs built recently at the site. The 25 wall sections of SDU 8 are being constructed using high-strength, reinforced concrete and will be wrapped with seven layers of more than 300 miles of steel cable for added strength.
The flooring of SDU 8 is more than halfway complete. The concrete floor sits on top of a multilayer foundation: a geosynthetic clay liner and high-density plastic liner sandwiched between two concrete layers called “mud mats.” The floor is being completed in 14 sections.
The disposal units are built to safely and permanently contain decontaminated salt solution processed at Savannah River, the DOE reported on March 9.