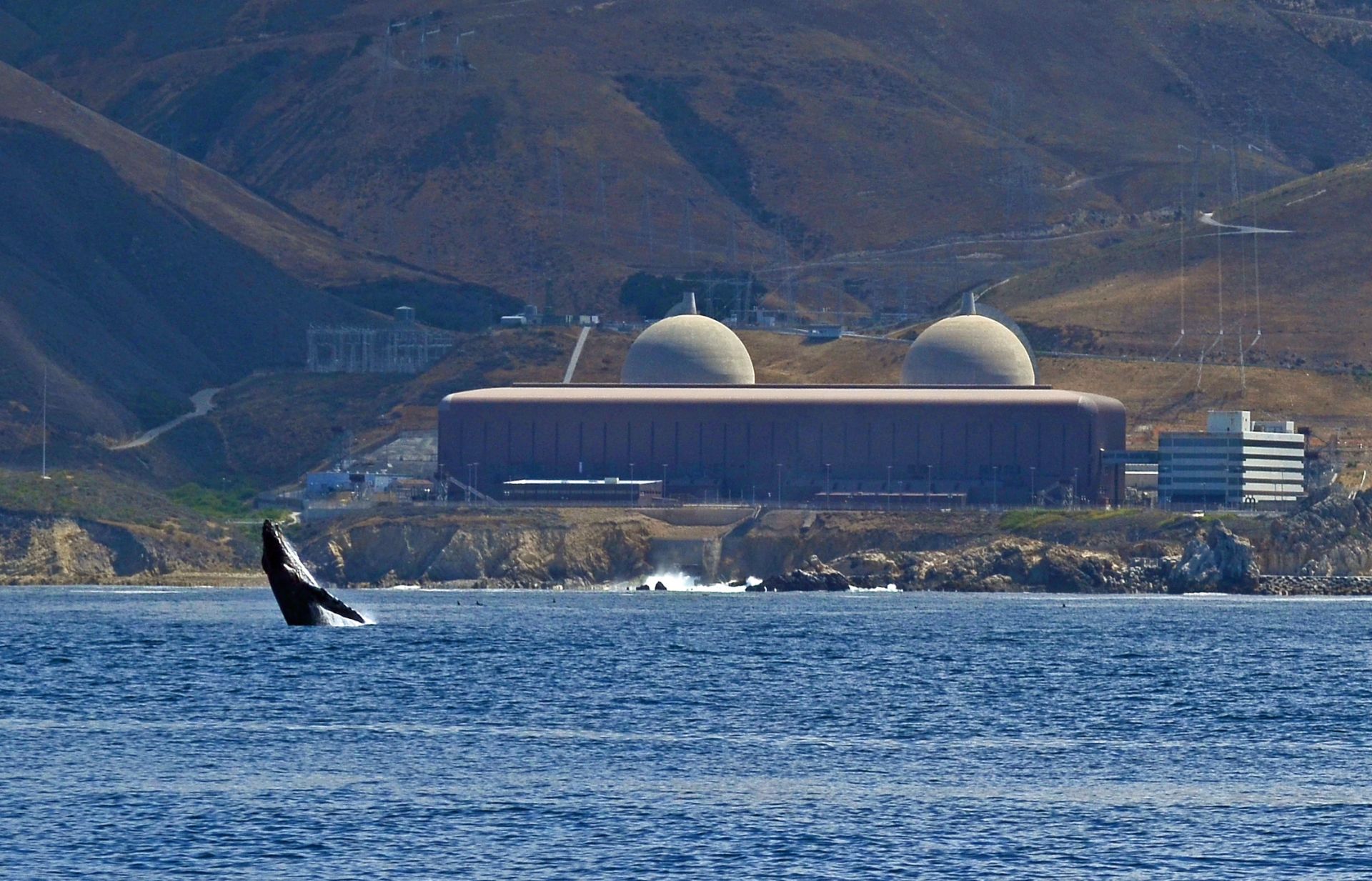
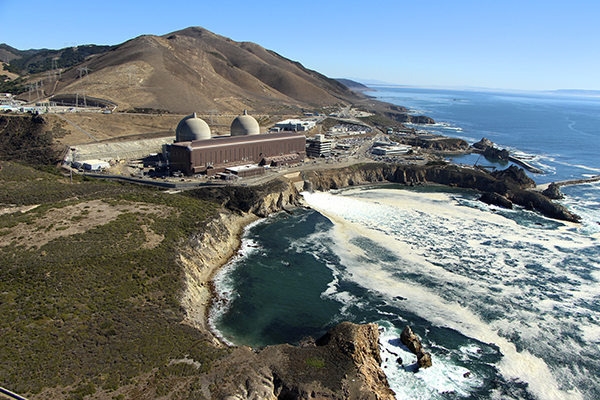
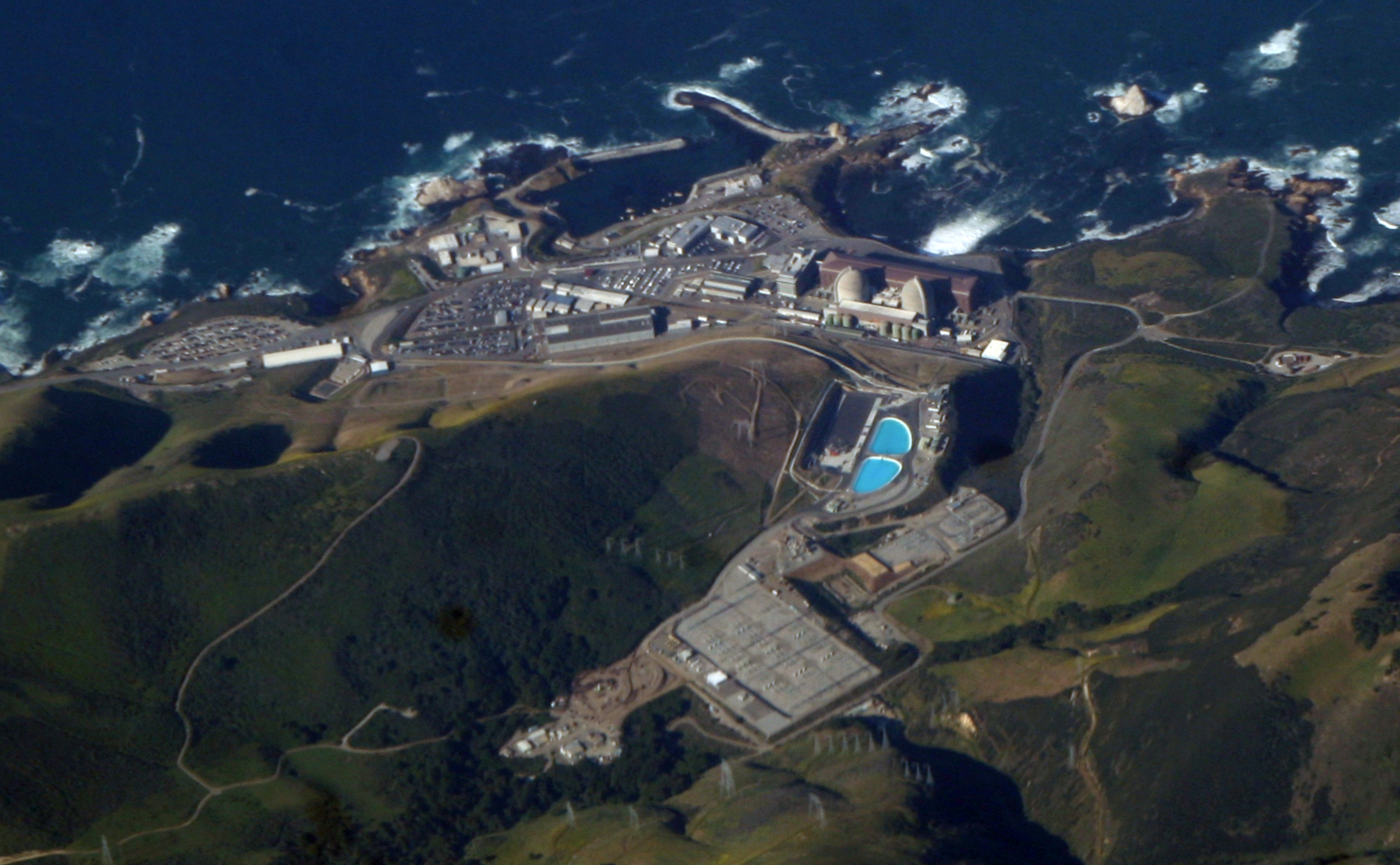
The Diablo Canyon nuclear power plant.
Bowing at last to the unflagging efforts of nuclear advocates over the past few years—as well as to more recent pressure from a former nuclear opponent, Gov. Gavin Newsom—the California legislature late last night approved S.B. 846, a measure that provides the option of extending operations at the Diablo Canyon nuclear power plant for five years beyond its scheduled 2025 closure date.
Pacific Gas and Electric, Diablo Canyon’s owner and operator, had agreed in June 2016 to an early shuttering of the facility, following discussions with organized labor and environmental organizations. PG&E’s application to close the plant was approved by the California Public Utilities Commission in January 2018.
The bill passed easily through both legislative chambers: 67–3 in the General Assembly and 31–1 in the Senate.
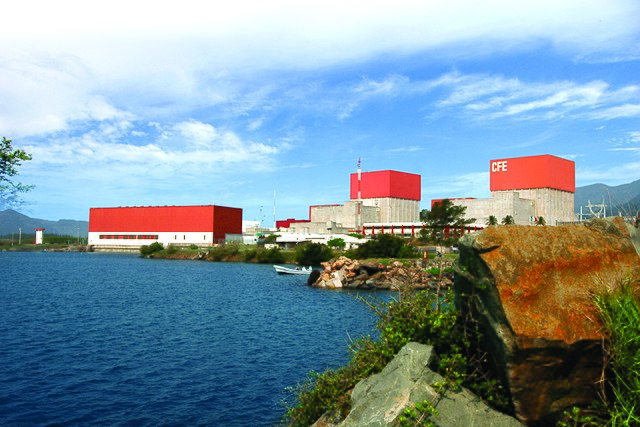
The Laguna Verde nuclear power plant. (Photo: HFStudio)
Unit 2 at Mexico’s Laguna Verde nuclear plant has been given the go-ahead to operate into the 2050s, plant owner and operator Comisión Federal de Electricidad (CFE) announced last week.
Mexico’s secretary of energy, Norma Rocío Nahle García, approved a 30-year extension to the unit’s operating license on August 25, following a review by the country’s National Commission for Nuclear Safety and Safeguards. The reactor, one of two at the plant, is now authorized to run until April 10, 2055.
California's Diablo Canyon nuclear power plant.
A bill to extend operations at California’s Diablo Canyon nuclear plant beyond 2025 debuted last evening in the California legislature. Lawmakers have until Wednesday—the end of the current legislative session—to vote on the measure.
Coauthored by State Sen. Bill Dodd (D., Napa) and Assemblymember Jordan Cunningham (R., San Luis Obispo), Senate Bill 846 includes a $1.4 billion forgivable loan to Pacific Gas and Electric (PG&E), the plant’s owner and operator, matching the amount in the August 12 proposal from Calif. Gov. Gavin Newsom. Instead of Newsom’s proposed option for a 10-year life extension for the facility, however, SB 846 would keep the plant running for an additional five years only.
Francesco Venneri (left), USNC CEO, and Hyeon Sung Hong, Hyundai Engineering CEO, at a framework agreement signing for MMR project development and deployment.
Representatives of Ultra Safe Nuclear Corporation (USNC) of Seattle, Wash., and Hyundai Engineering of Seoul, South Korea, traveled last week between USNC project sites in Oak Ridge, Tenn., and Ontario, Canada, to sign two agreements extending their collaboration on the deployment of USNC’s high-temperature, gas-cooled Micro Modular Reactor (MMR). The agreements expand on a business cooperation agreement signed in January 2022 and an engineering agreement signed in June, and follow the closure earlier this month of a previously announced $30 million equity investment after its review by the U.S. Treasury Department’s Committee on Foreign Investment in the United States.
From left: Bas Sujis (ULC-Energy), Sophie Macfarlane-Smith (Rolls-Royce SMR), Joanna Roper CMG (U.K. ambassador to the Netherlands), Alan Woods (Rolls-Royce SMR), and Dirk Rabelink (ULC-Energy). (Photo: Rolls-Royce SMR)
The United Kingdom’s Rolls-Royce SMR has signed an exclusive agreement with ULC-Energy—a Dutch nuclear development company established in 2021—to deploy small modular reactor stations in the Netherlands. (ULC stands for Ultra Low Carbon.)
Artistic rendering of a NuScale nuclear power plant. (Image: NuScale Power)
NuScale Power yesterday announced the signing of a memorandum of understanding with Estonia’s Fermi Energia, a company focused on small modular reactor development to address the Baltic state’s climate and energy security goals.
Under the MOU, Fermi Energia will evaluate the Portland, Ore. – based firm’s small modular reactor design for deployment in Estonia. (There are no nuclear power facilities in Estonia or in the other Baltic countries, Latvia and Lithuania.)
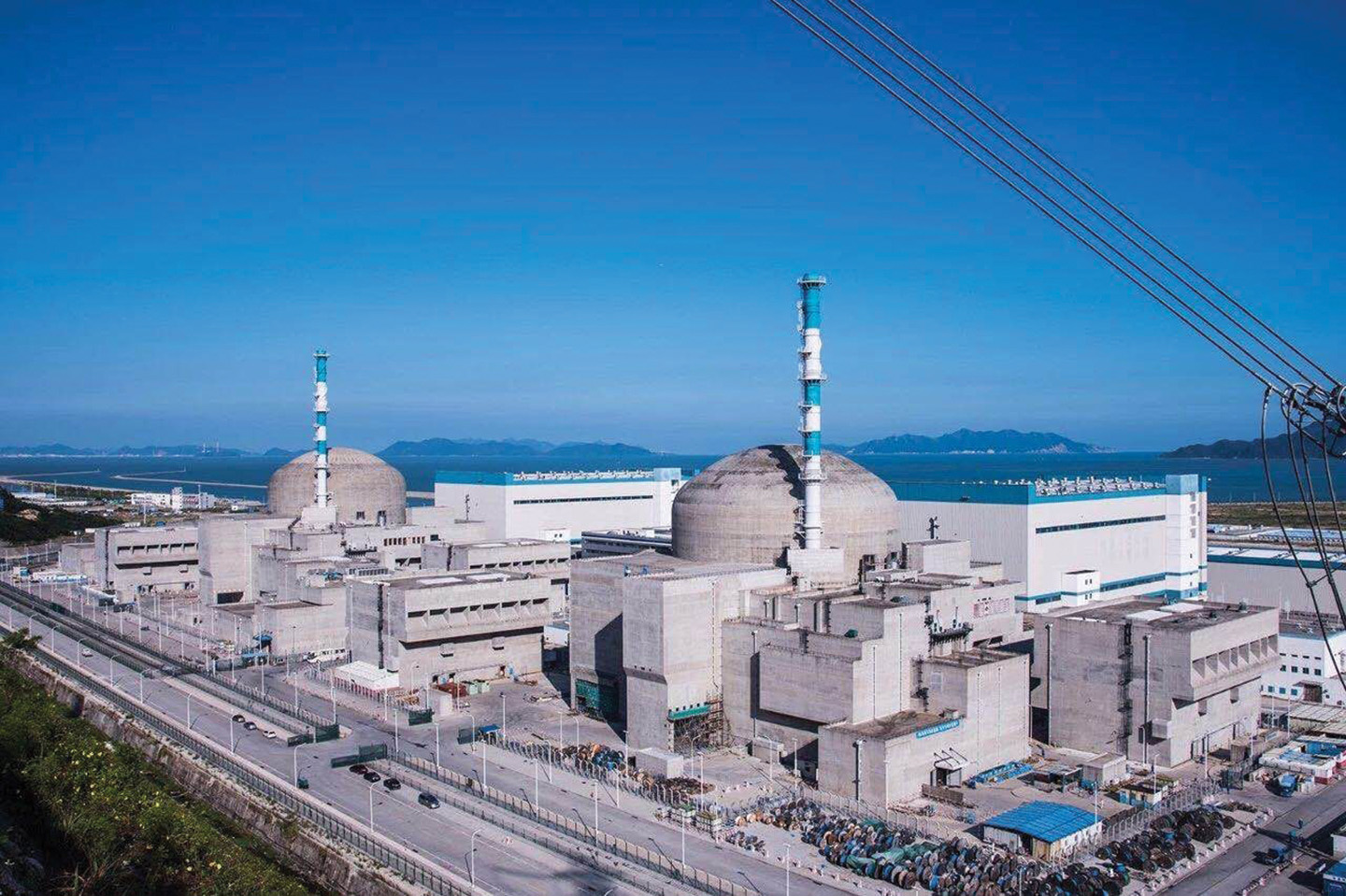
The Taishan nuclear power plant in China. (Photo: CGN)
China’s Taishan-1, which was shut down last summer due to damaged fuel rods, resumed operations on August 15.
The plant briefly made headlines last summer—as much for the damage inside the reactor as for the media fallout. In June 2020, plant operators found damage to the cladding on about five of the 60,000 fuel rods in Taishan-1, one of the plant’s two 1,660-MW EPRs. What happened next seemed like a bad game of “telephone.”
Turkey’s Akkuyu-1 receives its polar crane. (Photo: Akkuyu Nuclear)
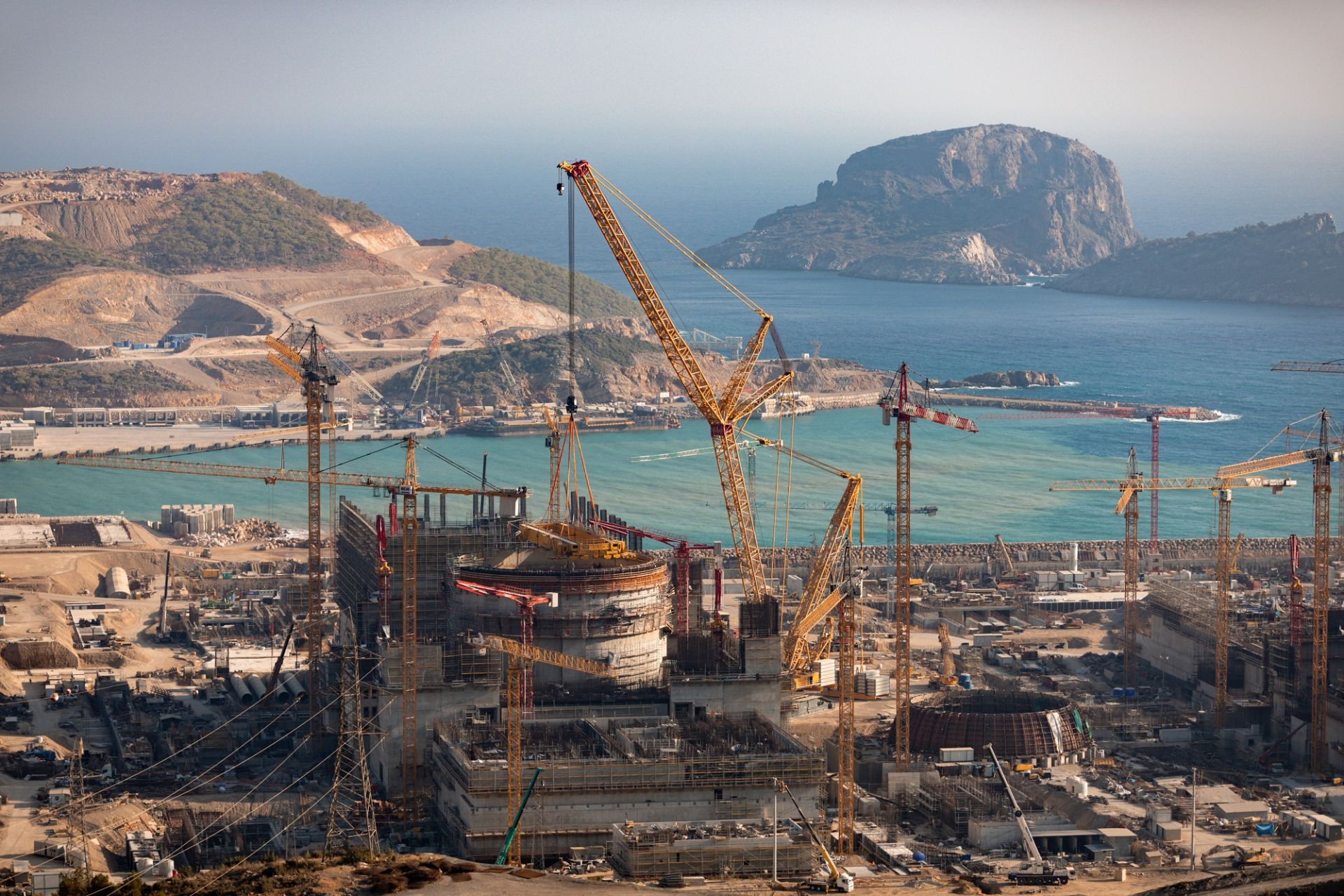
Akkuyu Nuclear, the Ankara-based Rosatom subsidiary established to manage Turkey’s Akkuyu nuclear plant project, has announced the successful mounting of the Unit 1 polar crane. The operation was carried out using a Liebherr LR 13000 crane and took approximately four hours, according to Akkuyu Nuclear.
Also referred to as a circular bridge crane, the polar crane operates on a circular runway located near the spring line of the containment building. It is used for a wide range of loading and lifting tasks within containment, including reactor-head removal/replacement and fuel loading/unloading.
The Darlington-3 reactor face. (Photo: OPG)
Ontario Power Generation has announced that refurbishment of Unit 3 at its Darlington nuclear plant is progressing ahead of schedule, with an expected return to service by late 2023, rather than early 2024.
The Zaporizhzhia nuclear power plant. (Photo: Ralf1969, Wikimedia Commons)
The latest news on Ukraine’s Zaporizhzhia nuclear power plant—under occupation by the Russian military since early March—sparks some hope, but also more anxiety.
The good: This morning, Russia requested that the United Nations Security Council hold a meeting tomorrow on the situation at the six-unit pressurized water reactor plant, according to RIA Novosti, a Russian state-owned news agency. The RIA report cited a post via the Telegram messaging app from Dmitry Polyansky, Russia’s first deputy minister at the UN. In the post, Polyansky said the meeting is scheduled for “22:00 Moscow time on August 23.”
Artist’s rendering of the IMSR Core-Unit. (Credit: Terrestrial Energy)
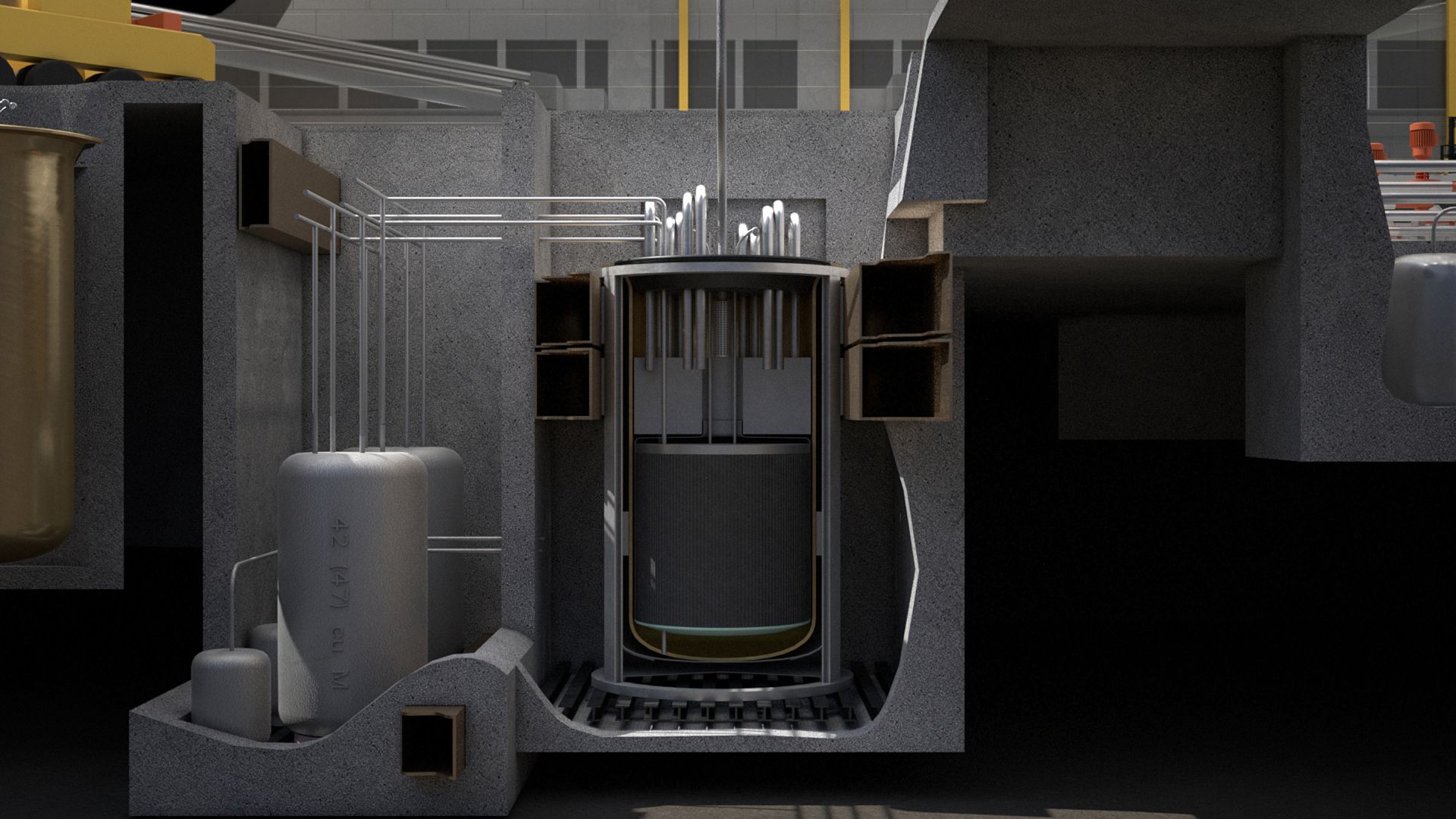
In the ongoing quest to mitigate the effects of climate change, new technology can create new solutions. Even today, however, coal is still a main source of power around the globe, often out of necessity. Many coal-burning plants have already been converted for gas or biomass, but these measures alone are not nearly enough to meet net-zero carbon goals. There is a better solution, however: repowering coal plants with nuclear technology—specifically, Generation IV reactors.
The Neckarwestheim nuclear power plant in Germany.
For the few members of the nuclear community who haven’t already been made aware, the Wall Street Journal yesterday published a story headlined “Germany to Keep Last Three Nuclear Power Plants Running in Policy U-Turn.” According to the WSJ, the German government plans to postpone retirement of the plants—all of which had been slated for closure by the end of 2022—fearing an inadequate energy supply this winter.
The Diablo Canyon nuclear power plant.
There is still a chance for California’s last remaining nuclear power plant to stay open.
Last Friday, more than 50 nuclear advocates testified in support of the Diablo Canyon nuclear power plant at a California Energy Commission workshop. Many spoke of the need for California to shore up its electricity grid in the face of coming heat waves and power outages. Others emphasized that closing the plant, which generates 2.2 GW of electricity and currently provides 8.6 percent of the state’s total supply and about 15 percent of its low-carbon electricity, would be devastating to California’s emission-reduction goals.




 The National Association of Regulatory Utility Commissioners (NARUC) has published
The National Association of Regulatory Utility Commissioners (NARUC) has published  The deadline for first-round applications to the Department of Energy’s
The deadline for first-round applications to the Department of Energy’s