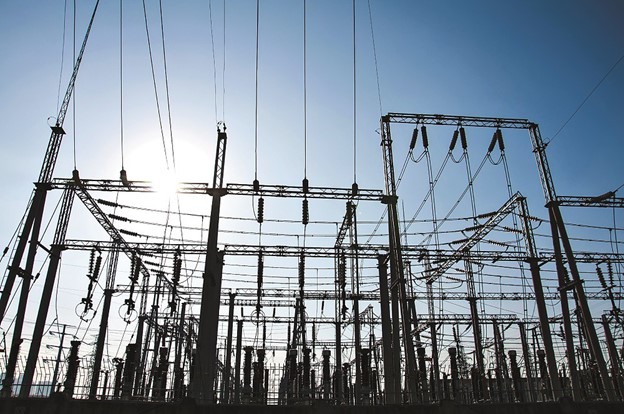
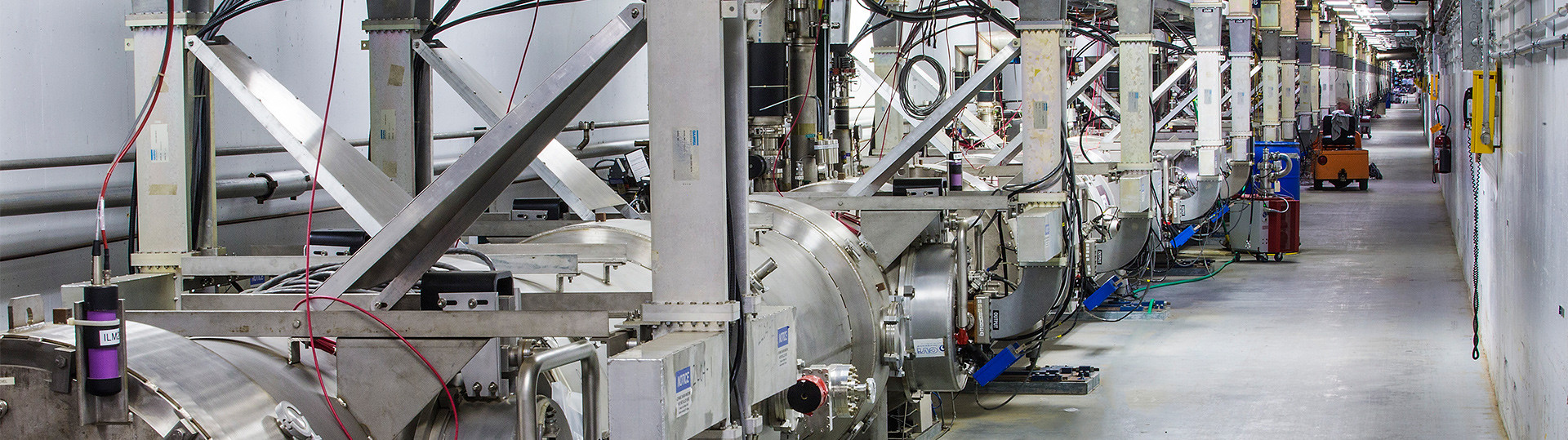
The Continuous Electron Beam Accelerator Facility at Jefferson Lab. (Source: Jefferson Lab)
Research with the Department of Energy’s Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility (Jefferson Lab) has revealed new insights into short-range correlations—the brief pairings of nucleons (protons with neutrons, protons with protons, or neutrons with neutrons) in the nuclei of atoms. The study, published in Nature, used precision measurements to determine that short-range correlations differ depending on the density of the nucleus, that is, how many nucleons it contains.
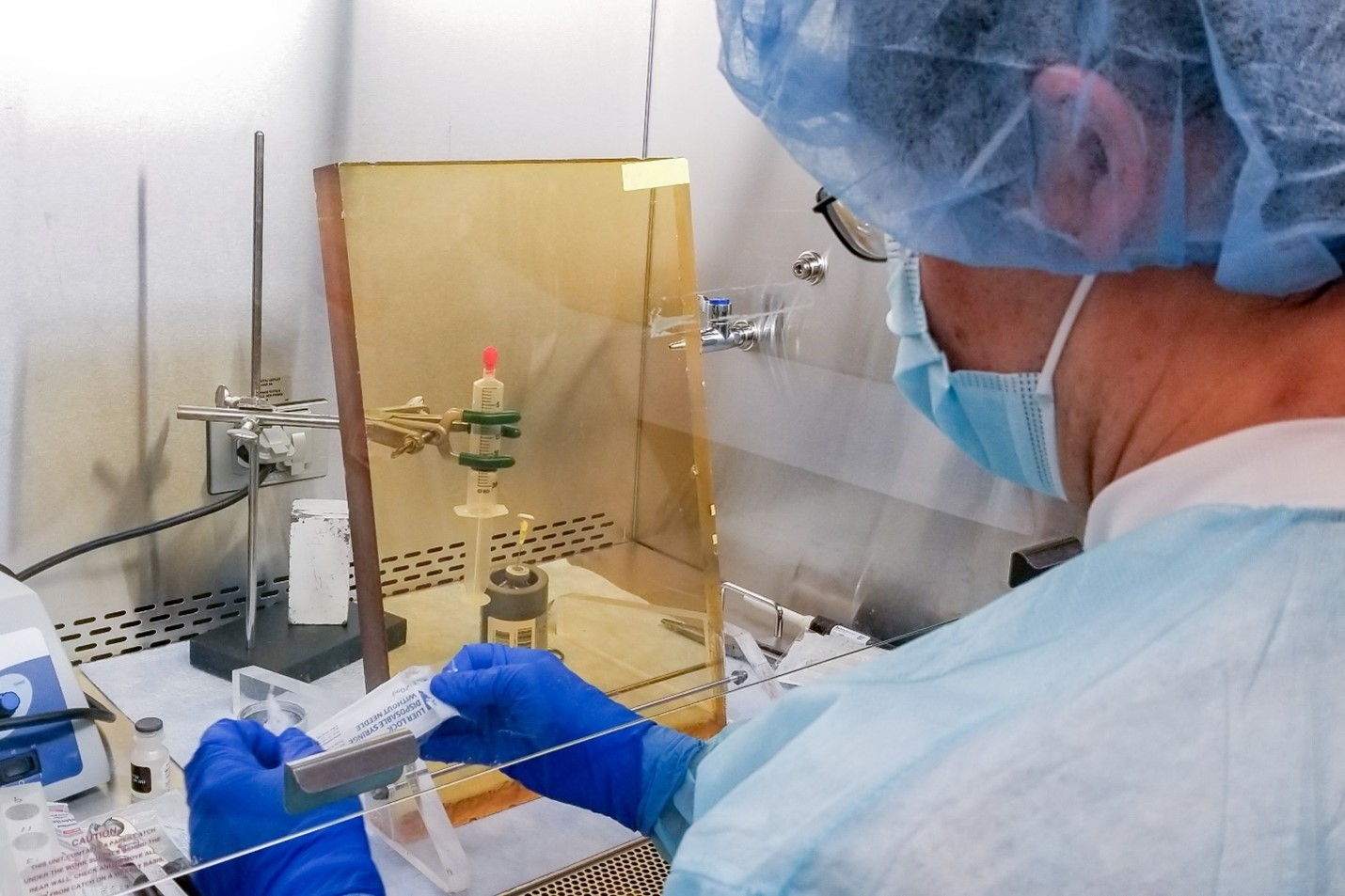
A clinical dose of At-211 is prepared at the University of Washington for use in a Fred Hutchison Cancer Center clinical trial. (Photo: UW/Don Hamlin)
Scientists in the Departments of Radiation Oncology and Medicine at the University of Washington (UW) and Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center (Fred Hutch) are directly targeting cancerous cells traveling through patients’ bloodstreams with diseases such as leukemia and lymphoma using an intravenous injection of the radioactive isotope astatine-211 (At-211). The work, its challenges, and its promise were described in a recent news release from the National Isotope Development Center (NIDC), which is managed by the Department of Energy’s Isotope Program.
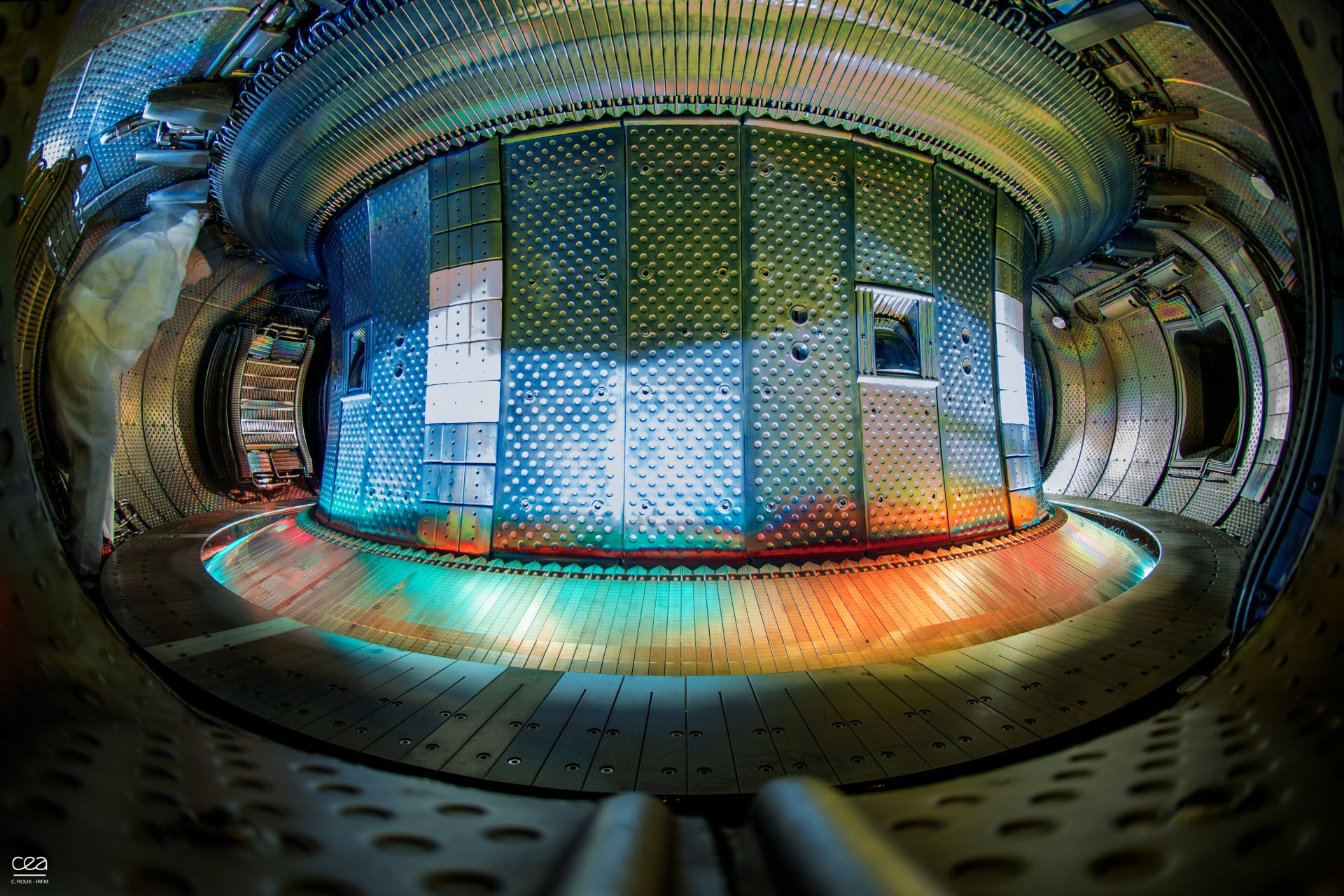
The vacuum vessel of the WEST. (Photo: CEA)
Research by scientists at the Department of Energy’s Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) and collaborating institutions has the potential to improve plasma performance in tokamak nuclear fusion reactors, according to a recent paper in Nuclear Fusion. The research focused on the use of a PPPL-developed dropper to apply coatings of boron powder to the tungsten components inside a tokamak, thereby helping protect the tungsten against the intensely hot plasma. According to lead author Grant Bodner, this process offers “a way to deposit boron coatings without turning off the tokamaks’ magnetic field.”
The NNSA’s Savannah Blalock announces that the agency has reallocated $10 million to support peaceful uses. (Photo: NNSA)
The Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration has redirected about $10 million from the International Atomic Energy Agency’s low-enriched uranium fuel bank to efforts supporting the peaceful uses of nuclear technology and to fight cancer.
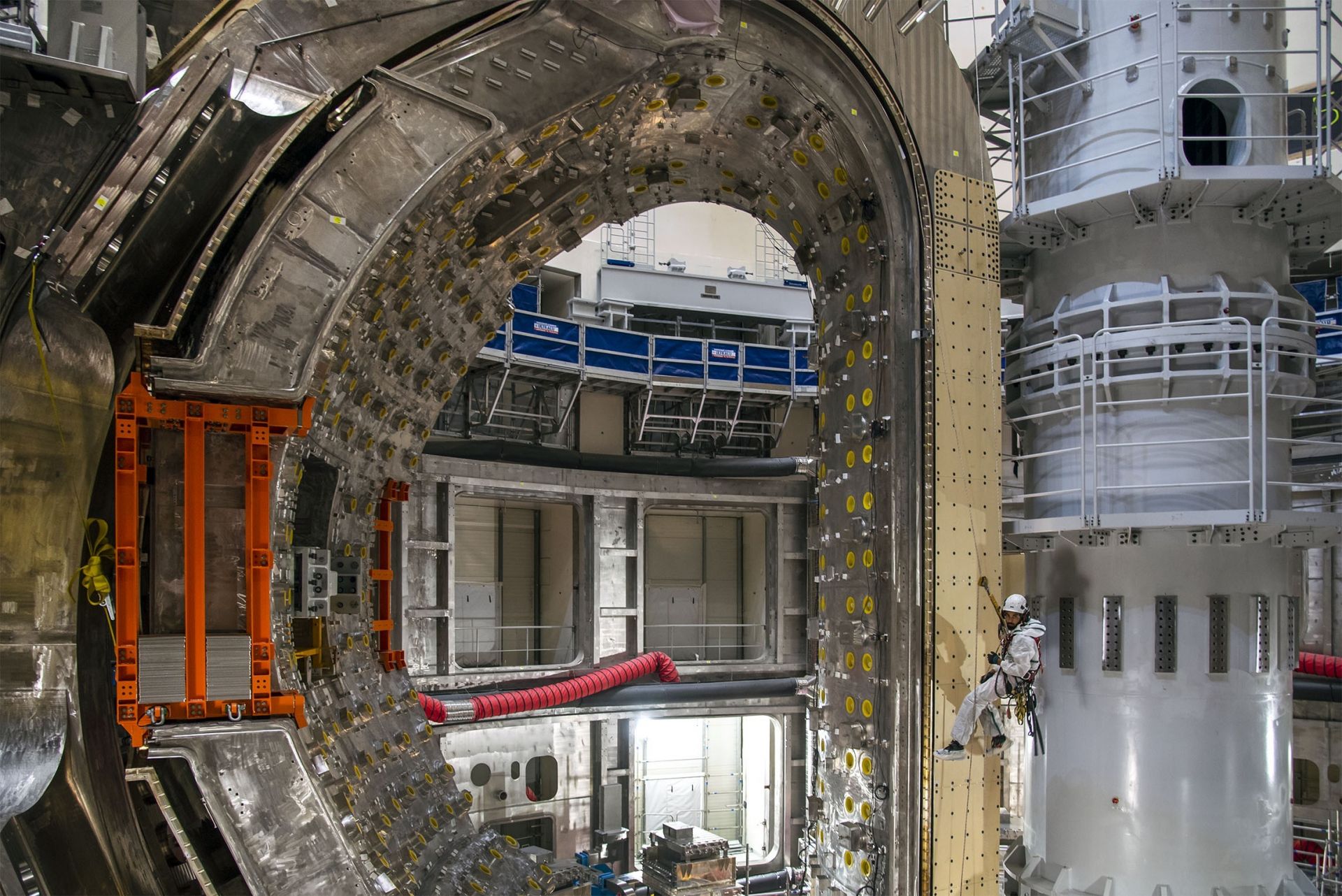
The first sector of the ITER vacuum vessel was placed in the assembly pit in May. Here, a technician positions targets on the surface of the component to be used in laser metrology. (Photo: ITER Organization)
Delivery of electricity from fusion is considered by the National Academies of Engineering to be one of the grand challenges of the 21st century. The tremendous progress in fusion science and technology is underpinning efforts by nuclear experts and advocates to tackle many of the key challenges that must be addressed to construct a fusion pilot plant and make practical fusion possible.
The NS Savannah—the first merchant ship powered by a nuclear reactor.
The American Bureau of Shipping (ABS) has announced the launch of a research project that will look into barriers to the adoption of advanced nuclear propulsion for commercial vessels.
The $794,000 project, awarded to ABS last year by the Department of Energy’s Office of Nuclear Energy, is now being formally contracted through the DOE’s U.S. Industry Opportunities for Advanced Nuclear Technology Development funding opportunity, according to ABS’s August 17 announcement. Support is to be provided by Idaho National Laboratory’s National Reactor Innovation Center (NRIC).
Research being done at INL’s Energy Systems Laboratory is providing information on how nuclear power plants can contribute to effective energy storage and discharge, to aid in arbitrage. (Photo: INL)
Can nuclear power plants prosper in the grid of 2030 or 2035, when new wind and solar farms will make electricity prices even more volatile? Can plants install energy storage that will help them keep running at full power, 24/7, to ride out times of surplus and sell their energy only when prices are high?
A stylized image of a cryogenic target used in NIF experiments. (Image: James Wickboldt/LLNL)
A release box containing about 15 million sterile male fruit flies is loaded into a Cessna aircraft for release over Colima, Mexico, earlier this year. (Photo: DGSV SENASICA)
Mexican authorities announced last week that the Mediterranean fruit fly, more commonly known as the medfly, had been successfully eradicated in the state of Colima using a nuclear technique described by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) as “birth control for pests.” Mexico used the sterile insect technique (SIT) in cooperation with the IAEA and the Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations (FAO) to protect fruit and vegetable crops, farmers’ livelihoods, and the country’s economy.
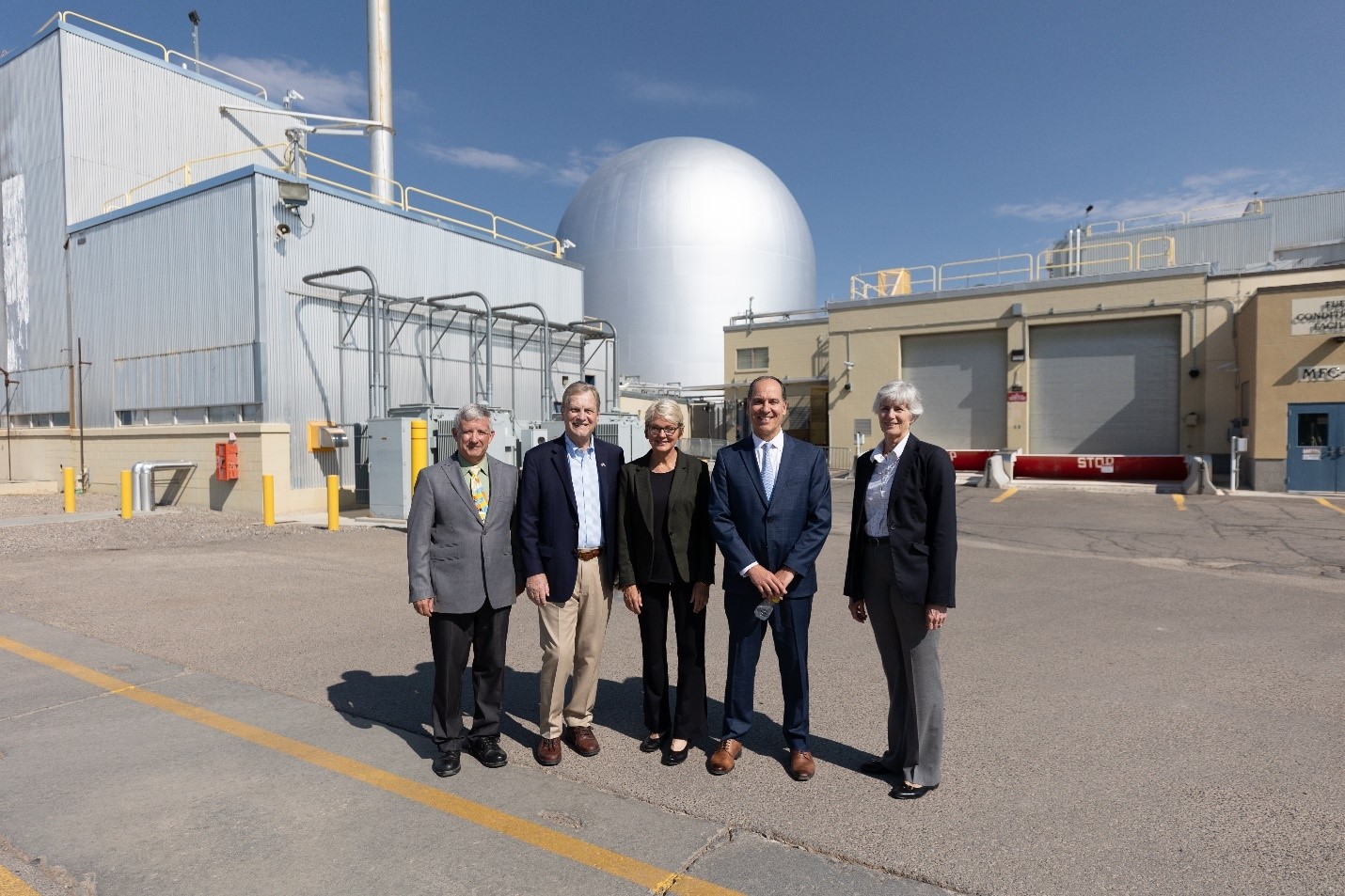
Pictured during a tour of the EBR-II site are, from left, Robert Boston, DOE-ID manager; Rep. Mike Simpson (R., Idaho); Secretary Granholm; Director Wagner; and Marianne Walck, INL deputy laboratory director for science and technology. (Photo: INL)
Energy Secretary Jennifer Granholm visited Idaho National Laboratory on August 3 to meet with INL staff, including director John Wagner, as she toured key research facilities on INL’s 890-square-mile site and the lab’s campus in Idaho Falls.
NIST's Center for Neutron Research in suburban Gaithersburg, Md. (Photo: NIST)
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission announced on August 2 that it had issued a confirmatory order to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) for violating NRC requirements during a February 2021 fuel failure at the 20-MWt NIST Center for Neutron Research (NCNR) research reactor in Gaithersburg, Md. NIST committed to improving its training for fuel handing procedures and related management activities, safety culture program, reactor facility operations staff and management, corrective action program and operational procedures, and emergency response resources and procedures, among other things.
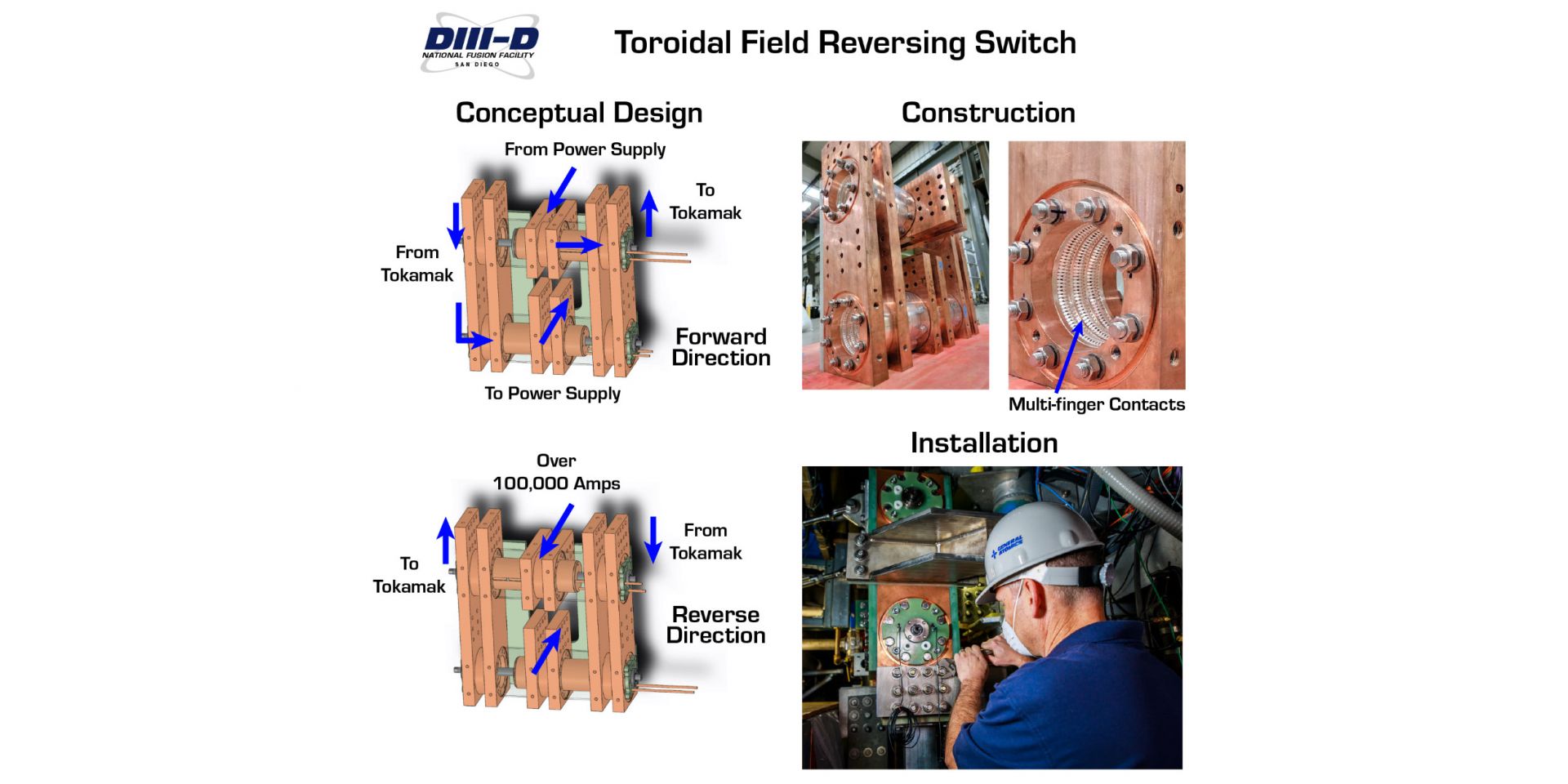
The new TRFS provides for automated adjustment of the direction of the DIII-D primary magnetic field. (Photos: GA and PPPL)
The DIII-D National Fusion Facility now boasts a unique automated system that allows for a quick reversal of the direction of its magnetic field, expanding the range of possible fusion experiments while reducing downtime. General Atomics, which operates the DIII-D for the Department of Energy’s Office of Science, announced the new Toroidal Field Reversing Switch (TFRS) on July 26.