Curie and Meitner (Photos: Wikicommons)
Marie Curie was born in Warsaw in 1867 on this day, 155 years ago. Exactly 11 years later, in 1878, Lise Meitner was born in Vienna. November 7 is also the date when, in 1911, the Swedish Royal Academy of Science decided to award Curie a second Nobel Prize for her 1898 discovery of the elements radium and polonium (coincidentally, her 44th birthday). Curie, who at age 36 had shared the 1903 Nobel Prize in Physics with her husband, Pierre Curie, and Henri Becquerel, later accepted the chemistry prize on December 10, 1911. She remains to this day the only person—man or woman—to receive two Nobel Prizes in two different fields of science. (Linus Pauling was also awarded Nobel Prizes in two categories: chemistry and peace.) On this unofficial day of women in nuclear science, let’s take a moment to acknowledge the fundamental discoveries of both Curie and Meitner.
One of two cases that display the impressive belt-buckle collection.
Collecting belt buckles from nearly every nuclear power plant in the U.S. wasn’t the goal for Don Hildebrant when he obtained his first one. Over time, it just turned out that way.
One day years ago, Hildebrant came across a buckle from the nuclear plant where he worked, and it seemed before he knew it, he had collected more than 250 of them—some from plants that were never even completed. “When you look at the collection, you will see an interesting story of where nuclear power has been, and how far it has come,” he said.
Then energy secretary Bill Richardson decided to permanently shut down the HFBR in November 1999. (Photo: DOE)
“Why did a tiny leak bring down a hugely successful research reactor 25 years ago?”
That’s how Robert P. Crease, an academic who writes a regular column for Physics World, introduces The Leak: Politics, Activists, and Loss of Trust at Brookhaven National Laboratory, a book he wrote with former interim BNL director Peter D. Bond that was published this month by MIT Press.
“Were this story fiction, its characters, plot twists and ironies would be entertaining,” Crease writes in his October 5 Physics World post about the book. “But because it’s fact, it’s a tragicomedy.”
G. Robert Keepin, of Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory, author of a three-part feature on the IAEA published in Nuclear News in January, February, and March of 1966; the cover of the January 1966 issue, featuring the IAEA’s first headquarters in the Grand Hotel of Vienna, Austria; and a February 1966 IAEA photo of remote handling of radioisotope standard sources at the Seibersdorf laboratory.
A groundbreaking ceremony held last week at the International Atomic Energy Agency’s laboratories in Seibersdorf, Austria, marked the start of construction on a nuclear applications building that will host three state-of-the-art laboratories: Plant Breeding and Genetics, Terrestrial Environment and Radiochemistry, and Nuclear Science and Instrumentation.It was a significant achievement for the second phase of the Renovation of the Nuclear Applications Laboratories initiative, known as ReNuAL2—and a fitting way to observe the 60th anniversary of the nuclear applications laboratories at Seibersdorf, about an hour’s drive south the IAEA’s headquarters in Vienna. For Nuclear Newswire, it was all the reason we needed to dig into the Nuclear News archives and explore the bygone days of research at the IAEA.
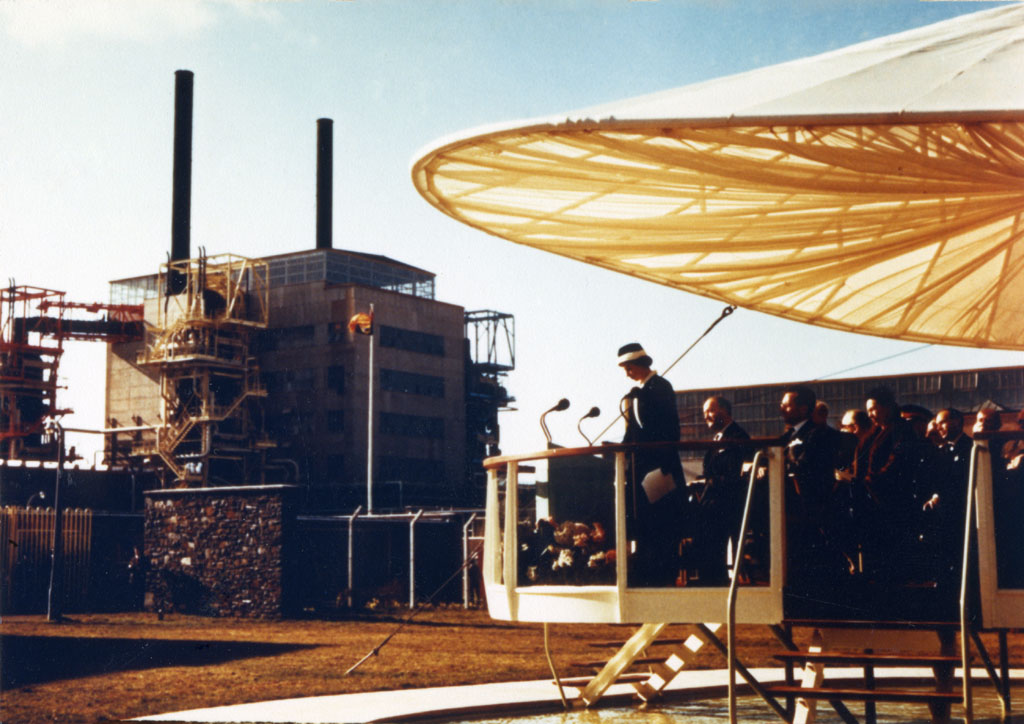
Queen Elizabeth II visits Calder Hall for its ceremonial opening in 1956. (Photo: U.K. Nuclear Decommissioning Authority)
As citizens of the United Kingdom and others around the world mourn the death of Queen Elizabeth II, many have reflected on how the world has changed during the seven decades of the queen’s reign—the same decades that saw the rise of civilian nuclear power.
Calder Hall was already under construction at the Sellafield site in West Cumbria when Princess Elizabeth became queen in 1953. Queen Elizabeth traveled to the site in October 1956 and declared, in a televised ceremony, that “It is with pride that I now open Calder Hall, Britain’s first atomic power station.” Watch the fanfare in a historical clip uploaded to YouTube by Sellafield Ltd below.
The USS Enterprise (CVN-65)
The Naval Academy ANS student section, with support from the Washington, D.C., local section, held its semiannual dinner on March 29 in Annapolis, Md. The event was attended by more than 100 people, including midshipmen, professors from the U.S. Naval Academy, local ANS members, and ANS President Steve Nesbit.
The evening’s program was hosted by the student chapter president, Midshipman First Class Sara Perkins, and was headlined by the director of the Naval History and Heritage Command, Rear Admiral (retired) Samuel Cox.
Cover of the April 1962 issue of Nuclear News (left), ATR core diagram appearing in October 1969 issue of Nuclear News (center), and cover of the October 1969 issue of Nuclear News (right).
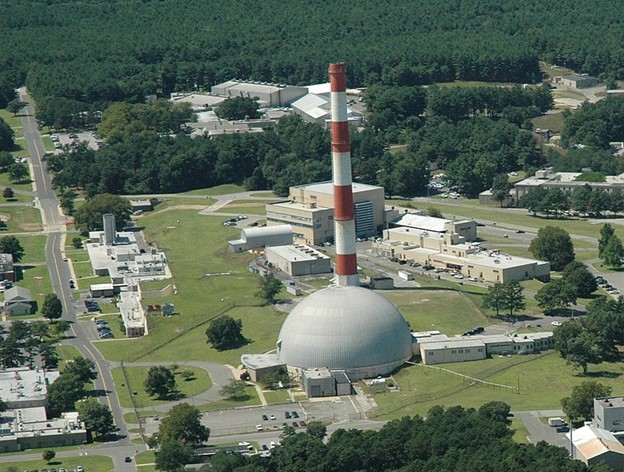
The Department of Energy and Idaho National Laboratory announced this week that the sixth major core overhaul of the Advanced Test Reactor (ATR) is complete, after an 11-month outage that began in April 2021. The ATR was built as a key piece of mission support for U.S. Navy programs and first reached full power in 1969. Today it remains “the world’s largest, most powerful and flexible materials test reactor,” in the words of INL—quite a feat for a reactor that was planned over 60 years ago.
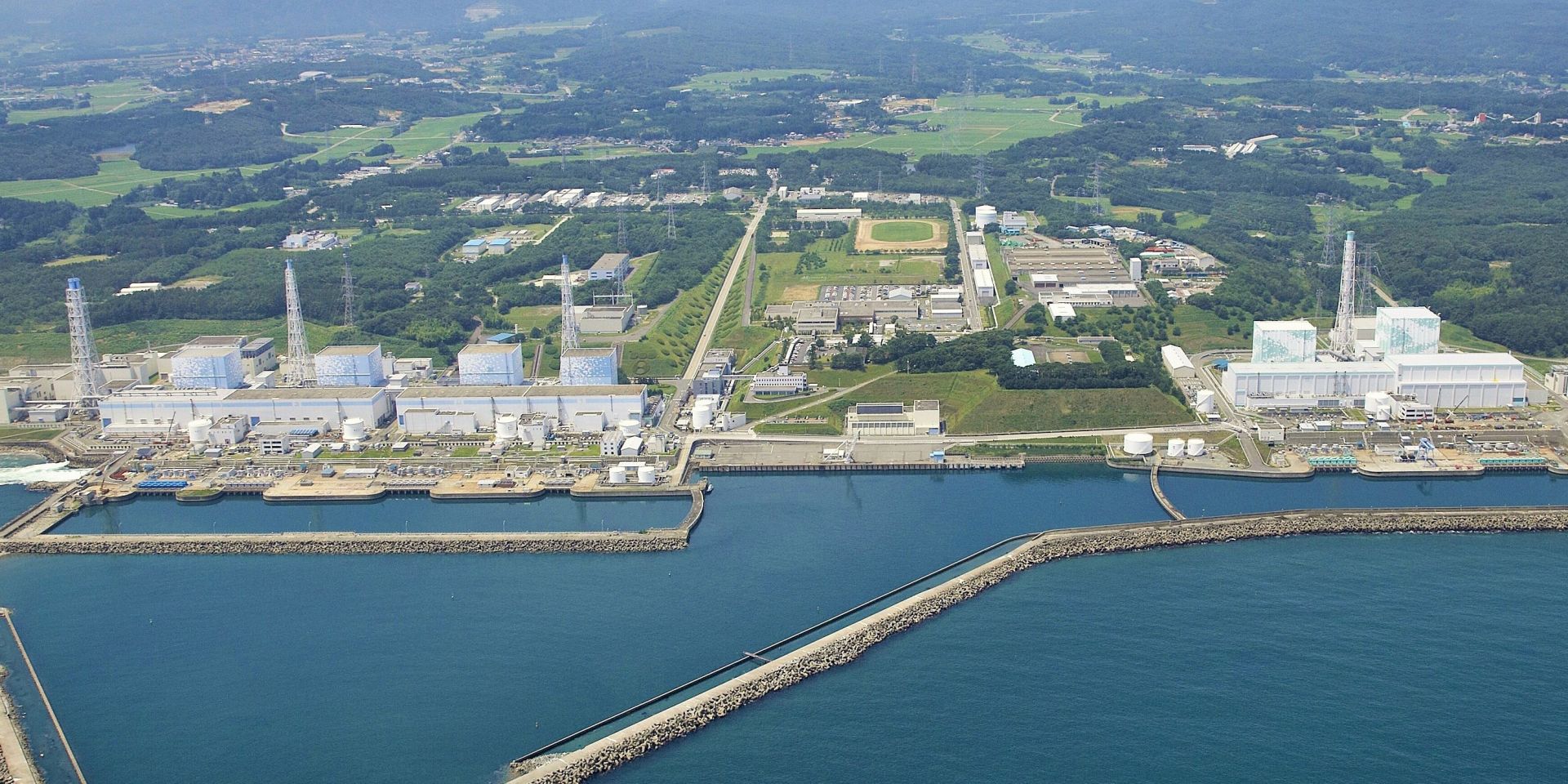
The Fukushima Daiichi site before the accident.
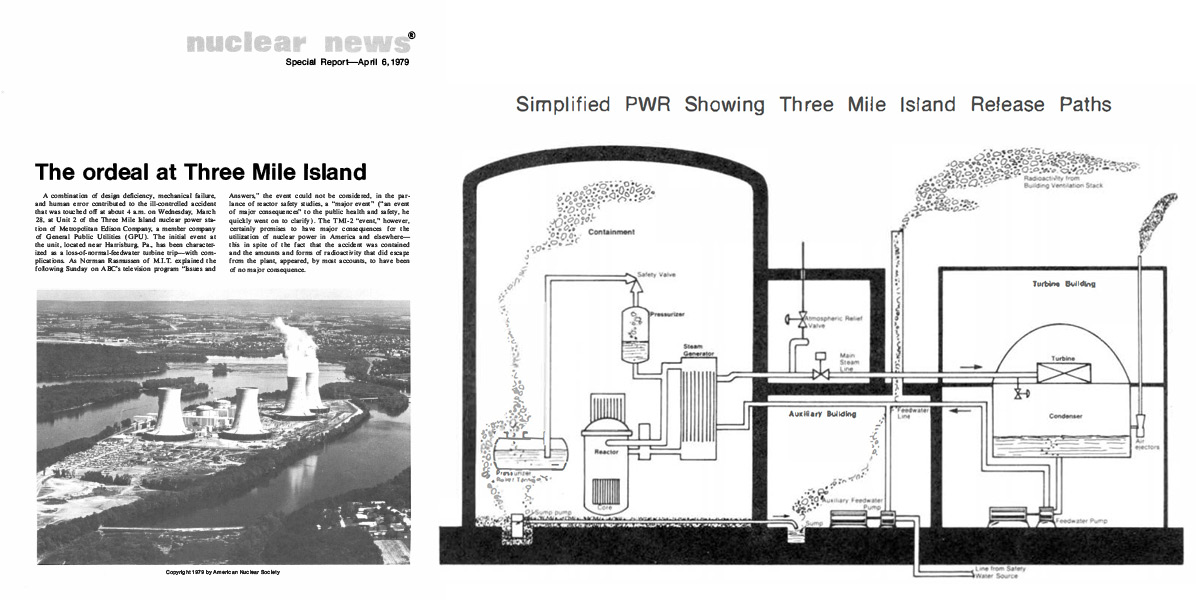
Today’s #ThrowbackThursday post looks back at some of Nuclear News’s reporting on the Fukushima Daiichi accident, which was initiated 11 years ago tomorrow. The news reporting includes the initial coverage of the event from the pages of Nuclear News in April 2011 and the in-depth coverage of the 2011 ANS Annual Meeting, where special sessions focused on the accident.
An advanced nuclear reactor technology park is hoped for the 935-acre Clinch River site. Image: TVA
Last week’s announcement from the Tennessee Valley Authority about its “New Nuclear Program,” which outlines the potential development of the Clinch River site near Oak Ridge National Laboratory in Eastern Tennessee, is the catalyst for this week’s #ThrowbackThursday post. The Clinch River site was originally planned to be the location for the Clinch River Breeder Reactor, a project that, at the time, was meant to be the future of the nuclear industry in the United States.
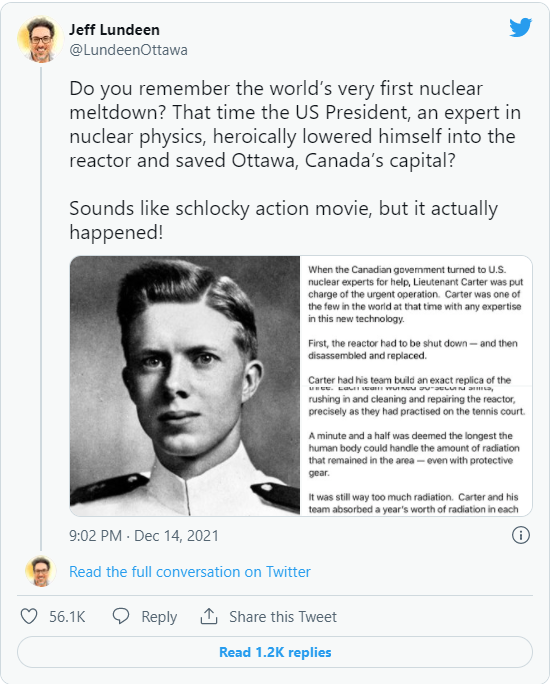
The young Jimmy Carter, years before his presidency. (Click to view entire graphic.)
Jimmy Carter is trending on Twitter this week because of his ties to nuclear power. Carter, the 39th president of the United States, was a member of Rickover’s nuclear navy about 70 years ago when he was assigned to help in the aftermath of an accident at the Chalk River Laboratory in Ontario, Canada.
















.jpg)
 Today’s #ThrowbackThursday post looks at the initial debate surrounding the conversion of research reactor fuel from high-enriched uranium to low-enriched uranium. An article published in the
Today’s #ThrowbackThursday post looks at the initial debate surrounding the conversion of research reactor fuel from high-enriched uranium to low-enriched uranium. An article published in the