Oklo Inc. (Image: Gensler)
Fast reactor developer Oklo, which recently went public on the New York Stock Exchange, announced on May 13 that it has signed a memorandum of understanding with Atomic Alchemy to cooperate on the production of radioisotopes for medical, energy, industry, and science applications.
Data from Fukushima ALPS-treated water discharge. (Image: IAEA)
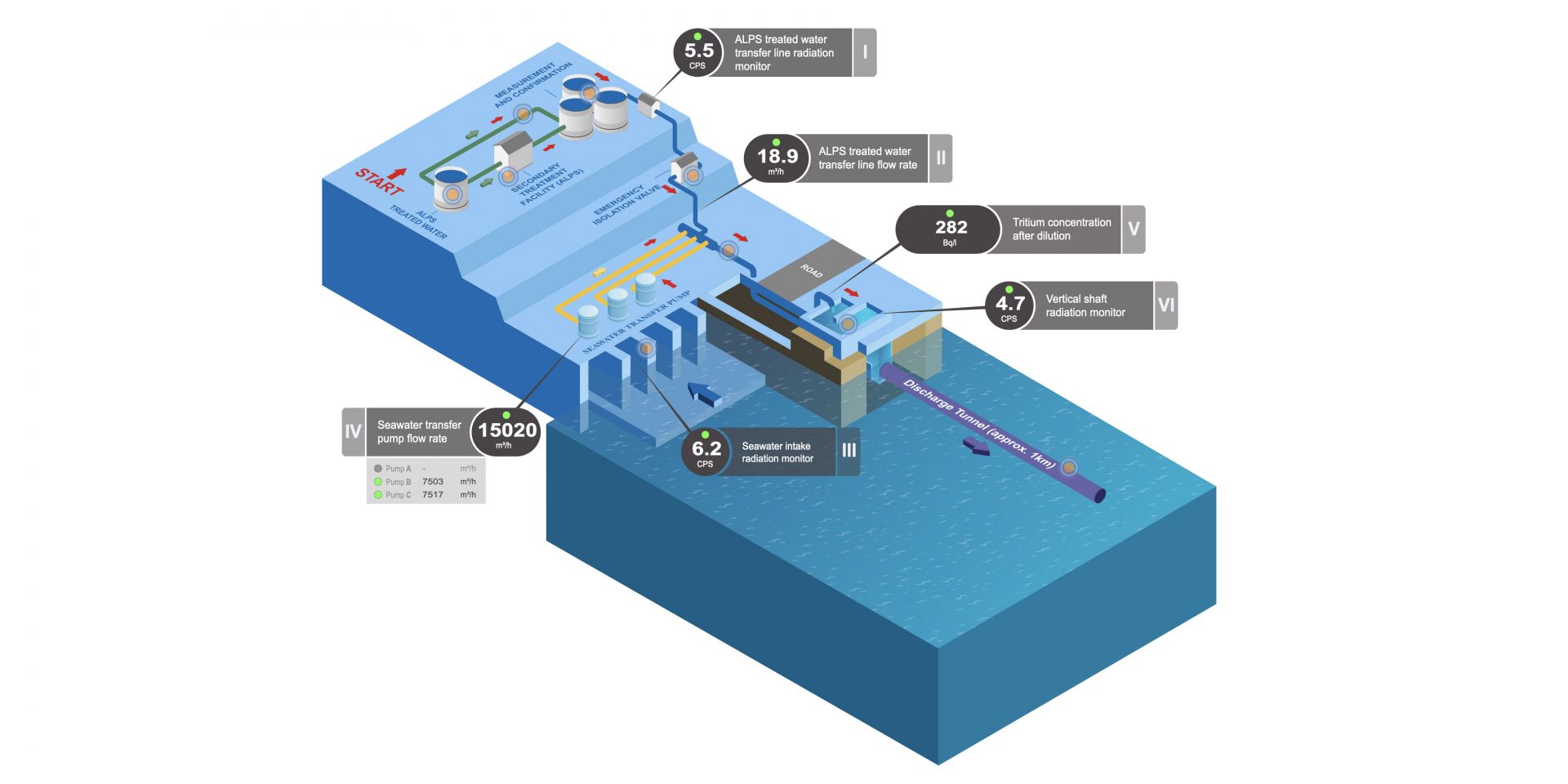
An International Atomic Energy Agency task force has confirmed that the discharge of treated water from Japan's Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant is progressing in accordance with the plan approved by Japan’s Nuclear Regulation Authority.
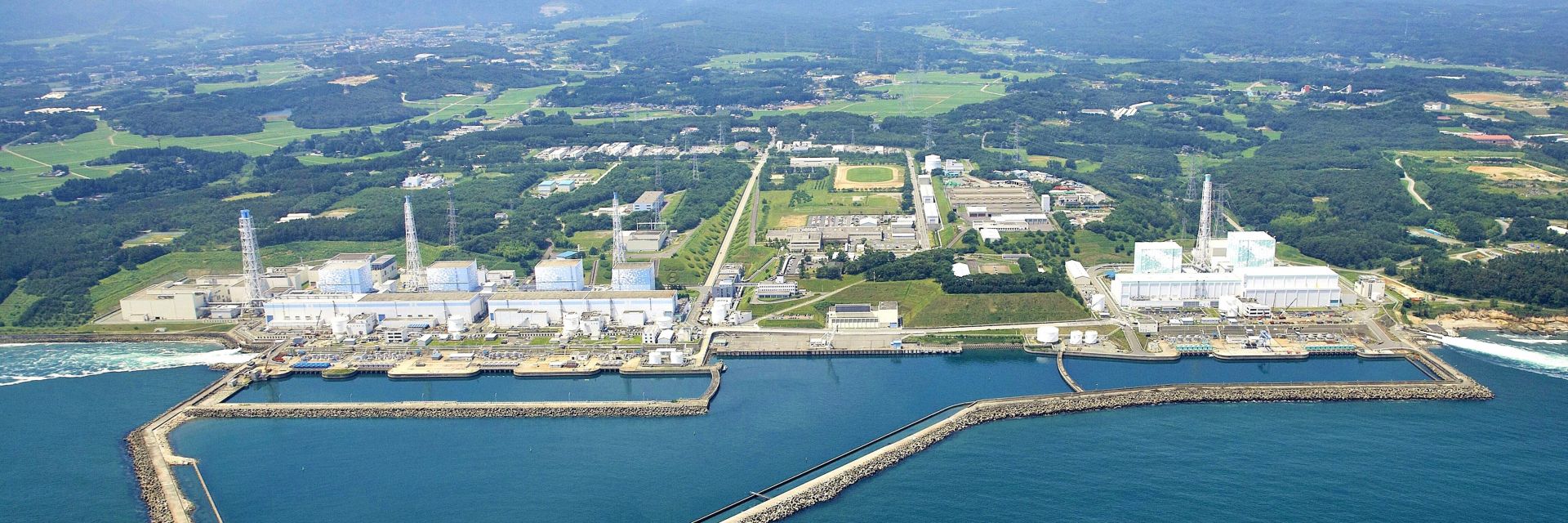
March 1, 2021, 3:01PMUpdated August 25, 2023, 3:21PMNuclear NewsJohn Fabian The Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power station site. Image: Courtesy of TEPCO.
Earlier this week, Japan announced its intention to move ahead with its plan to discharge re-treated, diluted tritiated wastewater from the damaged Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant into the ocean. This plan has been a topic of discussion--and for many a source of contention--since 2013. After a decade of talks, and with the endorsement of nuclear scientists, experts, and organizations around the globe, the time has come to act. By following safety standards in place and endorsed by the IAEA, the release of wastewater will pose no threat to the public or the environment.
The article below was originally published in the March 2021 issue of Nuclear News. (Also included in that issue is a great review article from Lake Barrett outlining the current status of the decontamination and decommissioning going on at Fukushima .) That month marked 10 years since the Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami devastated Japan and crippled the Fukushima plant. The words that follow remain timely, since various news outlets continue to report on the dangers of Fukushima's wastewater without providing context to the Japanese plan to discharge it.
Treated water is safer than world standards, essential for decommissioning
Washington, D.C. – The American Nuclear Society (ANS) supports the start of Japan’s controlled release of re-treated, diluted tritium wastewater into the sea from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (NPP), which sustained damage in the aftermath of a 2011 earthquake and tsunami.
A photo from 2021 of the Fukushima nuclear power station with the more than 1,000 water storage tanks on site. (Photo: TEPCO)
We’ve all seen the headlines such as “Should Japan Dump Fukushima's Radioactive Water into the Ocean?” along with “Japan Set to Pour Fukushima Waste into Pacific, Irking China” and “Japan Is Slowly but Surely Releasing Wastewater from the Fukushima Nuclear Plant into the Pacific Ocean.” The most recent spate of fearmongering was triggered by the IAEA’s July 4 announcement that the agency had finished its independent assessment of Japan’s plans to release the treated wastewater stored at the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power station and found the plan “consistent with IAEA Safety Standards.”
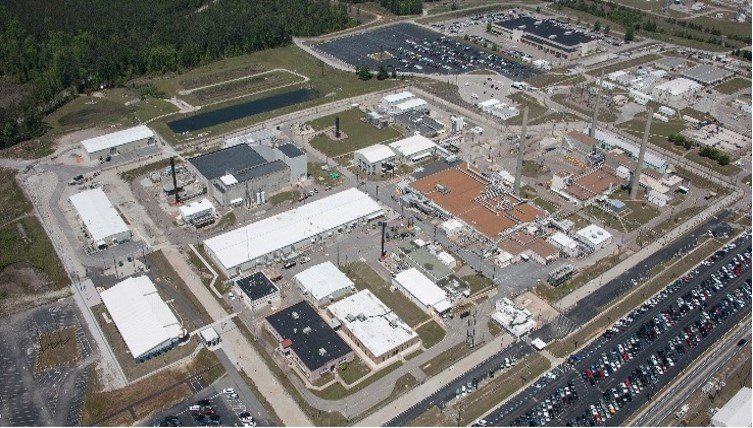
The DOE's Savannah River Site. (Photo: DOE)
The Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board (DNFSB) is scheduled to visit the Department of Energy’s Savannah River Site in South Carolina the week of May 8 to discuss ongoing safety concerns and the protection of the public and workforce, as well as the DOE’s effectiveness in addressing those concerns.
The Monticello nuclear power plant. (Photo: NRC)
An Xcel Energy news release issued last week regarding the leak of some 400,000 gallons of tritium-containing water at Minnesota’s Monticello nuclear power plant in 2022 has sparked a flood of news stories over the past few days—in large part because the general public had previously been unaware of the leak. (A low-level beta emitter, tritium is a common byproduct of nuclear reactor operation.)
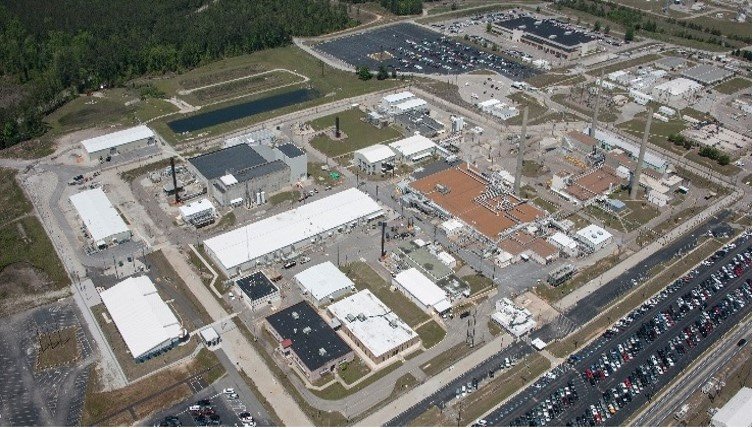
Savannah River National Laboratory (Photo: DOE)
When the Department of Energy announced Innovation Network for Fusion Energy (INFUSE) awards earlier this month, Savannah River National Laboratory was named a recipient of two of the 18 awards. SRNL released a statement on July 19 explaining how a national lab with a long history of supporting environmental management and national security missions can lend a hand in the development of future commercial fusion power.
U.S. Forest Service employees Secunda Hughes (left) and Andrew Thompson inspect irrigation piping and sprinkler heads, part of a 62-acre pine plantation used to safely disperse tritium at the Savannah River Site.
The Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management (EM) is managing the release of tritiated water using a 62-acre plantation of pine trees and other natural resources to limit radioactively contaminated groundwater from reaching waterways on the Savannah River Site in South Carolina.
Don Perrie (left), of OPG, and Michael Lefebvre, of Laurentis Energy Partners, examine the He-3 extraction tool installed at Darlington NPP
Laurentis Energy Partners, a subsidiary of Ontario Power Generation (OPG), has launched a new program to produce helium-3. The He-3 will be obtained from tritium stored at OPG’s Darlington nuclear power plant, a four-unit CANDU station located about 100 kilometers east of Toronto.
Darlington houses one of the world’s largest reserves of tritium, which is a by-product of the heavy water used in CANDU reactors.
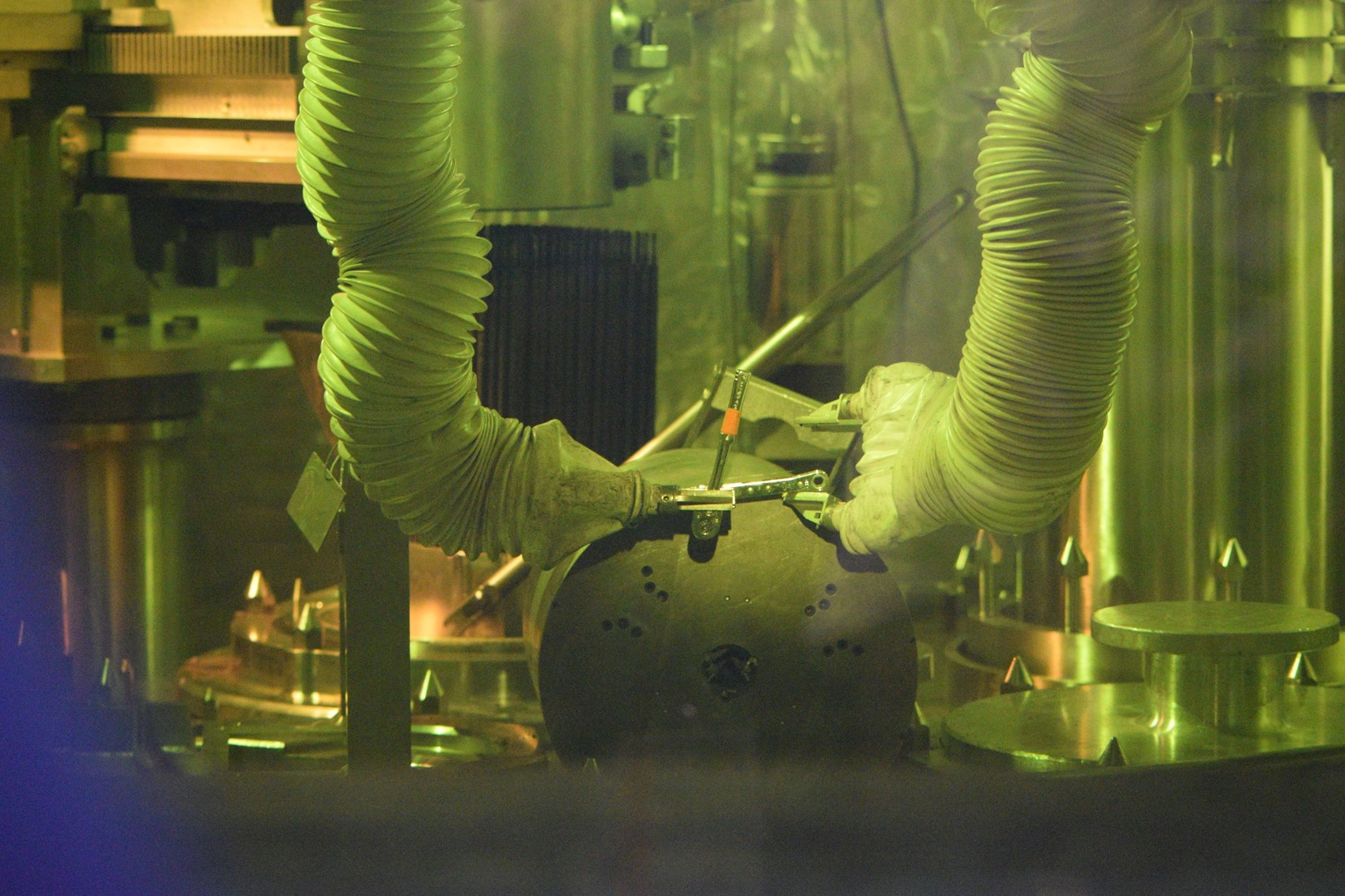
Operators disassemble a cutter head inside a module at the Savannah River's Tritium Extraction Facility using manipulators and hand tools. (Photo: SRNS)
Using basic hand tools and remote manipulators, operators at Savannah River Nuclear Solutions (SRNS) were able to reduce radiation exposure to workers performing cutter head maintenance in the Savannah River Site’s Tritium Extraction Facility (TEF).
According to SRNS, the innovative procedure proved to be an excellent example of real-world application of As Low As Reasonably Achievable (ALARA) principles of time, distance, and shielding.
A current picture of the Fukushima nuclear power station with the more than 1,000 water storage tanks on site. Photo: Courtesy of TEPCO.
The Japanese government will soon announce the decision to dispose of stockpiled Fukushima wastewater into the Pacific Ocean, according to an AP News story published last Friday. The decision is years in the making and follows the guidelines from a panel of government-appointed experts named the Subcommittee on Handling of the ALPS-Treated Water (ALPS Subcommittee).




.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)

 and Andrew Thompson.jpg)
. of OPG, and Michael Lefebvre, of Laurentis Energy Partners, examine tew He-3 extraction tool installed at Darlington NPP.jpg)