Scientists studied the migration of six butterflies (from top left to bottom right): American Snout butterfly, Queen butterfly, Cloudless Sulphur butterfly, Empress Leilia butterfly, Variegated Fritillary butterfly, and Southern Dogface butterfly. (Composite photo: IAEA; photo credits: S. Bright, V. Charny, J. Gallagher, J. Green)
While scientists can tag migrating birds, mammals, and other animals to track their movements, the precise migration patterns of butterflies and other insects too small for tagging evaded scientists’ scrutiny for decades. That changed in 1996, when Leonard Wassenaar and Keith Hobson, working at the time as isotope scientists for Environment Canada, demonstrated that isotopic techniques could be used to determine the origin of individual monarch butterflies and deduce the species’ annual migration routes. Now, the same technique is being used to study other butterfly species.
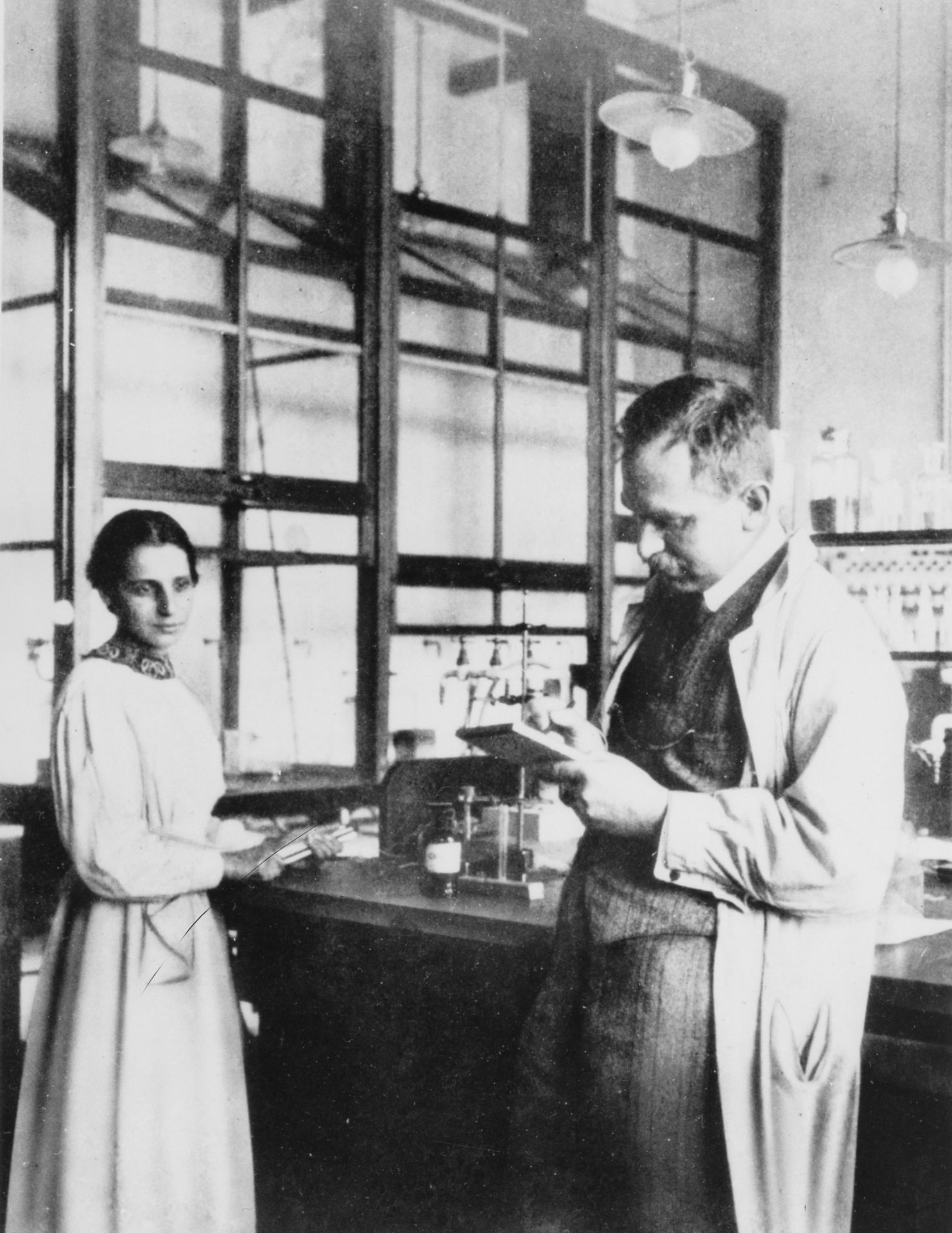
Lise Meitner and Otto Hahn in their lab in Germany in 1913.
Comparing matter to a “lush tapestry, woven from a complex assortment of threads,” physics writer Emily Conover traces the evolution of our understanding of the atom over the past century in the recent Science News article, “How matter’s hidden complexity unleashed the power of nuclear physics.” Conover uncovers how our vision of matter changed from that of a “no-nonsense plaid” to one of an “ornate brocade,” ultimately transforming nuclear physics from an arcane academic pursuit to something that forever changed the world.
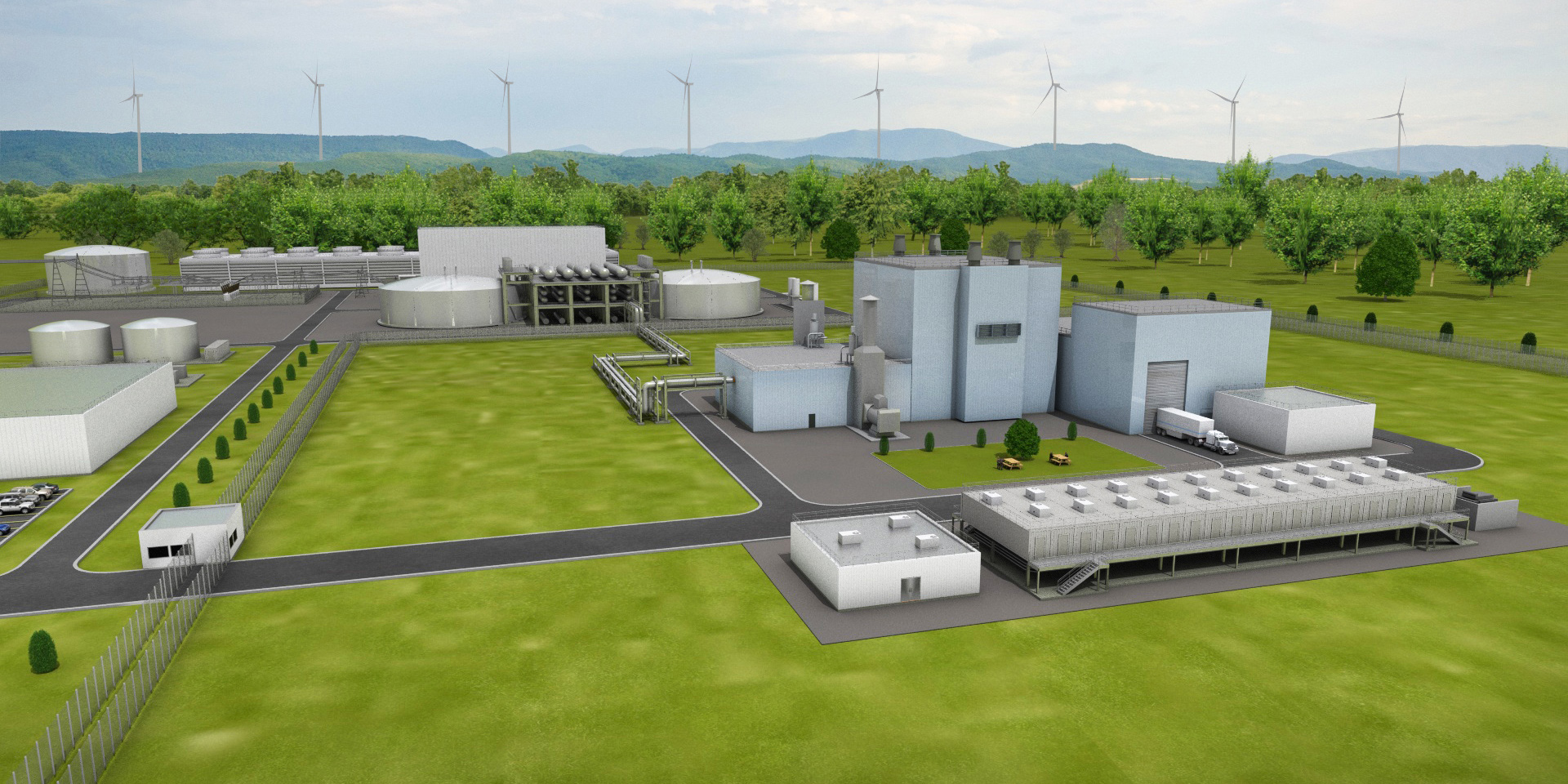
Construction of Norman was completed in 2017. Photo: TAE Technologies
TAE Technologies has announced that it has produced a stable plasma of over 50 million degrees celsius inside a fusion device using a beam-driven, field-reversed configuration. “By generating such stable high-temperature plasmas, TAE has now validated that the company’s unique approach can scale to the conditions necessary for an economically viable commercial fusion power plant by the end of the decade,” the company declared in its April 8 press release. The company added that the results indicate the design’s linear configuration improves plasma confinement as temperatures rise.
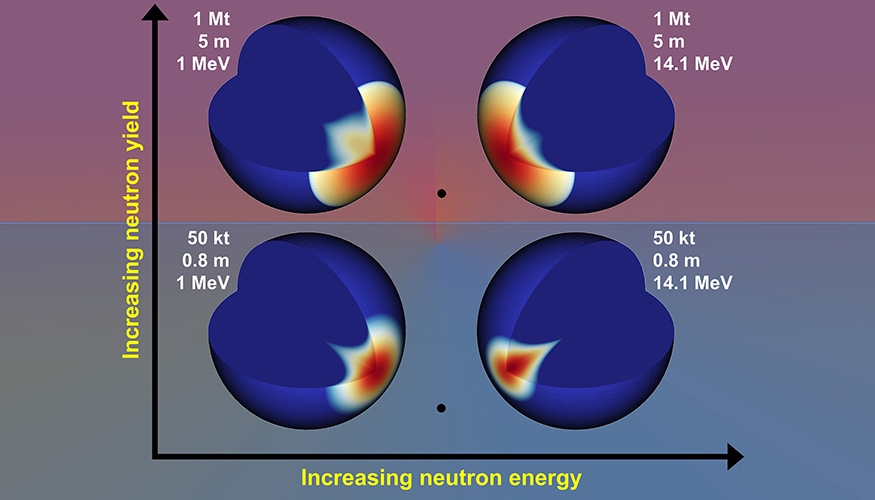
In this illustration of the effects of two neutron yields (50 kt and 1 Mt) and two neutron energies (14.1 MeV and 1 MeV), the black dots represent the location of a nuclear device. Dark blue indicates where the asteroid remains solid, while all other colors show where material has been melted or vaporized. The illustration depicts asteroids with 0.8-m and 5-m diameters—much smaller than the 300-m asteroid simulated in the study—to enhance the visibility of the area of the energy deposition. Image: LLNL
A research collaboration between Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory and the Air Force Institute of Technology (AFIT) has investigated how the neutron energy generated by the detonation of a nuclear device could affect the path and speed of an asteroid on a collision course with Earth by melting and vaporizing a portion of the asteroid. The research, which compared the deflection caused by two different neutron energies—14.1 MeV and 1 MeV, representing fusion and fission neutrons, respectively—is described in an article published by LLNL on April 8.
The Maryland University Training Reactor, one of 12 TRIGA reactors currently operating at universities in the United States. Photo: University of Maryland
TRIGA International, the only supplier of TRIGA reactor fuel in the world, recently completed a major renovation project at its fuel fabrication facility in Romans, France. The Department of Energy, which provided both technical and financial support for the project, said the upgrades ensure the continued operation of 36 TRIGA reactors around the world, including 18 in the United States.
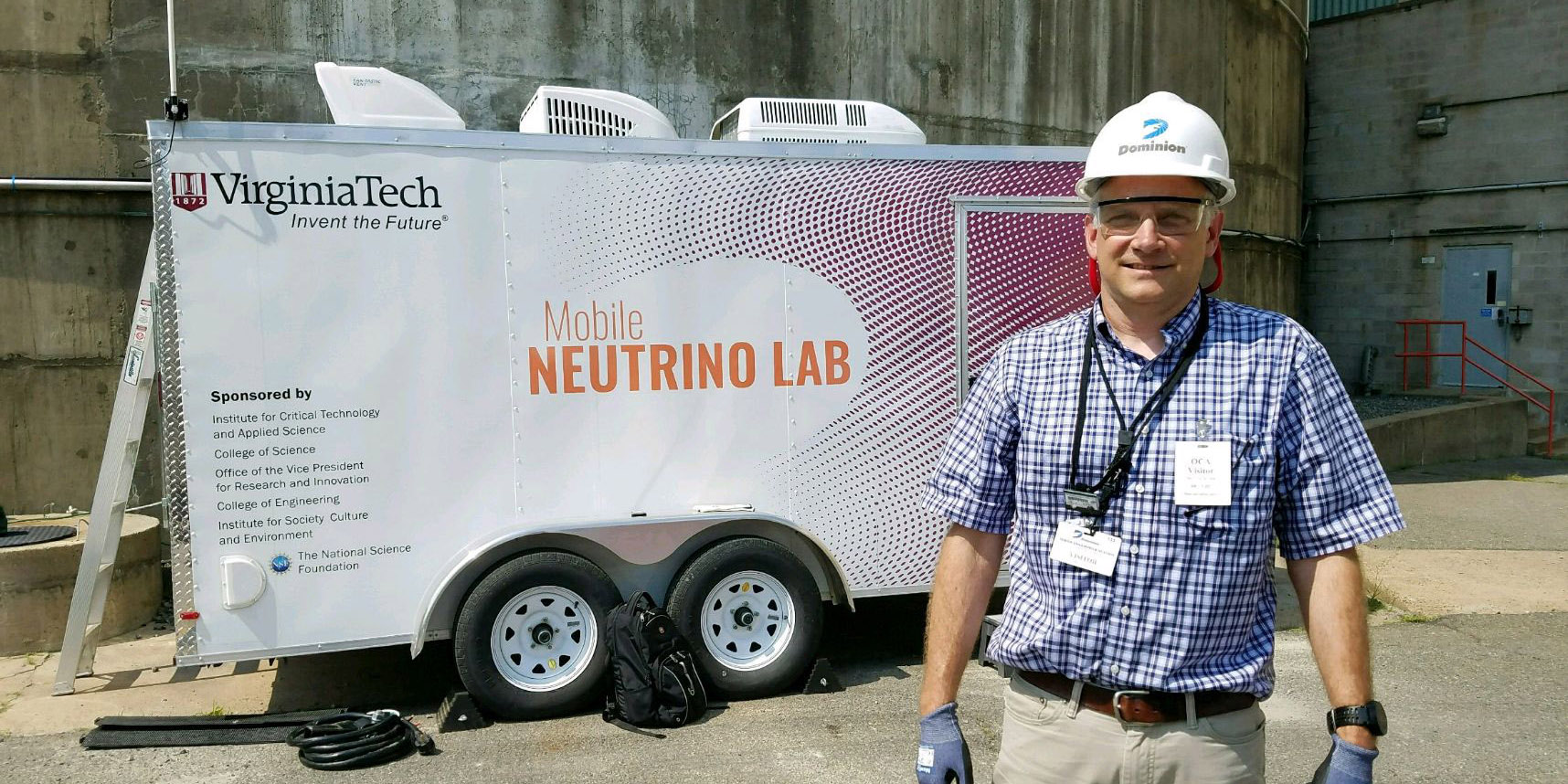
A prototype neutrino detector deployed outside Unit 2 at Dominion Power’s North Anna Generating Station in Mineral, Va. Photo: Steve Mackay, Virginia Tech
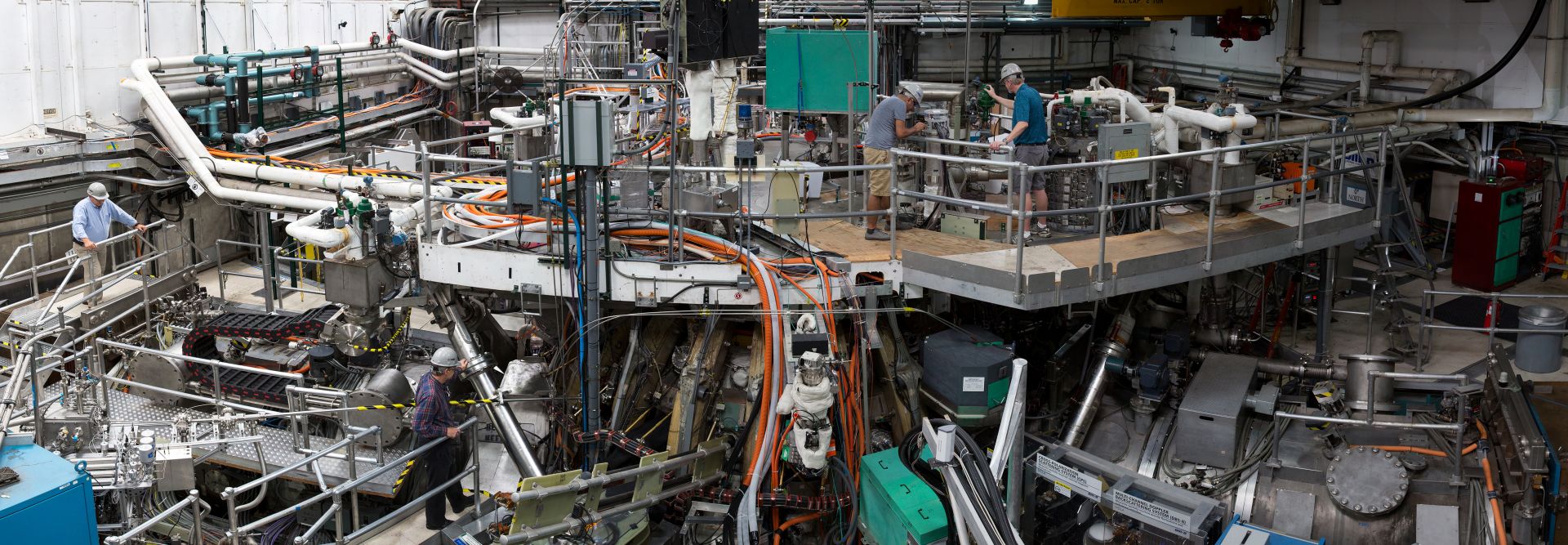
The outside of the DIII-D tokamak, where testing that supports the development of the Compact Advanced Tokamak has been performed. Photo: General Atomics
Scientists at the DIII-D National Fusion Facility have published research on a compact fusion reactor design they say could be used to develop a pilot-scale fusion power plant. According to General Atomics (GA), which operates DIII-D as a national user facility for the Department of Energy’s Office of Science, the Compact Advanced Tokamak (CAT) concept uses a self-sustaining configuration that can hold energy more efficiently than in typical pulsed configurations, allowing the plant to be built at a reduced scale and cost.
An artist’s rendering of Natrium. Image: TerraPower
Around the world, national and local policymakers and business leaders are making bold and ambitious commitments to clean energy goals. In the United States, one in three Americans now lives in a city or state that has committed to or has achieved 100 percent clean electricity, according to the Luskin Center for Innovation at the University of California–Los Angeles.
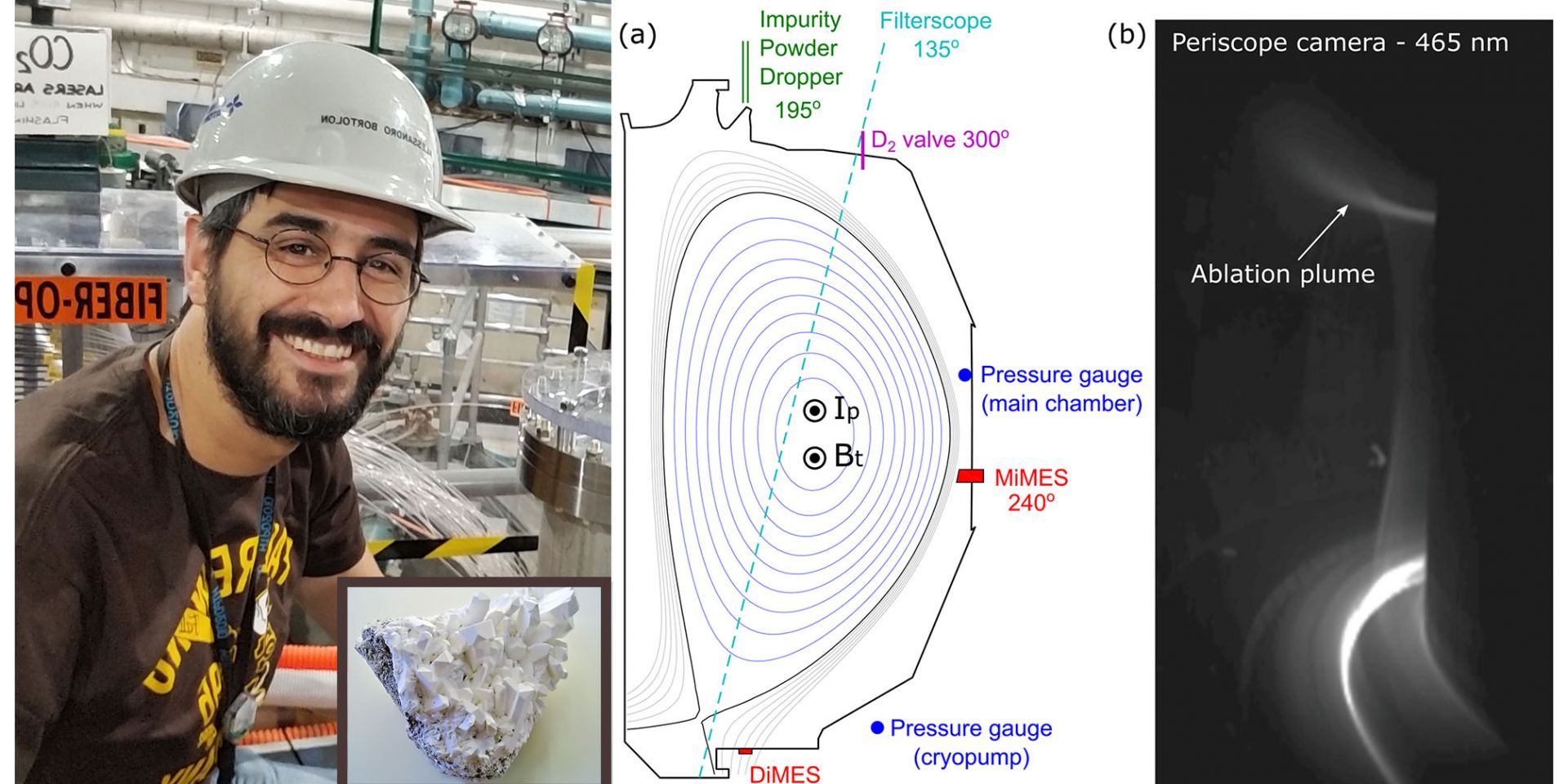
Photos of physicist Alessandro Bortolon and the element boron; graph and photo showing the interior of a tokamak. Credit: Alexander Nagy and Alessandro Bortolon/Collage courtesy of Elle Starkman, PPPL
Research led by scientists at the Department of Energy's Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) provides new evidence that particles of boron, the main ingredient in Borax household cleaner, can coat internal components of doughnut-shaped plasma devices known as tokamaks and improve the efficiency of the fusion reactions, according to an article published on Phys.org on April 2.
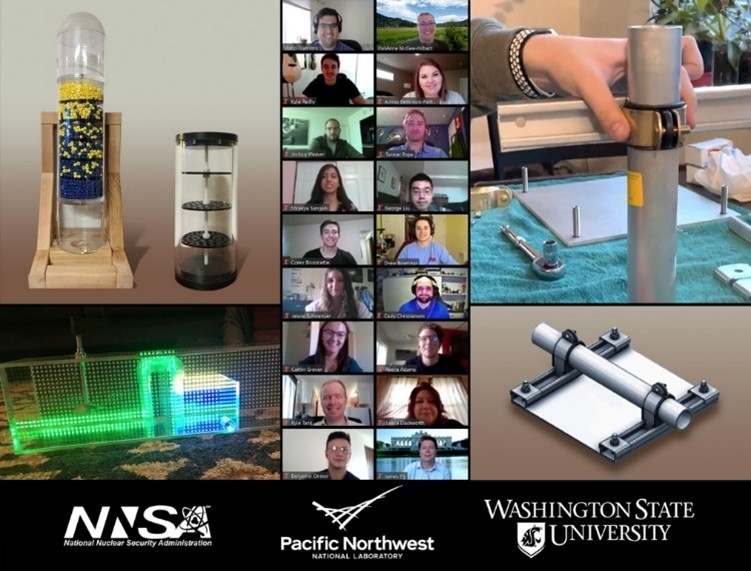
Rethinking seismic design may be key for making nuclear plant construction affordable.
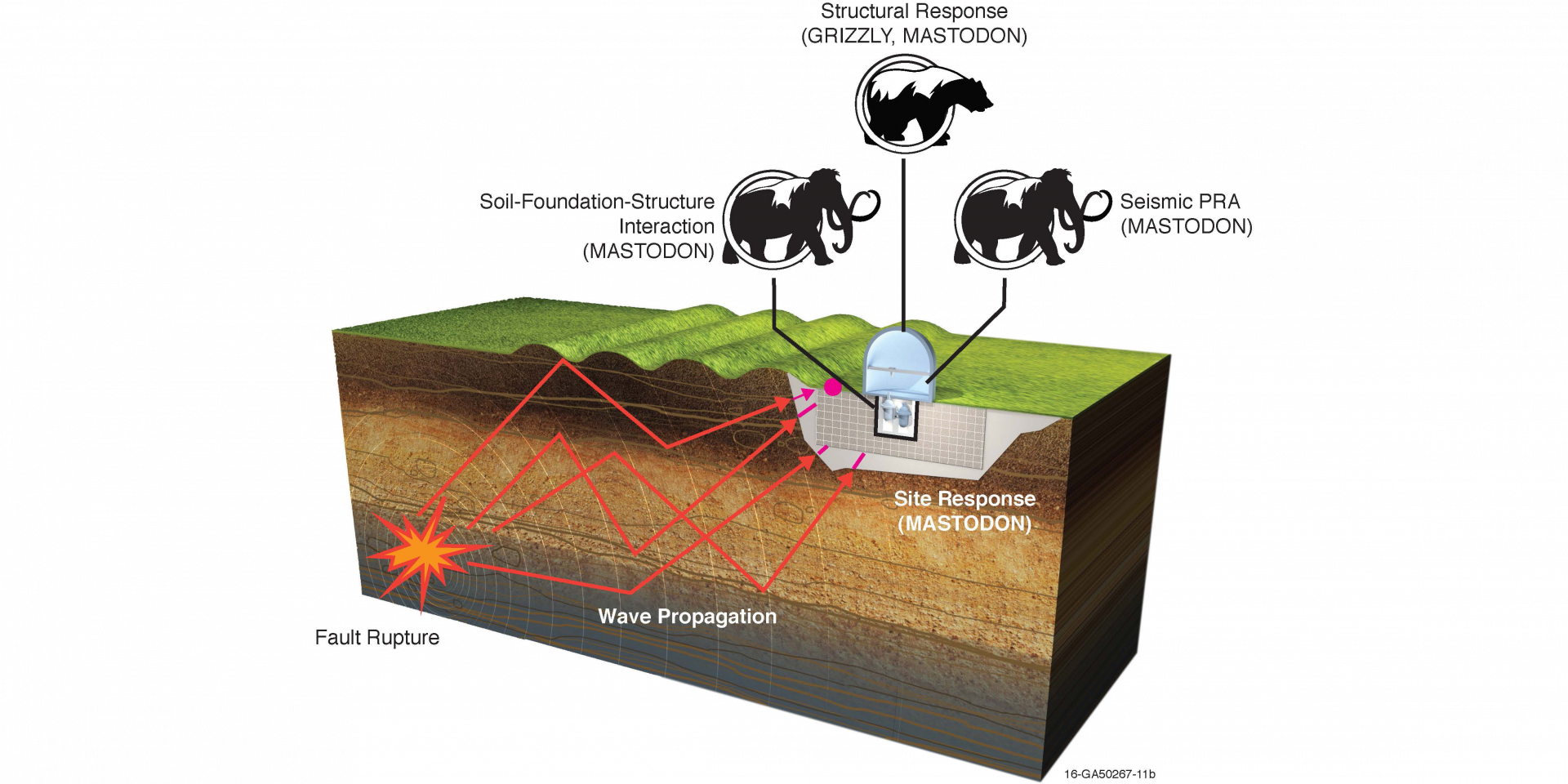
Nuclear power plants not only provide the nation’s largest source of carbon-free electricity, they also can operate 24 hours a day, 365 days a year to augment intermittent renewables such as wind and solar. Further, studies show that nuclear energy is among the safest forms of energy production, especially when considering factors such as industrial accidents and disease associated with fossil fuel emissions. All said, nuclear has the potential to play a key role in the world’s energy future. Before nuclear can realize that potential, however, researchers and industry must overcome one big challenge: cost.
A team at Idaho National Laboratory is collaborating with experts around the nation to tackle a major piece of the infrastructure equation: earthquake resilience. INL’s Facility Risk Group is taking a multipronged approach to reduce the amount of concrete, rebar, and other infrastructure needed to improve the seismic safety of advanced reactors while also substantially reducing capital costs. The effort is part of a collaboration between INL, industry, the Department of Energy’s Advanced Research Projects Agency–Energy (ARPA-E), and the State University of New York–Buffalo (SUNY Buffalo).










 The North Carolina State University (NCSU) Libraries Department and the Department of Nuclear Engineering are collaborating to build
The North Carolina State University (NCSU) Libraries Department and the Department of Nuclear Engineering are collaborating to build 

 The Gateway for Accelerated Innovation in Nuclear (GAIN) announced that three nuclear technology companies—Radiant, Oklo, and Lightbridge—will receive GAIN nuclear energy vouchers to accelerate the innovation and application of advanced nuclear technologies.
The Gateway for Accelerated Innovation in Nuclear (GAIN) announced that three nuclear technology companies—Radiant, Oklo, and Lightbridge—will receive GAIN nuclear energy vouchers to accelerate the innovation and application of advanced nuclear technologies. 
