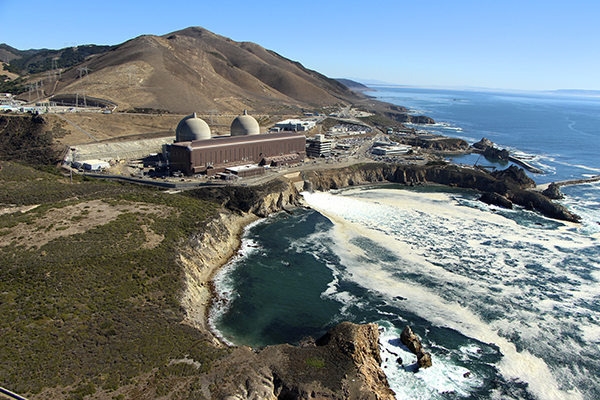
Fort St. Vraine (Photo: NRC)
In a May 15 piece, the editorial board of The Denver Gazette has weighed in on Colorado’s continuing controversy regarding how the state gets its electricity. While the current discourse in the state primarily pits fossil fuels against wind and solar, the board asks, “How about an energy source that generates almost limitless power, leaves no carbon footprint, and produces practically no emissions? It’s nuclear power—as green as you can get.”
Energy Harbor’s Beaver Valley plant houses two reactors: Unit 1, a 939-MWe pressurized water reactor, and Unit 2, a 933-MWe PWR. (Photo: Energy Harbor)
Energy Harbor has signed a memorandum of understanding with blockchain company Standard Power to develop a large-scale carbon-free data infrastructure operation adjacent to the Beaver Valley nuclear plant, located in Shippingport, Pa.
In its May 9 announcement, Energy Harbor described Standard Power as “a leading infrastructure service provider for advanced data processing companies and a leading hosting provider for blockchain mining companies.”
Energy Harbor is based in Akron, Ohio.
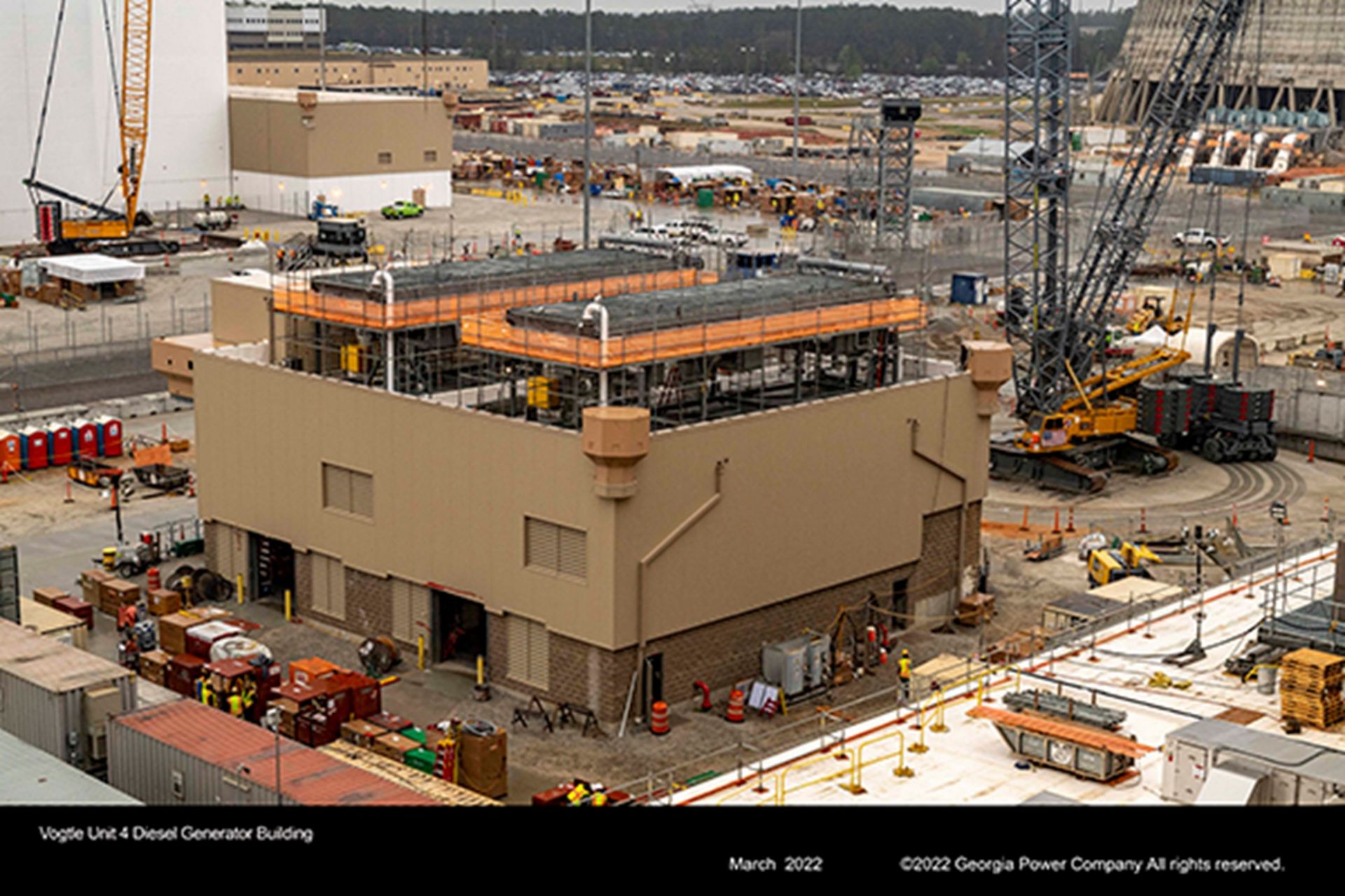
The Vogtle-4 diesel generator building in March. (Photo: Georgia Power)
The total bill for the reactor expansion project at the Vogtle nuclear plant in Georgia is now expected to exceed $30 billion, according to the Associated Press. The original price tag for the two Westinghouse AP1000 units was $14 billion.
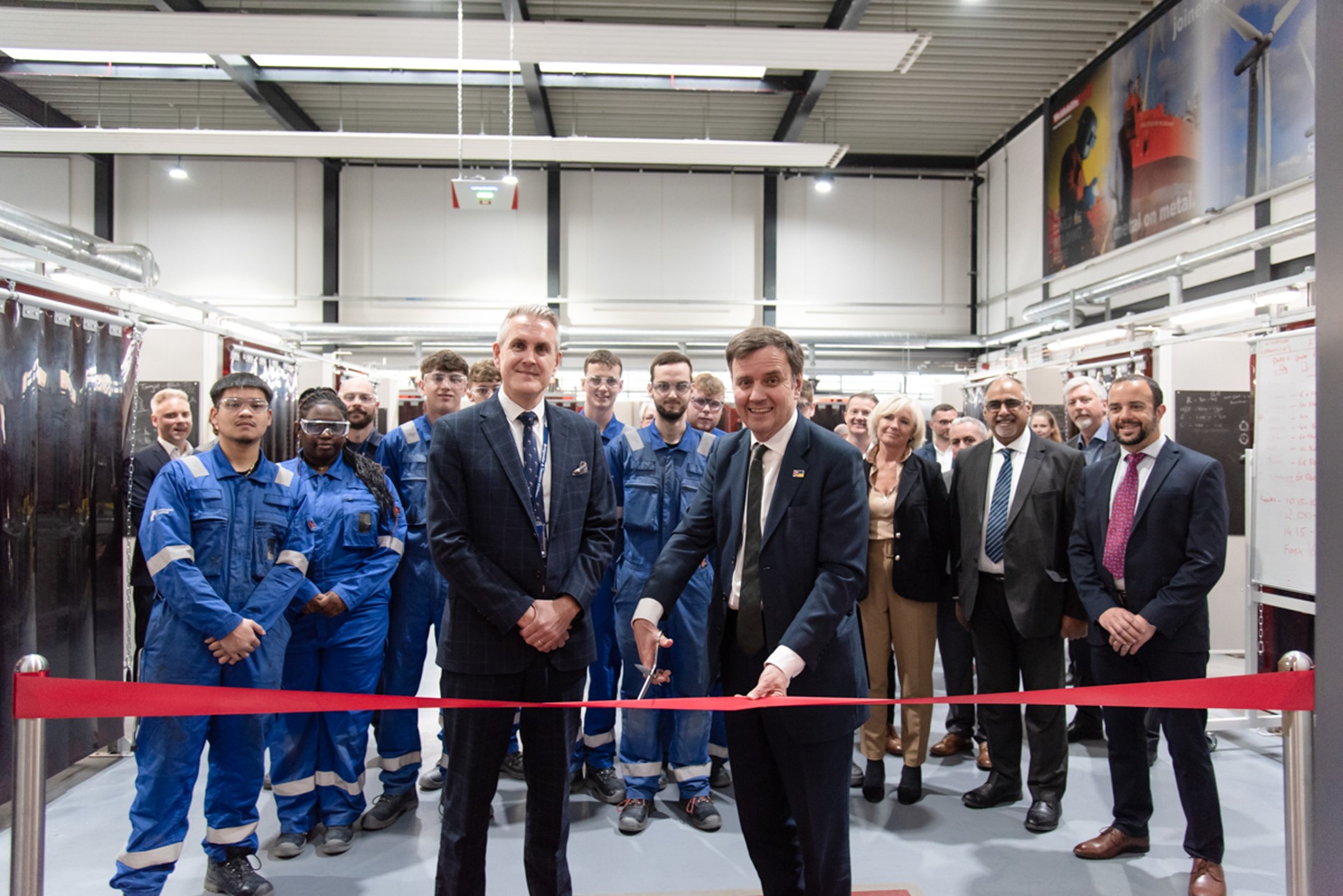
U.K. energy minister Greg Hands cuts the ribbon on the Welding Centre of Excellence at Bridgwater & Taunton College’s campus. (Photo: EDF Energy)
The United Kingdom’s energy minister, Greg Hands, recently presided over the opening of one of three new training centers in England aimed at supporting EDF Energy’s Hinkley Point C nuclear build project in Somerset. The centers, according to EDF, will provide locals with the skills necessary to join the ranks of about 4,000 additional workers expected to be needed for the next phase of the power station’s construction. Hands unveiled the Welding Centre of Excellence, located on the Bridgwater & Taunton College campus in Bridgwater.
The accident at Three Mile Island revealed many areas for improvement in the safety of nuclear power that have been addressed continuously in the past 40 years.
Part one of this article, published in the May 2019 issue of Nuclear News[1] and last Friday on Nuclear Newswire, presented insights from the 1979 accident at Three Mile Island-2 and addressed several issues raised by a previous Nuclear News piece on the accident[2]. Part two discusses safety improvements that have been made by both the industry and the Nuclear Regulatory Commission over the past 40 years.
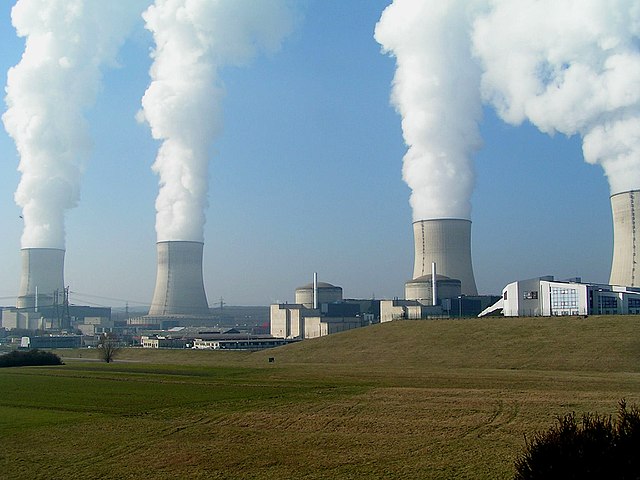
The nuclear power plant in Cattenom, France. (Photo: Stefan Kühn)
Bloomberg recently reported that nuclear power production in France declined to its lowest level in almost two years in April, with power output during that month falling to 21.7 TWh. The decline occurred as Électricité de France (EDF), one of the country’s major energy suppliers, dealt with long-term inspection-and maintenance-related halts to the operation of many of its 56 domestic nuclear reactors.
An artist’s rendering of the Hanhikivi plant. (Image: Rosatom)
Finnish energy company Fennovoima has terminated, effective immediately, its engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) contract with RAOS Project Oy, a subsidiary of Russia’s Rosatom, for the delivery of a 1,200-MWe VVER-1200 pressurized water reactor at the Hanhikivi site in Finland’s Pyhäjoki municipality.
A pair of Westinghouse AP1000 reactors at China's Haiyang nuclear power plant.
China’s State Council recently approved the construction of four Westinghouse AP1000 reactors—two at China’s Sanmen plant in Zhejiang Province and two at the Haiyang plant in Shandong Province.
The plants currently house two AP1000 units each. Sanmen’s reactors are rated at 1,157 MWe and Haiyang’s at 1,170 MWe. Sanmen-1 and -2 began commercial operation in 2018. Haiyang-1 started commercial operation in 2018, and Haiyang-2 in 2019.