Since 1957, the Advisory Committee on Reactor Safeguards has had a continuing statutory responsibility for providing independent reviews of, and advising on, the safety of proposed or existing reactor facilities and the adequacy of proposed reactor safety standards in the United States.
The 1957 amendment to the Atomic Energy Act of 1954 established the Advisory Committee On Reactor Safeguards as a statutory committee with an independent advisory role and the responsibility to “review safety studies and facility license applications” and advise the U.S. Atomic Energy Commission “with regard to the hazards of proposed or existing reactor facilities and the adequacy of reactor safety standards.” With the enactment of the Energy Reorganization Act of 1974, the ACRS was assigned to the newly established Nuclear Regulatory Commission with its statutory requirements intact.
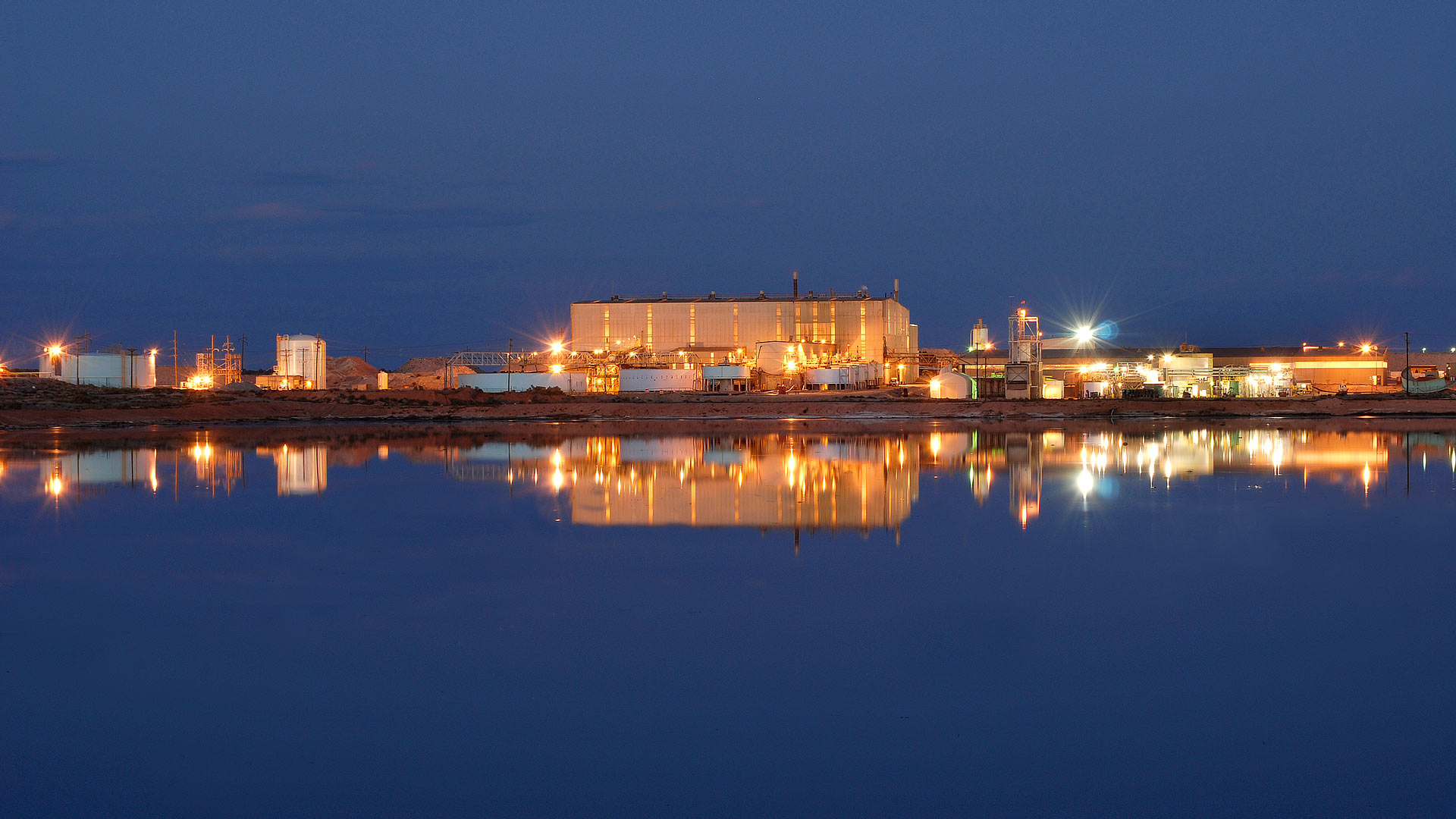
Energy Fuels’ White Mesa Mill in southeastern Utah is the only operating conventional uranium mill in the United States. (Photo: Energy Fuels)
The bipartisan Nuclear Fuel Security Act (NFSA), introduced in the Senate last week, would authorize the Department of Energy to establish a Nuclear Fuel Security Program to “ensure a disruption in Russian uranium supply would not impact the development of advanced reactors or the operation of the United States’ light water reactor fleet.” The bill was introduced by Sen. Joe Manchin (D., W.V.), chairman of the Senate Energy and Natural Resources (ENR) Committee; Sen. John Barrasso (R., Wyo.), ranking member of the Senate ENR committee; and Sen. Jim Risch (R., Idaho).
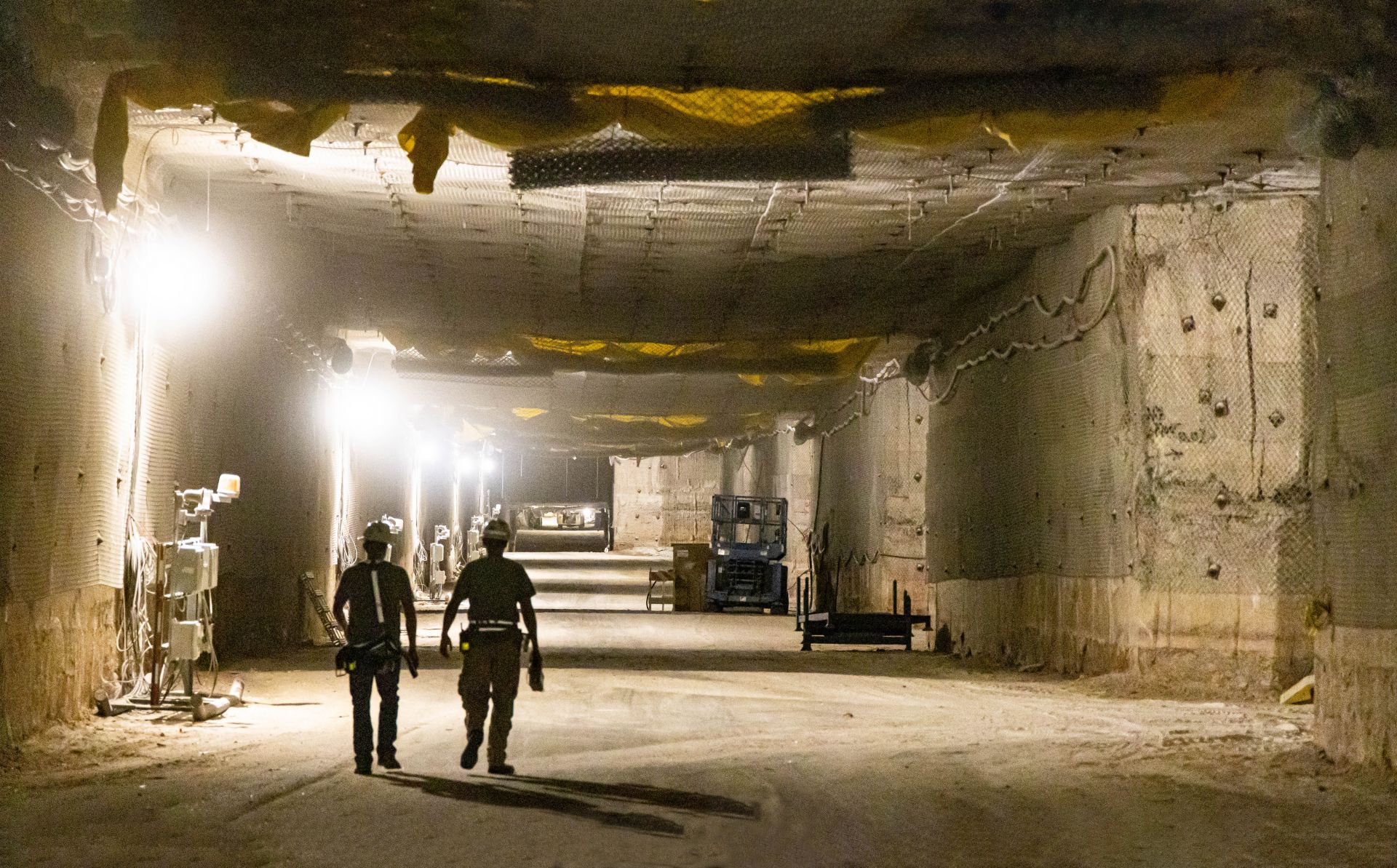
Two workers walk down an underground passageway at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant transuranic waste repository in New Mexico. (Photo: DOE)
While still lacking a deep geological repository for the permanent disposal of its commercial used nuclear fuel and high-level radioactive waste, the United States does have regulatory standards for geological nuclear waste disposal.
Having been written nearly 40 years ago, however, those standards are outmoded and lack transparency, according to a special committee of the American Nuclear Society, which has released draft recommendations on revising public health and safety standards for future geological repository projects in the United States.
 One of the biggest challenges in the nuclear community identified by ANS in 2017 is the continuous availability of radioisotopes. Working to meet that challenge is the ANS-led Source Security Working Group (SSWG), an alliance of industry sectors—including energy, health care, and industrial radiography—that seeks to ensure continued access to radiological sources. The SSWG serves as a strong voice to protect the continued availability of radiological sources, ensuring that laws and policies are risk informed, science based, and support the highest levels of public health and safety.
One of the biggest challenges in the nuclear community identified by ANS in 2017 is the continuous availability of radioisotopes. Working to meet that challenge is the ANS-led Source Security Working Group (SSWG), an alliance of industry sectors—including energy, health care, and industrial radiography—that seeks to ensure continued access to radiological sources. The SSWG serves as a strong voice to protect the continued availability of radiological sources, ensuring that laws and policies are risk informed, science based, and support the highest levels of public health and safety. 











 Nuclear energy “has exceptional characteristics that make it uniquely qualified to address all three facets of the energy trilemma: affordability, sustainability, and reliability,” according to a new report,
Nuclear energy “has exceptional characteristics that make it uniquely qualified to address all three facets of the energy trilemma: affordability, sustainability, and reliability,” according to a new report, 

